Abstract
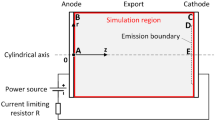
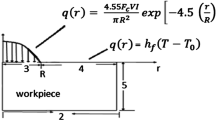
In silicon single crystal micro-electrical discharge machining (Micro-EDM), the plasma channel and workpiece temperature field directly affect the machined parts. For Si single crystal, with short single discharge time and small inter-electrode gap, the temperature cannot be easily measured directly. Based on the theory of energy conservation and heat conduction, combined with Micro-EDM process, in this paper, thermodynamic analysis of plasma in Micro-EDM process is conducted, and a plasma temperature distribution model considering latent heat of fusion is established. Adopting Gaussian distribution heat flux boundary condition and the temperature field distribution of the workpiece surface is simulated by FLUENT. The relationship between material removal rate (MRR) and surface roughness (SR) corresponding to temperature distribution under different peak current and pulse width conditions is analyzed. The results show that plasma temperature has a positive correlation with peak current and pulse width. The increase of peak current and pulse width within the processing parameter range leads to the increase of MRR and SR. The experimental results verify the correctness of the model.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jahan MP, Rahman M, Wong YS (2014) Micro-electrical discharge machining (micro-EDM): processes, varieties, and applications. Compr Mater Process 11:333–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-096532-1.01107-9
Fazli Shahri HR, Mahdavinejad R, Ashjaee M, Abdullah A (2017) A comparative investigation on temperature distribution in electric discharge machining process through analytical, numerical and experimental methods. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 114:35–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.12.005
Mujumdar SS, Curreli D, Kapoor SG, Ruzic D (2014) A model of micro electro-discharge machining plasma discharge in deionized water. J Manuf Sci Eng 136(3):031011. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4026298
Kitamura T, Kunieda M, Abe K (2013) High-speed imaging of EDM gap phenomena using transparent electrodes. Procedia CIRP 6:314–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2013.03.082
Tang JJ, Yang XD (2016) A thermo-hydraulic modeling for the formation process of the discharge crater in EDM. Procedia CIRP 42:685–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.302
Joshi K, Bhandarkar U, Samajdar I, Joshi SS (2018) Microstructural characterization of thermal damage on silicon wafers sliced using wire-electrical discharge machining. J Manuf Sci Eng ASME 140(9):091001. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4039647
Salah NB, Ghanem F, Atig KB (2008) Thermal and mechanical numerical modelling of electric discharge machining process. Commun Numer Methods Eng 24(12):2021–2034. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnm.1091
Natsu W, Ojima S, Kobayashi T, Kunieda M (2004) Temperature distribution measurement in EDM arc plasma using spectroscopy. JSME Int J Ser C 47(1):384–390. https://doi.org/10.1299/jsmec.47.384
Dhanik S, Joshi SS (2005) Modeling of a single resistance capacitance pulse discharge in micro-electro discharge machining. J Manuf Sci Eng 127(4):759. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2034512
Albinski K, Musiol K, Miernikiewicz A, Labuz S, Malota M (1996) The temperature of a plasma used in electrical discharge machining. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 5(4):736–742. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/5/4/015
Joshi SN, Pande SS (2010) Thermo-physical modeling of die-sinking EDM process. J Manuf Process 12(1):45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2010.02.001
Algodi SJ, Clare AT, Brown PD (2017) Modelling of single spark interactions during electrical discharge coating. J Mater Process Technol 252:760–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.10.029
DiBitonto DD, Eubank PT, Patel MR, Barrufet MA (1989) Theoretical models of the electrical discharge machining process. I A simple cathode erosion model. J Appl Phys 66(9):4095–4103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.343994
Yeo SH, Kurnia W, Tan PC (2008) Critical assessment and numerical comparison of electro-thermal models in EDM. J Mater Process Technol 203(1–3):241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.10.026
Yadav V, Jain VK, Dixit PM (2002) Thermal stresses due to electrical discharge machining. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42(8):877–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0890-6955(02)00029-9
Tlili A, Ghanem F, Salah NB (2015) A contribution in EDM simulation field. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79(5–8):921–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6880-1
