Abstract
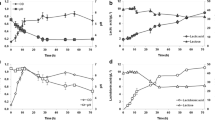
Single so-called booster substances were added to the fermentation medium of the probiotic strain Lactobacillus (L.) paracasei ssp. paracasei F19 to enhance its growth. A wide screening was carried out in microtiter plates and a statistical analysis of the growth parameters was performed. CFU counts were used to correlate the increase in OD590nm with the increase in viable cell number. Sodium ascorbate, sodium pyruvate, manganese sulfate and cysteine had a remarkable boosting effect on the growth of L. paracasei F19. Three of the boosters increased the growth rate of the strain and led to a higher cell density and biomass yield in laboratory conditions. Cysteine significantly shortened the lag phase, therefore reducing the fermentation times. The boosters were tested on four additional Lactobacillus species and their growth boosting activity was retained. To investigate whether the growth boosters could improve the tolerance of L. paracasei F19 to the adverse condition in the GI tract, additional tests were performed. Sodium ascorbate and sodium pyruvate exerted a certain antioxidant effect, as they improved the tolerance of L. paracasei F19 to H2O2. Sodium ascorbate enhanced the growth of the strain in low pH.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasen IM, Moretro T, Katla T, Axelsson L, Storro I (2000) Influence of complex nutrients, temperature and pH on bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus sakei CCUG 42687. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53(2):159–166
Aguirre-Ezkauriatza EJ, Aguilar-Yáñez JM, Ramírez-Medrano A, Alvarez MM (2010) Production of probiotic biomass (Lactobacillus casei) in goat milk whey: Comparison of batch, continuous and fed-batch cultures. Bioresour Technol 101(8):2837–2844
Andrae U, Singh J, Ziegler-Skylakakis K (1985) Pyruvate and related alpha-ketoacids protect mammalian cells in culture against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity. Toxicol Lett 28(2–3):93–98
Anvari M, Khayati G, Rostami S (2014) Optimisation of medium composition for probiotic biomass production using response surface methodology. J Dairy Res 81(1):59–64
Aronsson L, Huang Y, Parini P, Korach-Andre M, Hakansson J, Gustafsson JA, Pettersson S, Arulampalam V, Rafter J (2010) Decreased fat storage by Lactobacillus paracasei is associated with increased levels of angiopoietin-like 4 protein (ANGPTL4). PLoS One 5(9):e13087. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013087
Aureli P, Capurso L, Castellazzi AM, Clerici M, Giovannini M, Morelli L, Poli A, Pregliasco F, Salvini F, Zuccotti GV (2011) Probiotics and health: an evidence-based review. Pharmacol Res 63(5):366–376
Barlow S, Chesson A, Collins JD, Dybing E, Flynn A, Hardy A, Knaap A, Kuiper H, Le Neindre P, Schans J, Schlatter J, Silano V, Skerfving S, Vannier P (2007) Introduction of a qualified presumption of safety (QPS) approach for assessment of selected microorganisms referred to EFSA. Opinion of the Scientific Committee. EFSA J 587:1–16
Begtrup LM, de Muckadell OB, Kjeldsen J, Christensen RD, Jarbol DE (2013) Long-term treatment with probiotics in primary care patients with irritable bowel syndrome–a randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Scand J Gastroenterol 48(10):1127–1135
Bendich A, Machlin LJ, Scandurra O, Burton GW, Wayner DDM (1986) The antioxidant role of vitamin C. Adv Free Radic Biol Med 2(2):419–444
Brasca M, Morandi S, Lodi R, Tamburini A (2007) Redox potential to discriminate among species of lactic acid bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 103(5):1516–1524
Buchanan RL, Whiting RC, Damert WC (1997) When is simple good enough: a comparison of the Gompertz, Baranyi, and three-phase linear models for fitting bacterial growth curves. Food Microbiol 14(4):313–326
Capuani A, Behr J, Vogel RF (2013) Influence of lactic acid bacteria on redox status and on proteolytic activity of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) sourdoughs. Int J Food Microbiol 165(2):148–155
Charteris WP, Kelly PM, Morelli L, Collins JK (1998) Development and application of an in vitro methodology to determine the transit tolerance of potentially probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species in the upper human gastrointestinal tract. J Appl Microbiol 84(5):759–768
Cheng X, Dong Y, Su P, Xiao X (2014) Improvement of the fermentative activity of lactic acid bacteria starter culture by the addition of Mn2+. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 174(5):1752–1760
