Abstract
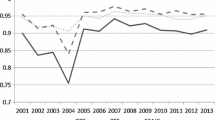
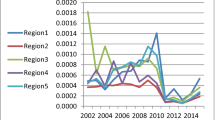
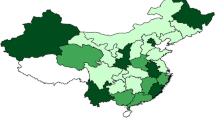
Energy efficiency improvement has been a key objective of China’s long-term energy policy. In this paper, we derive single-factor technical energy efficiency (abbreviated as energy efficiency) in China from multi-factor efficiency estimated by means of a translog production function and a stochastic frontier model on the basis of panel data on 29 Chinese provinces over the period 2003–2011. We find that average energy efficiency has been increasing over the research period and that the provinces with the highest energy efficiency are at the east coast and the ones with the lowest in the west, with an intermediate corridor in between. In the analysis of the determinants of energy efficiency by means of a spatial Durbin error model both factors in the own province and in first-order neighboring provinces are considered. Per capita income in the own province has a positive effect. Furthermore, foreign direct investment and population density in the own province and in neighboring provinces have positive effects, whereas the share of state-owned enterprises in Gross Provincial Product in the own province and in neighboring provinces has negative effects. From the analysis it follows that inflow of foreign direct investment and reform of state-owned enterprises are important policy handles.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We analyze panel data of 29 Chinese provinces over the period 2003–2011. Tibet, Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan are excluded because of lack of data. Guizhou is not included in the analysis because of incomplete data.
We similarly consider spatially lagged controls in model (2).
References
Adetutu MO (2014) Energy efficiency and capital-energy substitutability: evidence from four OPEC countries. Appl Energy 119:363–370
Aigner D, Lovell CAL, Schmidt P (1977) Formulation and estimation of stochastic frontier production function models. J Econom 6:21–37
Alcalá F, Ciccone A (2004) Trade and productivity. Q J Econ 119:613–646
Alguacil M, Cuadros A, Orts V (2011) Inward FDI and growth: the role of macroeconomic and institutional environment. J Policy Model 33:481–496
Ang BW (2006) Monitoring changes in economy-wide energy efficiency: from energy-GDP ratio to composite efficiency index. Energy Policy 34:574–582
Battese G, Coelli T (1992) Frontier production functions, technical efficiency and panel data: with application to paddy farmers in India. J Prod Anal 3:153–169
Blalock G, Gertler PJ (2008) Welfare gains from foreign direct investment through technology transfer to local suppliers. J Int Econ 74:402–421
Boyd G (2007) Estimating the distribution of plant-level manufacturing energy efficiency with stochastic frontier regression. Soc Sci Res Netw. http://ssrn.com/abstract=1015593
BP (2013) Statistical review of world energy 2013. BP. http://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/pdf/statistical-review/statistical_review_of_world_energy_2013.pdf
Buck J, Young D (2007) The potential for energy efficiency gains in the Canadian commercial building sector: a stochastic frontier study. Energy 32:1769–1780
Cattaneo C, Manera M, Scarpa E (2011) Industrial coal demand in China: a provincial analysis. Resour Energy Econ 33:12–35
Chai J, Guo JE, Wang SY, Lai KK (2009) Why does energy intensity fluctuate in China? Energy Policy 37:5717–5731
Cheung KY, Lin P (2004) Spillover effects of FDI on innovation in China: evidence from the provincial data. China Econ Rev 15:25–44
Christensen L, Jorgensen D, Lau L (1973) Transcendental logarithmic production frontiers. Rev Econ Stat 4:28–45
Coe DT, Helpman E, Hoffmaister AW (1997) North-South R&D spillovers. Econ J 107:134–149
Crompton P, Wu Y (2005) Energy consumption in China: past trends and future directions. Energy Econ 27:195–208
Davis B (2013) China’s leaders press on with urbanization as tool for growth. Wall Str J. http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304202204579259221407331500