Shao B, Rajurkar KP (2015) Modelling of the crater formation in micro-EDM. Procedia CIRP 33:376–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2015.06.085
Yeo SH, Kurnia W, Tan PC (2007) Electro-thermal modelling of anode and cathode in micro-EDM. J Phys D Appl Phys 40(8):2513–2521. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/40/8/015
Tao J, Ni J, Shih AJ (2012) Modeling of the anode crater formation in electrical discharge machining. J Manuf Sci Eng 134(1):011002. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4005303
Zhang F, Gu L, Zhao W (2015) Study of the Gaussian distribution of heat flux for micro-EDM. Proceedings of the ASME 2015 international manufacturing science and engineering conference. https://doi.org/10.1115/MSEC20159276
Bin X, Shujuan L, Yuxi L (2017) Experimental research and optimization of process parameters in the electrical discharge machining of Monocrystalline silicon. Acta Armamentarii 38(09):1854–1861. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.09.024
Bin X, Shujuan L, Xiong L, Yongheng D, Weichao S (2017) Modeling analysis and experimental research of the material removal rate of the Monocrystalline silicon in the course of the electrical discharge machining. J Mech Strength 39(03):557–563. https://doi.org/10.16579/j.issn.1001.9669.2017.03.011
Yildiz Y (2016) Prediction of white layer thickness and material removal rate in electrical discharge machining by thermal analyses. J Manuf Process 23:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.05.018
Asad ABMA, Islam MT, Masaki T, Rahman M, Wong YS (2018) Analysis of micro-EDM electric characteristics employing plasma property. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 20:36–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirpj.2017.09.005
Rich JA (1961) Resistance heating in the arc cathode spot zone. J Appl Phys 32(6):1023–1031. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1736153
Zhao YH, Kunieda M, Abe K (2016) EDM mechanism of single crystal SiC with respect to thermal, mechanical and chemical aspects. J Mater Process Technol 236:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.05.010
Kojima A, Natsu W, Kunieda M (2008) Spectroscopic measurement of arc plasma diameter in EDM. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 57(1):203–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2008.03.097
Liu Gao Huang (1990) Numerical simulation of temperature field [M]. Chongqing University Press (in chinese)
Gao D, Tian L (2007) Analysis and simulation of micro electro discharge machining Process. First International Conference on Integration and Commercialization of Micro and Nanosystems 1377–1382. https://doi.org/10.1115/MNC2007-21269
Wang K, Zhang Q, Zhu G, Liu Q, Huang Y, Zhang J (2017) Research on the energy distribution of micro EDM by utilization of electro-thermal model. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(9–12):4179–4186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0822-z
Patel MR, Barrufet MA, Eubank PT, DiBitonto DD (1989) Theoretical models of the electrical discharge machining process. II The anode erosion model. J Appl Phys 66(9):4104–4111. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.343995
Jithin S, Bhandarkar UV, Joshi SS (2017) Analytical simulation of random textures generated in electrical discharge texturing. J Manuf Sci Eng 139(11):111002. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4037322
Tang J, Yang X (2017) A novel thermo-hydraulic coupling model to investigate the crater formation in electrical discharge machining. J Phys D Appl Phys:50. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aa7bb7
Yamasue E, Susa M, Fukuyama H, Nagata K (2002) Thermal conductivities of silicon and germanium in solid and liquid states measured by non-stationary hot wire method with silica coated probe. J Cryst Growth 234:121–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0248(01)01673-6
Saxena KK, Agarwal S, Das R (2018) Evaluation of micro-EDM (μEDM) characteristics of conductive silicon carbide using a coupled thermo-structural process model. J Adv Manuf Syst 17(03):415–443. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219686718500245
Kimoto T, Cooper JA (2014) Fundamentals of silicon carbide technology (growth, characterization, devices and applications) [M]. IEEE Press. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118313534
Funding
The research is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51575442) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No. 2016JZ011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Yin, X., Jia, Z. et al. Modeling of plasma temperature distribution during micro-EDM for silicon single crystal. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 107, 1731–1739 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05135-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-020-05135-x