CocaignBousquet M, Garrigues C, Loubiere P, Lindley ND (1996) Physiology of pyruvate metabolism in Lactococcus lactis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Int J Gen Mol Microbiol 70(2–4):253–267
Compare D, Rocco A, Sgamato C, Coccoli P, Campo SM, Nazionale I, Larussa T, Luzza F, Chiodini P, Nardone G (2015) Lactobacillus paracasei F19 versus placebo for the prevention of proton pump inhibitor-induced bowel symptoms: a randomized clinical trial. Dig Liver Dis 47(4):273–279
Crittenden R, Saarela M, Mättö J, Ouwehand AC, Salminen S, Pelto L, Vaughan EE, Vos WMD, Wright AV, Fondén R, Mattila-Sandholm T (2002) Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei F19: survival, ecology and safety in the human intestinal tract—a survey of feeding studies within the PROBDEMO Project. Microb Ecol Health Dis 14(1):22–26
Cui S, Zhao J, Liu X, Chen YQ, Zhang H, Chen W (2016) Maximum-biomass prediction of homofermentative Lactobacillus. J Biosci Bioeng 122(1):52–57
Dave RI, Shah NP (1997) Effectiveness of ascorbic acid as an oxygen scavenger in improving viability of probiotic bacteria in yoghurts made with commercial starter cultures. Int Dairy J 7(6–7):435–443
Di Cerbo A, Palmieri B (2013) Lactobacillus Paracasei subsp Paracasei F19; a farmacogenomic and clinical update. Nutr Hosp 28(6):1842–1850
Du C, Yan H, Zhang Y, Li Y, Cao Z (2006) Use of oxidoreduction potential as an indicator to regulate 1,3-propanediol fermentation by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69(5):554–563
Figueroa-Gonzalez I, Quijano G, Ramirez G, Cruz-Guerrero A (2011) Probiotics and prebiotics–perspectives and challenges. J Sci Food Agric 91(8):1341–1348
Fitzpatrick JJ, Ahrens M, Smith S (2001) Effect of manganese on Lactobacillus casei fermentation to produce lactic acid from whey permeate. Process Biochem 36(7):671–675
Giandomenico AR, Cerniglia GE, Biaglow JE, Stevens CW, Koch CJ (1997) The importance of sodium pyruvate in assessing damage produced by hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic Biol Med 23(3):426–434
Gill RT, Cha HJ, Jain A, Rao G, Bentley WE (1998) Generating controlled reducing environments in aerobic recombinant Escherichia coli fermentations: effects on cell growth, oxygen uptake, heat shock protein expression, and in vivo CAT activity. Biotechnol Bioeng 59(2):248–259
Guilbaud M, Zagorec M, Chaillou S, Champomier-Verges MC (2012) Intraspecies diversity of Lactobacillus sakei response to oxidative stress and variability of strain performance in mixed strains challenges. Food Microbiol 29(2):197–204
Heller KJ (2001) Probiotic bacteria in fermented foods: product characteristics and starter organisms. Am J Clin Nutr 73(2):374s–379s
Hickey MW, Hillier AJ, Jago GR (1983) Metabolism of pyruvate and citrate in lactobacilli. Aust J Biol Sci 36(5–6):487–496
Kahm M, Hasenbrink G, Lichtenberg-Frate H, Ludwig J, Kschischo M (2010) “Grofit: fitting biological growth curves with R. J Stat Softw 33(7):1–21
Kehres DG, Maguire ME (2003) Emerging themes in manganese transport, biochemistry and pathogenesis in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27(2–3):263–290
Lew LC, Liong MT, Gan CY (2013) Growth optimization of Lactobacillus rhamnosus FTDC 8313 and the production of putative dermal bioactives in the presence of manganese and magnesium ions. J Appl Microbiol 114(2):526–535
Lew LC, Choi SB, Tan PL, Liong MT (2014) Mn2 + and Mg2 + synergistically enhanced lactic acid production by Lactobacillus rhamnosus FTDC 8313 via affecting different stages of the hexose monophosphate pathway. J Appl Microbiol 116(3):644–653
Linares D, Michaud P, Delort AM, Traikia M, Warrand J (2011) Catabolism of L-ascorbate by Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. J Agric Food Chem 59(8):4140–4147
Liu CG, Lin YH, Bai FW (2011) Development of redox potential-controlled schemes for very-high-gravity ethanol fermentation. J Biotechnol 153(1–2):42–47
Ljungh Å, Lan J, Yanagisawa N (2002) Isolation, selection and characteristics of Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei F19. Microb Ecol Health Dis 14(1):4–6
Lombardo L (2008) New insights into Lactobacillus and functional intestinal disorders. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 54(3):287–293
Mattessich J, Cooper JR (1989) The spectrophotometric determination of diacetyl. Anal Biochem 180(2):349–350
Mattila-Sandholm T (1999) The PROBDEMO project: Demonstration of the nutritional functionality of probiotic foods. Trends Food Sci Technol 10(12):385–386
Matto J, Fonden R, Tolvanen T, von Wright A, Vilpponen-Salmela T, Satokari R, Saarela M (2006) Intestinal survival and persistence of probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains administered in triple-strain yoghurt. Int Dairy J 16(10):1174–1180.