Dinda S (2004) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a survey. Ecol Econ 49:431–455
Dougherty S, Herd R, He P (2007) Has a private sector emerged in China’s industry? Evidence from a quarter of a million Chinese firms. China Econ Rev 18:309–334
Elhorst JP (2014) Spatial econometrics: from cross-sectional data to spatial panels. Springer, Berlin
Elliott RJ, Sun P, Chen S (2013) Energy intensity and foreign direct investment: a Chinese city-level study. Energy Econ 40:484–494
Fang Y, Zeng Y (2007) Balancing energy and environment: the effect and perspective of management instruments in China. Energy 32:2247–2261
Filippini M, Hunt LC (2011) Energy demand and energy efficiency in the OECD countries: a stochastic demand frontier approach. Energy J 32:59–80
Filippini M, Hunt LC (2012) US residential energy demand and energy efficiency: a stochastic demand frontier approach. Energy Econ 34:1484–1491
Fisher-Vanden K, Hu Y, Jefferson GH, Rock MT, Toman M (2013) Factors influencing energy intensity in four Chinese industries. In: World Bank Policy Research Working Paper
Fisher-Vanden K, Jefferson GH, Ma JK, Xu JY (2006) Technology development and energy productivity in China. Energy Econ 28:690–705
Fisher-Vanden K, Jefferson G, Liu H, Tao Q (2004) What is driving China’s decline in energy intensity? Resour Energy Econ 26:77–97
Fouquau J, Destais G, Hurlin C (2009) Energy demand models: a threshold panel specification of the ‘Kuznets curve’. Appl Econ Lett 16:1241–1244
Fu F, Liu H, Polenske KR, Li Z (2013) Measuring the energy consumption of China’s domestic investment from 1992 to 2007. Appl Energy 102:1267–1274
Goldsmith RW (1951) A perpetual inventory of national wealth. In: Studies in income and wealth, NBER. http://www.nber.org/chapters/c9716.pdf
Hang L, Tu M (2007) The impacts of energy prices on energy intensity: evidence from China. Energy Policy 35:2978–2988
Harrison A (1996) Openness and growth: a time-series, cross-country analysis for developing countries. J Dev Econ 48:419–447
Henry M, Kneller R, Milner C (2009) Trade, technology transfer and national efficiency in developing countries. Eur Econ Rev 53:237–254
Herrerias MJ, Cuadros A, Orts V (2013) Energy intensity and investment ownership across Chinese provinces. Energy Econ 36:286–298
Holz CA (2004) China’s statistical system in transition: challenges, data problems, and institutional innovations. Rev Income Wealth 50:381–409
Hu AG, Jefferson GH (2002) FDI impact and spillover: evidence from China’s electronic and textile industries. World Econ 25:1063–1076
Hu JL, Wang SC (2006) Total-factor energy efficiency of regions in China. Energy Policy 34:3206–3217
Hübler M, Keller A (2010) Energy saving via FDI? Empirical evidence from developing countries. Environ Dev Econ 15:59–80
IEA (2009) World energy outlook 2009. International Energy Agency. http://www.worldenergyoutlook.org/media/weowebsite/2009/WEO2009.pdf
IEA (2010) World energy outlook 2010. International Energy Agency. http://www.worldenergyoutlook.org/media/weo2010.pdf
IEA (2011) World energy outlook 2011. International Energy Agency. http://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/WEO2011_WEB.pdf
IMF (2013) World economic outlook: transitions and tensions. International Monetary Fund. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/02/pdf/text.pdf
Jones DW (1991) How urbanization affects energy-use in developing countries. Energy Policy 19:621–630
Karagiannis G, Tzouvelekas V, Xepapadeas A (2003) Measuring irrigation water efficiency with a stochastic production frontier. Environ Resour Econ 26(1):57–72
Keller W (2002) Trade and the transmission of technology. J Econ Growth 7:5–24
Keller W (2004) International technology diffusion. J Econ Lit 42:752–782
Komen MH, Gerking S, Folmer H (1997) Income and environmental R&D: empirical evidence from OECD countries. Environ Dev Econ 2:505–515
Kouser S, Qaim M (2015) Bt cotton, pesticide use and environmental efficiency in Pakistan. J Agr Econ 66(1):66–86
