Abstract
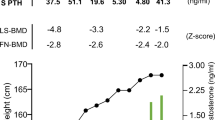
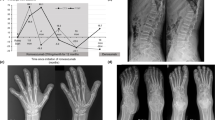
Juvenile Paget’s disease (JPD) is a rare autosomal recessive osteopathy. There is still a question about the most effective treatment modality in long-term prognosis. A 9-month-old boy who suffered from bone pain and deformities with a very high alkaline phosphatase level was diagnosed as JPD by radiographic findings. Genetic analysis showed a homozygous large deletion in TNFRSF11B gene encoding osteoprotegerin. Clinical improvement was observed with intravenous pamidronate therapy. However, the effect of drug reduced in time so the annual dose per kilogram body weight was increased after 2 years. Despite this increment, bone fractures developed and bone pain recurred with high-ALP levels, which suggested resistance to pamidronate. Switching to zoledronate resulted a significant improvement in bone findings radiographically and ALP level. Severe hypocalcemia requiring intravenous calcium treatment complicated the first dose of zoledronate, but not recurred thereafter. Intravenous pamidronate therapy is effective in reducing bone pain, improving bone deformities and motor development in infantile onset JPD. However, this effect can be transient. Switching to another bisphosphonate like zoledronate may provide long-term clinical and biochemical improvement as an alternative treatment in case of resistance to pamidronate therapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Polyzos SA, Cundy T, Mantzoros CS (2017) Juvenile Paget disease. Metabolism pii: S0026–0495 (17)30281–0. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2017.10.007
Whyte MP, Obrecht SE, Finnegan PM, Jones JL, Podgornik MN, McAlister WH, Mumm S (2002) Osteoprotegerin deficiency and juvenile Paget’s disease. N Engl J Med 347:175–184
Naot D, Choi A, Musson DS, Simsek Kiper PÖ, Utine GE, Boduroglu K, Peacock M, DiMeglio LA, Cundy T (2014) Novel homozygous mutations in the osteoprotegerin gene TNFRSF11B in two unrelated patients with juvenile Paget’s disease. Bone 68:6–10
Cundy T, Hegde M, Naot D, Chong B, King A, Wallace R, Mulley J, Love DR, Seidel J, Fawkner M, Banovic T, Callon KE, Grey AB, Reid IR, Middleton-Hardie CA, Cornish J (2002) A mutation in the gene TNFRSF11B encoding osteoprotegerin causes an idiopathic hyperphosphatasia phenotype. Hum Mol Genet 11:2119–2127
Whyte MP, Tau C, McAlister WH, Zhang X, Novack DV, Preliasco V, Santini-Araujo E, Mumm S (2014) Juvenile Paget’s disease with heterozygous duplication within TNFRSF11A encoding RANK. Bone 68:153–161
Chong B, Hegde M, Fawkner M, Simonet S, Cassinelli H, Coker M, Kanis J, Seidel J, Tau C, Tüysüz B, Yüksel B, Love D, International Hyperphosphatasia Collaborative Group (2003) Idiopathic hyperphosphatasia and TNFRSF11B mutations: relationships between phenotype and genotype. J Bone Miner Res 18:2095–2104
Brunetti G, Marzano F, Colucci S, Ventura A, Cavallo L, Grano M, Faienza MF (2012) Genotype-phenotype correlation in juvenile Paget disease: role of molecular alterations of the TNFRSF11B gene. Endocrine 42:266–271
Singer F, Siris E, Shane E, Dempster D, Lindsay R, Parisien M (1994) Hereditary hyperphosphatasia: 20 year follow-up and response to disodium etidronate. J Bone Miner Res 9:733–738
Cassinelli HR, Mautalen CA, Heinrich JJ, Miglietta A, Bergada C (1992) Familial idiopathic hyperphosphatasia (FIH): response to long-term treatment with pamidronate (APD). Bone Miner 19:175–184
Cundy T, Wheadon L, King A (2004) Treatment of idiopathic hyperphosphatasia with intensive bisphosphonate therapy. J Bone Miner Res 19:703–711
Tau C, Mautalen C, Casco C, Alvarez V, Rubinstein M (2004) Chronic idiopathic hyperphosphatasia: normalization of bone turnover with cyclical intravenous pamidronate therapy. Bone 35:210–216
Saki F, Karamizadeh Z, Nasirabadi S, Mumm S, McAlister WH, Whyte MP (2013) Juvenile Paget’s disease in an Iranian kindred with vitamin D deficiency and novel homozygous TNFRSF11B mutation. J Bone Miner Res 28:1501–1508
Joshua F, Epstein M, Major G (2003) Bisphosphonate resistance in Paget’s disease of bone. Arthritis Rheum 48:2321–2323
Papapoulos SE, Eekhoff EM, Zwinderman AH (2006) Acquired resistance to bisphosphonates in Paget’s disease of bone. J Bone Miner Res 21(Suppl 2):88–91
Sanchez-Sanchez LM, Cabrera-Pedroza AU, Palacios-Saucedo G, de la Fuente-Cortez B (2015) Zoledronic acid (zoledronate) in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Gac Med Mex 151:164–168
Green JR, Rogers MJ (2002) Pharmacologic profile of zoledronic acid: a highly potent inhibitor of bone resorption. Drug Dev Res 55:210–224
Devogelaer JP, Geusens P, Daci E, Gielen E, Denhaerynck K, Macdonald K, Hermans C, Vancayzeele S, Abraham I, Boonen S (2014) Remission over 3 years in patients with Paget disease of bone treated with a single intravenous infusion of 5 mg zoledronic acid. Calcif Tissue Int 94:311–318
Merlotti D, Gennari L, Martini G, Valleggi F, De Paola V, Avanzati A, Nuti R (2007) Comparison of different intravenous bisphosphonate regimens for Paget’s disease of bone. J Bone Miner Res 22:1510–1517
Polyzos SA, Anastasilakis AD, Litsas I, Efstathiadou Z, Kita M, Arsos G, Moralidis E, Papatheodorou A, Terpos E (2010) Profound hypocalcemia following effective response to zoledronic acid treatment in a patient with juvenile Paget’s disease. J Bone Miner Metab 28:706–712
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonc, E.N., Ozon, A., Buyukyilmaz, G. et al. Acquired resistance to pamidronate treated effectively with zoledronate in juvenile Paget’s disease. Osteoporos Int 29, 1471–1474 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-018-4443-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-018-4443-7