Abstract
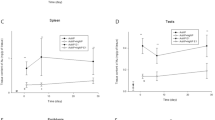
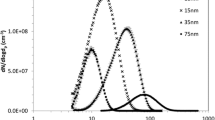
Gold nanoparticles are known to be distributed to many tissues following their oral, inhalation, or intravenous exposure. Information on the biodistribution and clearance of gold nanoparticles from these tissues is, therefore, important to understand their behavior in vivo. To study the effect of size on the biodistribution of gold nanoparticles, Sprague–Dawley rats were exposed by inhalation to small gold nanoparticles (13 nm in diameter on average) at an exposure concentration of 12.8 ± 2.42 µg/m3, and to large gold nanoparticles (105 nm in diameter on average) at an exposure concentration of 13.7 ± 1.32 µg/m3. The experimental animals were exposed to the gold nanoparticles and the control animals to fresh air for 5 days (6 h/day), followed by a recovery period of 1, 3, and 28 days in fresh air. None of the exposed animals exhibited any toxic response to the gold nanoparticles. Despite the difference in size, both small and large gold nanoparticles deposited mainly in rat lungs. Their biodistribution from the lungs to secondary target organs was significantly higher with the small compared to the large gold nanoparticles. While the large gold nanoparticles were only found in the blood, the small gold nanoparticles were detected in the liver, spleen, brain, testes, and blood. In addition, the elimination half-life of the small gold nanoparticles from the lungs was significantly shorter than that of the large gold nanoparticles. The present data may, therefore, suggest that the smaller gold nanoparticles are able to translocate from the lungs, the primary exposure organ to extrapulmonary organs at a faster rate than the larger gold nanoparticles and thus confirming previous observations reported in the literature.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasubramanian SK, Jittiwat J, Manikandan J, Ong CN, Yu LE, Ong WY (2010) Biodistribution of gold nanoparticles and gene expression changes in the liver and spleen after intravenous administration in rats. Biomaterials 31:2034–2042
Balasubramanian SK, Poh KW, Ong CN, Kreyling WG, Ong WY, Yu LE (2013) The effect of primary particle size on biodistribution of inhaled gold nano-agglomerates. Biomaterials 34:5439–5452
De Jong WH, Hagens WI, Krystek P, Burger MC, Sips AJ, Geertsma RE (2008) Particle size-dependent organ distribution of gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration. Biomaterials 29:1912–1919
Hainfeld JF, Slatkin DN, Smilowitz HM (2004) The use of gold nanoparticles to enhance radiotherapy in mice. Phys Med Biol 19:N309–N315
Hirn S, Semmler-Behnke M, Schleh C, Wenk A, Lipka J, Schäffler M, Takenaka S, Möller W, Schmid G, Simon U, Kreyling WG (2011) Particle size-dependent and surface charge-dependent biodistribution of gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 77:407–416
Klein CL, Wiench K, Wiemann M, Ma-Hock L, van Ravenzwaay B, Landsiedel R (2012) Hazard identification of inhaled nanomaterials: making use of short-term inhalation studies. Arch Toxicol 86:1137–1151
Kreyling WG, Semmler-behnke M (2006) Ultrafine particle-lung interaction: does size matter? J Aerosol Med 19:74–83
Lee JH, Kim YS, Song KS, Ryu HR, Sung JH, Park JD, Park HM, Song NW, Shin BS, Marshak D, Ahn K, Lee JE, Yu IJ (2013) Biopersistence of silver nanoparticles in tissues from Sprague–Dawley rats. Part Fibre Toxicol 10:36
Ma-Hock L, Burkhardt S, Strauss V, Gamer A, Wienc K, van Ravenzwaay B, Landsiedel R (2009) Development of a short-term inhalation test in rats using nano-titanium dioxide as a model substance. Inhal Toxicol 21:102–118
McIntyre RA (2012) Common nano-materials and their use in real world applications. Sci Prog 95:1–22
NIOSH (1994) NIOSH manual of analytical methods (NMAM): Method No. 7402. Asbestos by TEM, 4th edn. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati, pp 2–7
NIOSH (2003) NIOSH manual of analytical methods (NMAM): Method No. 7300. Elements by ICP (Nitric/Perchloric Acid Ashing), 4th edn. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati, pp 2–8
OECD (2010) List of manufactured nanomaterials and list of endpoints for phase one of the sponsorship program for the testing of manufactured nanomaterials: Revision. Series on the safety of manufactured nanomaterials No. 27. ENV/JM/MONO (2010)46. OECD Website. http://search.oecd.org/officialdocuments/displaydocumentpdf/?cote=env/jm/mono(2010)46&doclanguage=en. Accessed 24 Jan 2014
Qian X, Peng XH, Ansari DO, Yin-Goen Q, Chen GZ, Shin DM, Yang L, Young AN, Wang MD, Nie S (2008) In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags. Nat Biotechnol 26:83–90
Schleh C, Semmler-Behnke M, Lipka J, Wenk A, Hirn S, Schäffler M, Schmid G, Simon U, Kreyling WG (2012) Size and surface charge of gold nanoparticles determine absorption across intestinal barriers and accumulation in secondary target organs after oral administration. Nanotoxicology 6:36–46
Semmler-Behnke M, Kreyling WG, Lipka J, Fertsch S, Wenk A, Takenaka S, Schmid G, Brandau W (2008) Biodistribution of 1.4- and 18- nm gold particles in rats. Small 4:2108–2111
Sung JH, Ji JH, Park JD, Song MY, Song KS, Ryu HR, Yoon JU, Jeon KS, Jeong J, Han BS, Chung YH, Chang HK, Lee JH, Kim DW, Kelman BJ, Yu IJ (2011) Subchronic inhalation toxicity of gold nanoparticles. Part Fibre Toxicol 8:16
US Food and Drug Administration Chemical Selection Working Group (2006) Nomination and Review of Toxicological Literature. National Toxicology Program Website. http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/Chem_Background/ExSumPdf/Nanoscale_materials_508.pdf. Accessed 12 Nov 2013
van der Zande M, Vandebriel RJ, Van Doren E, Kramer E, Herrera Rivera Z, Serrano-Rojero CS, Gremmer ER, Mast J, Peters RJ, Hollman PC, Hendriksen PJ, Marvin HJ, Peijnenburg AA, Bouwmeester H (2012) Distribution, elimination, and toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions in rats after 28-day oral exposure. ACS Nano 6:7427–7442
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by NanoMaterial Technology Development Program (Green Nano Technology Development Program) (2011-0020504) and Nano R&D Program (2011-0019171) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, S.G., Lee, J.S., Ahn, K. et al. Size-dependent clearance of gold nanoparticles from lungs of Sprague–Dawley rats after short-term inhalation exposure. Arch Toxicol 89, 1083–1094 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1292-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1292-9