Kugler M (2006) Spillovers from foreign direct investment: within or between industries? J Dev Econ 80:444–477
Li X, Liu X, Parker D (2001) Foreign direct investment and productivity spillovers in the Chinese manufacturing sector. Econ Syst 25:305–321
Lin B, Du K (2013) Technology gap and China’s regional energy efficiency: a parametric metafrontier approach. Energy Econ 40:529–536
Lin JY, Tan G (1999) Policy burdens, accountability, and the soft budget constraint. Am Econ Rev 89:426–431
Liu W, Li H (2011) Improving energy consumption structure: a comprehensive assessment of fossil energy subsidies reform in China. Energy Policy 39:4134–4143
Liu Y (2009) Exploring the relationship between urbanization and energy consumption in China using ARDL (autoregressive distributed lag) and FDM (factor decomposition model). Energy 34:1846–1854
López-Casero A (2010) Navigating U.S. export controls requirements when exporting commercial products from the U.S. to China. Nixon Peabody. http://www.nixonpeabody.com/files/China_Alert_11_11_2010.pdf
López RE, Yoon SW (2013) Sustainable economic growth: the ominous potency of structural change. Int Rev Environ Resour Econ 7:179–203
Ma L, Feng S, Reidsma P, Qu F, Heerink N (2014) Identifying entry points to improve fertilizer use efficiency in Taihu Basin. China. Land use policy 37(2):52–59
Madlener R, Sunak Y (2011) Impacts of urbanization on urban structures and energy demand: what can we learn for urban energy planning and urbanization management? Sustain Cities Soc 1:45–53
Meeusen W, Van den Broeck J (1977) Efficiency estimation from Cobb-Douglas production functions with composed error. Int Econ Rev 18:435–444
Metcalf GE (2008) An empirical analysis of energy intensity and its determinants at the state level. Energy J 29(3):1–26
Miller SM, Upadhyay MP (2000) The effects of openness, trade orientation, and human capital on total factor productivity. J Dev Econ 63:399–423
Mulder P, de Groot HL (2012) Structural change and convergence of energy intensity across OECD countries, 1970–2005. Energy Econ 34:1910–1921
OECD Territorial Review (2009) Trans-border urban co-operation in the Pan Yellow Sea Region. OECD. https://geopousp.files.wordpress.com/2010/05/oecd-trans-border-urban-cooperation-in-the-pan-yellow-sea-region.pdf
Panayotou T (1993) Empirical tests and policy analysis of environmental degradation at different stages of economic development. International Labour Office. http://www.ilo.org/public/libdoc/ilo/1993/93B09_31_engl.pdf
Pavelescu FM (2011) Some aspects of the translog production function estimation. Rom J Econ 32:131–150
Peterson S (2008) Greenhouse gas mitigation in developing countries through technology transfer? A survey of empirical evidence. Mitig Adapt Strateg Glob Chang 13:283–305
Reinhard S, Lovell CK, Thijssen G (1999) Econometric estimation of technical and environmental efficiency: an application to Dutch dairy farms. Am J Agric Econ 81:44–60
Ren S, Yuan B, Ma X, Chen X (2014) International trade, FDI (foreign direct investment) and embodied \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) emissions: a case study of Chinas industrial sectors. China Econ Rev 28:123–134
Rodriguez-Clare A (1996) Multinationals, linkages, and economic development. Am Econ Rev 86(4):852–873
Segal D (2003) A multi-product cost study of the U.S. life insurance industry. Rev Quant Financ Acc 20:169–186
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Tahir MI (2013) The dynamic links between energy consumption, economic growth, financial development and trade in China: fresh evidence from multivariate framework analysis. Energy Econ 40:8–21
Shan H (2008) Re-estimating the capital stock of China: 1952–2006. J Quant Tech Econ 10:17–31 (in Chinese)
Song F, Zheng X (2012) What drives the change in China’s energy intensity: combining decomposition analysis and econometric analysis at the provincial level. Energy Policy 51:445–453
Song M, Wang S, Yu H, Yang L, Wu J (2011) To reduce energy consumption and to maintain rapid economic growth: analysis of the condition in China based on expended IPAT model. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 15:5129–5134
