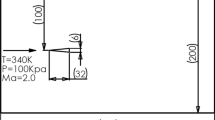
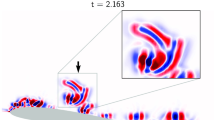
Abstract
The dynamics of oblique shock wave/turbulent boundary layer interactions is analyzed by mining a large-eddy simulation (LES) database for various strengths of the incoming shock. The flow dynamics is first analyzed by means of dynamic mode decomposition (DMD), which highlights the simultaneous occurrence of two types of flow modes, namely a low-frequency type associated with breathing motion of the separation bubble, accompanied by flapping motion of the reflected shock, and a high-frequency type associated with the propagation of instability waves past the interaction zone. Global linear stability analysis performed on the mean LES flow fields yields a single unstable zero-frequency mode, plus a variety of marginally stable low-frequency modes whose stability margin decreases with the strength of the interaction. The least stable linear modes are grouped into two classes, one of which bears striking resemblance to the breathing mode recovered from DMD and another class associated with revolving motion within the separation bubble. The results of the modal and linear stability analysis support the notion that low-frequency dynamics is intrinsic to the interaction zone, but some continuous forcing from the upstream boundary layer may be required to keep the system near a limit cycle. This can be modeled as a weakly damped oscillator with forcing, as in the early empirical model by Plotkin (AIAA J 13:1036–1040, 1975).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alizard, F., Pirozzoli, S., Bernardini, M., Grasso, F.: Optimal transient growth in compressible turbulent boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 770, 124–155 (2014)
Aubard, G., Gloerfelt, X., Robinet, J.: Large-eddy simulation of broadband unsteadiness in a shock/boundary-layer interaction. AIAA J. 51, 2395–2409 (2013)
Beresh, S., Clemens, N., Dolling, D.: Relationship between upstream turbulent boundary layer velocity fluctuations and separation shock unsteadiness. AIAA J. 40, 2412–2422 (2002)
Bermejo-Moreno, I., Campo, L., Larsson, J., Bodart, J., Helmer, D., Eaton, J.: Confinement effects in shock wave/turbulent boundary layer interactions through wall-modelled large-eddy simulations. J. Fluid Mech. 758, 5–62 (2014)
Clemens, N., Narayanaswamy, V.: Shock/turbulent boundary layer interactions: Review of recent work on sources of unsteadiness. In: 39th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference, San Antonio, Texas, aIAA Paper 2009-3710 (2009)
Clemens, N., Narayanaswamy, V.: Low-frequency unsteadiness of shock wave/turbulent boundary layer interactions. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 46, 469–492 (2014)
Crouch, J., Garbaruk, A., Magidov, D.: Predicting the onset of flow unsteadiness based on global instability. J. Comput. Phys. 224, 924–940 (2007)
Délery, J., Dussauge, J.P.: Some physical aspects of shock wave/boundary layer interactions. Shock Waves 19, 453–468 (2009)
Dolling, D.S.: Fifty years of shock-wave/boundary-layer interaction research: what next? AIAA J. 39, 1517–1530 (2001)
Eléna, M., Lacharme, J.: Experimental study of a supersonic turbulent boundary layer using a laser doppler anemometer. J. Méc. Théor. Appl. 7, 175–190 (1988)
Erengil, M., Dolling, D.: Correlation of separation shock motion with pressure fluctuations in the incoming boundary layer. AIAA J. 29, 1868–1877 (1991)
Ganapathisubramani, B., Clemens, N.T., Dolling, D.S.: Effects of upstream boundary layer on the unsteadiness of shock-induced separation. J. Fluid Mech. 585, 369–394 (2007)
Garnier, E., Sagaut, P., Deville, M.: Large-Eddy simulation of shock/boundary-layer interaction. AIAA J. 40, 1935–1944 (2002)
Grilli, M., Schmid, P., Hickel, S., Adams, N.: Analysis of unsteady behaviour in shockwave turbulent boundary layer interaction. J. Fluid Mech. 700, 16–28 (2012)
Hadjadj, A., Larsson, J., Morgan, B., Nichols, J., Lele, S.: Large-eddy simulation of shock/boundary-layer interaction. In: Proceedings of the 2010 CTR Summer Program, Stanford University (2010)
Hutchins, N., Marusic, I.: Evidence of very long meandering features in the logarithmic region of turbulent boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 579, 1–28 (2007)
Kennedy, C., Gruber, A.: Reduced aliasing formulations of the convective terms within the Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 1676–1700 (2008)
Konno, K., Ohmachi, T.: Ground-motion characteristics estimated from spectral ratio between horizontal and vertical components of microtremor. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 88(1), 228–241 (1998)