Monnet C, Schmitt P, Divies C (1994) Diacetyl production in milk by an alpha-acetolactic acid accumulating strain of Lactococcus-Lactis Ssp lactis biovar diacetylactis. J Dairy Sci 77(10):2916–2924
Morelli L (2000) In vitro selection of probiotic lactobacilli: a critical appraisal. Curr Issues Intest Microbiol 1(2):59–67
Morelli L, Campominosi E (2002) Genetic stability of Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei F19. Microb Ecol Health Dis 14(1):14–16
Morishita T, Fukada T, Shirota M, Yura T (1974) Genetic basis of nutritional requirements in Lactobacillus casei. J Bacteriol 120(3):1078–1084
Morishita T, Deguchi Y, Yajima M, Sakurai T, Yura T (1981) Multiple nutritional requirements of lactobacilli: genetic lesions affecting amino acid biosynthetic pathways. J Bacteriol 148(1):64–71
Niki E (1991) Action of ascorbic acid as a scavenger of active and stable oxygen radicals. Am J Clin Nutr 54(6 Suppl):1119s–1124s
Parvez S, Malik KA, S. Ah Kang, Kim HY (2006) Probiotics and their fermented food products are beneficial for health. J Appl Microbiol 100(6):1171–1185
Polak-Berecka M, Wasko A, Kordowska-Wiater M, Targonski Z, Kubik-Komar A (2011) Application of response surface methodology to enhancement of biomass production by Lactobacillus rhamnosus E/N. Braz J Microbiol 42(4):1485–1494
Salminen S, von Wright A, Morelli L, Marteau P, Brassart D, de Vos WM, Fondén R, Saxelin M, Collins K, Mogensen G, Birkeland S-E, Mattila-Sandholm T (1998) Demonstration of safety of probiotics—a review. Int J Food Microbiol 44(1–2):93–106
Sanders ME (2008a) Probiotics: definition, sources, selection, and uses. Clin Infect Dis 46(Suppl 2):S58–S61 (discussion S144–151)
Sanders ME (2008b) Probiotics: definition, sources, selection, and uses. Clin Infect Dis 46:S58–S61
Saxelin M, Grenov B, Svensson U, Fonden R, Reniero R, Mattila-Sandholm T (1999) The technology of probiotics. Trends Food Sci Technol 10(12):387–392
Schiraldi C, Adduci V, Valli V, Maresca C, Giuliano M, Lamberti M, Carteni M, De Rosa M (2003) High cell density cultivation of probiotics and lactic acid production. Biotechnol Bioeng 82(2):213–222
Smokvina T, Wels M, Polka J, Chervaux C, Brisse S, Boekhorst J, van Hylckama Vlieg JE, Siezen RJ (2013) Lactobacillus paracasei comparative genomics: towards species pan-genome definition and exploitation of diversity. PLoS One 8(7):e68731
Swinnen IA, Bernaerts K, Dens EJ, Geeraerd AH, Van Impe JF (2004) Predictive modelling of the microbial lag phase: a review. Int J Food Microbiol 94(2):137–159
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Parts of the presented work were funded by the German Federal Office of Agriculture and Food in project BLE 2817400111, http://www.ble.de. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brignone, D., Radmann, P., Behr, J. et al. Boosting the growth of the probiotic strain Lactobacillus paracasei ssp. paracasei F19. Arch Microbiol 199, 853–862 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1352-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1352-7