Stern DI (2004) The rise and fall of the environmental Kuznets curve. World Dev 32:1419–1439
Stern DI (2006) Reversal of the trend in global anthropogenic sulfur emissions. Global Environl Chang 16:207–220
Stern DI (2012) Modeling international trends in energy efficiency. Energy Econ 34:2200–2208
Suri V, Chapman D (1998) Economic growth, trade and energy: implications for the environmental Kuznets curve. Ecol Econ 25:195–208
Tanaka K (2008) Assessment of energy efficiency performance measures in industry and their application for policy. Energy Policy 36:2887–2902
Tang J, Folmer H, van der Vlist A, Xue J (2013) The impacts of management reform on irrigation water use efficiency in the Guanzhong plain, China. Pap Reg Sci 93:455–475
Tsekouras KD, Pantzios CJ, Karagiannis G (2004) Malmquist productivity index estimation with zero value variables: the case of Greek prefectural training councils. Int J Prod Econ 89:95–106
Wang HJ, Ho CW (2010) Estimating fixed effect panel stochastic frontier models by model transformation. J Econom 157:286–296
Wang XL, Meng L (2001) A reevaluation of China’s economic growth. China Econ Rev 12:338–346
Wei C, Ni J, Shen M (2009) Empirical analysis of provincial energy efficiency in China. China World Econ 17:88–103
Wei Y, Liu X, Song H, Romilly P (2001) Endogenous innovation growth theory and regional income convergence in China. J Int Dev 13:153–168
Wu Y (2012) Energy intensity and its determinants in China’s regional economies. Energy Policy 41:703–711
York R (2007) Demographic trends and energy consumption in European Union Nations, 1960–2025. Soc Sci Res 36:855–872
Yu S, Wei YM, Wang K (2012) China’s primary energy demands in 2020: predictions from an MPSO-RBF estimation model. Energy Convers Manag 61:59–66
Yuan JH, Kang JG, Zhao CH, Hu ZG (2008) Energy consumption and economic growth: evidence from China at both aggregated and disaggregated levels. Energy Econ 30:3077–3094
Yuan J, Xu Y, Hu Z, Zhao C, Xiong M, Guo J (2014) Peak energy consumption and \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) emissions in China. Energy Policy 68:205–523
Zhan BM (2006) Adjustment of US trade policies toward China and its implications for the Chinese economy. World Econ Polit 10:75–80 (in Chinese)
Zhang LY (2004) The roles of corporatization and stock market listing in reforming China’s state industry. World Dev 32:2031–2047
Zhang C, Lin Y (2012) Panel estimation for urbanization, energy consumption and \(\text{ CO }_{2}\) emissions: A regional analysis in China. Energy Policy 49:488–498
Zhang X, Ruoshui W, Molin H, Martinot E (2010) A study of the role played by renewable energies in China’s sustainable energy supply. Energy 35:4392–4399
Zhang D, Aunan K, Martin Seip H, Vennemo H (2011a) The energy intensity target in China’s 11th Five-Year-Plan period Local implementation and achievements in Shanxi Province. Energy Policy 39:4115–4124
Zhang J, Deng S, Shen F, Yang X, Liu G, Guo H, Li YW, Hong X, Zhang YZ, Peng H, Zhang XH, Li L, Wang Y (2011b) Modeling the relationship between energy consumption and economy development in China. Energy 36:4227–4234
Zhang N, Lior N, Jin H (2011c) The energy situation and its sustainable development strategy in China. Energy 36:3639–3649
Zhou P, Ang BW, Zhou DQ (2012) Measuring economy-wide energy efficiency performance: a parametric frontier approach. Appl Energy 90:196–200
Zhou X, Li KW, Li Q (2011) An analysis on technical efficiency in post-reform China. China Econ Rev 22:357–372
Zou G, Chen L, Liu W, Hong X, Zhang G, Zhang Z (2013) Measurement and evaluation of Chinese regional energy efficiency based on provincial panel data. Math Comput Model 58:1000–1009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Folmer, H., Ji, M. et al. Energy efficiency in the Chinese provinces: a fixed effects stochastic frontier spatial Durbin error panel analysis. Ann Reg Sci 58, 301–319 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-016-0782-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-016-0782-5