Lehoucq, R.B., Sorensen, D.C., Yang, C.: ARPACK Users’ Guide: Solution of Large-Scale Eigenvalue Problems with Implicitly Restarted Arnoldi Methods. SIAM, Philadelphia (1998)
Lele, S.: Compact finite difference schemes with spectral-like resolution. J. Comput. Phys. 103, 16–42 (1992)
Lund, T., Wu, X., Squires, K.: Generation of turbulent inflow data for spatially-developing boundary layer simulations. J. Fluid Mech. 140, 233–258 (1998)
Mani, A.: Analysis and optimization of numerical sponge layers as a nonreflective boundary treatment. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 704–716 (2012)
Moin, P., Squires, K., Cabot, W., Lee, S.: A dynamic subgrid-scale model for compressible turbulence and scalar transport. Phys. Fluids A 3, 2746–2757 (1991)
Morgan, B., Duraisamy, K., Nguyen, N., Kawai, S., Lele, S.: Flow physics and RANS modelling of oblique shock/turbulent boundary layer interaction. J. Fluid Mech. 729, 231–284 (2013)
Nichols, J., Lele, S.: Global modes and transient response of a cold supersonic jet. J. Fluid Mech. 669, 225–241 (2011)
Piponniau, S., Dussauge, J., Debiève, J., Dupont, P.: A simple model for low-frequency unsteadiness in shock-induced separation. J. Fluid Mech. 629, 87–108 (2009)
Pirozzoli, S.: Generalized conservative approximations of split convective derivative operators. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 7180–7190 (2010)
Pirozzoli, S., Bernardini, M.: Direct numerical simulation database for impinging shock wave/turbulent boundary-layer interaction. AIAA J. 49, 1307–1312 (2011)
Pirozzoli, S., Grasso, F.: Direct numerical simulation of impinging shock wave turbulent boundary layer interaction at \(M=2.25\). Phys. Fluids 18, 065113 (2006)
Pirozzoli, S., Bernardini, M., Grasso, F.: Direct numerical simulation of transonic shock/boundary layer interaction under conditions of incipient separation. J. Fluid Mech. 657, 361–393 (2010)
Pirozzoli, S., Larsson, J., Nichols, J., Bernardini, M., Morgan, B., Lele, S.: Analysis of unsteady effects in shock/boundary layer interactions. In: Proceedings of the 2010 CTR Summer Program, Stanford University (2010)
Plotkin, K.: Shock wave oscillation driven by turbulent boundary-layer fluctuations. AIAA J. 13, 1036–1040 (1975)
Poinsot, T., Lele, S.: Boundary conditions for direct simulations of compressible viscous flows. J. Comput. Phys. 101, 104–129 (1992)
Priebe, S., Wu, M., Martin, M.P.: Direct numerical simulation of a reflected shock wave/turbulent boundary layer interaction. AIAA J. 47(5), 1173–1184 (2009)
Reau, N., Tumin, A.: On harmonic perturbations in a turbulent mixing layer. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 21, 143–155 (2002)
Reynolds, W.C., Hussain, A.K.M.F.: The mechanics of an organized wave in turbulent shear flow. Part 3. Theoretical models and comparisons with experiments. J. Fluid Mech. 54, 263–288 (1972)
Robinet, J.C.: Bifurcations in shock-wave/laminar-boundary-layer interaction: global instability approach. J. Fluid Mech. 579, 85–112 (2007)
Rowley, C., Mezic, I., Bagheri, S., Schlatter, P., Henningson, D.: Spectral analysis of nonlinear flows. J. Fluid Mech. 641, 115–127 (2009)
Sansica, A., Sandham, N.D., Hu, Z.: Forced response of a laminar shock-induced separation bubble. Phys. Fluids 26(9), 093601 (2014)
Sayadi, T., Hamman, C., Schmid, P.: Parallel QR algorithm for data-driven decompositions. In: Proceedings of the 2010 CTR Summer Program, Stanford University (2014)
Schmid, P.: Dynamic mode decomposition of numerical and experimental data. J. Fluid Mech. 656, 5–28 (2010)
Simens, M., Jiménez, J., Hoyas, S., Mizuno, Y.: A high-resolution code for a turbulent boundary layers. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 4218–4231 (2009)
Souverein, L., Dupont, P., Debiève, J.F., Dussauge, J.P., van Oudheusden, B.W., Scarano, F.: Effect of interaction strength on unsteadiness in turbulent shock-wave-induced separations. AIAA J. 48, 1480–1493 (2010)
Touber, E., Sandham, N.: Large-eddy simulation of low-frequency unsteadiness in a turbulent shock-induced separation bubble. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 23, 79–107 (2009)
Touber, E., Sandham, N.: Low-order stochastic modelling of low-frequency motions in reflected shock-wave/boundary-layer. J. Fluid Mech. 671, 417–465 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Dr. M.R. Malik.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nichols, J.W., Larsson, J., Bernardini, M. et al. Stability and modal analysis of shock/boundary layer interactions. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 31, 33–50 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00162-016-0397-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00162-016-0397-6