Abstract
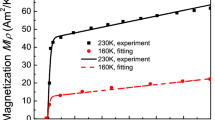
This is the concluding part III of a series of papers. The aim of the current paper is to simulate and analyze the procedure of variant reorientation in a magnetic shape-memory alloy (MSMA) sample and to predict the response of the sample subject to various loading conditions. The sample to be considered in this paper has a 3D cuboid shape and is subject to typical magneto-mechanical loading conditions. Variant reorientation in the sample is realized through twin interface movements. To investigate the key features of twin interface movements, the properties of configurational forces on the twin interfaces are analyzed. For both the stress-assisted MFIS tests and the field-assisted quasi-elasticity tests, the magneto-mechanical behavior of the MSMA sample during the whole loading procedure is simulated by using the finite element method. The influence of the initial variant distribution in the sample on its global response is discussed. The obtained numerical results are compared with the experimental results. It can be seen that the model predictions can fit the experimental results both at a qualitative as well as at a quantitative level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang J., Steinmann P.: On the modelling of equilibrium twin interfaces in a single-crystalline magnetic shape memory alloy sample. I: Theoretical formulation. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 26, 563–592 (2014)
Wang, J., Steinmann, P.: On the modelling of equilibrium twin interfaces in a single-crystalline magnetic shape memory alloy sample. II: Numerical algorithm. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. doi:10.1007/s00161-014-0403-4
Tickle R., James R.D.: Magnetic and magnetomechanical properties of Ni 2 MnGa. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 195, 627–638 (1999)
Murrey S.J., Marioni M., Allen S.M., O’Handley R.C., Lograsso T.A.: 6 magnetic-field-induced strain by twin-boundary motion in ferromagnetic Ni–Mn–Ga. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 886–888 (2000)
Heczko O., Glavatska N., Gavriljuk V., Ullakko K.: Influence of magnetic field and stress on large magnetic shape memory effect in single crystalline Ni–Mn–Ga ferromagnetic alloy at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Forum 373–376, 341–344 (2001)
Müllner P., Chernenko V.A., Kostorz G.: Stress-induced twin rearrangement resulting in change of magnetization in a Ni–Mn–Ga ferromagnetic martensite. Scr. Mater. 49, 129–133 (2003)
Straka L., Heczko O.: Superelastic response of NiCMnCGa martensite in magnetic fields and a simple model. IEEE Trans. Magn. 39, 3402–3404 (2003)
Chernenko V.A., L’vov V.A., Müllner P., Kostorz G., Takagi T.: Magnetic-field-induced superelasticity of ferromagnetic thermoelastic martensites: experiment and modeling. Phys. Rev. B 69, 134410 (2004)
Karaca H.E., Karaman I., Basaran B., Chumlyakov Y.I., Maier H.J.: Magnetic field and stress induced martensite reorientation in NiMnGa ferromagnetic shape memory alloy single crystals. Acta Mater. 54, 233–245 (2006)
Straka, L.: Magnetic and magneto-mechanical properties of Ni–Mn–Ga magnetic shape memory alloys. Doctoral dissertation, Helsinki University of Technology (2007)
Straka L., Lanska N., Ullakko K., Sozinov A.: Twin microstructure dependent mechanical response in Ni–Mn–Ga single crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 131903 (2010)
Chmielus M., Glavatskyy I., Hoffmann J.-U., Chernenko V.A., Schneiderd R., Mullner P.: Influence of constraints and twinning stress on magnetic field-induced strain of magnetic shape-memory alloys. Scr. Mater. 64, 888–891 (2011)
Chen X., He Y.J., Moumni Z.: Twin boundary motion in NiMnGa single crystals under biaxial compression. Mater. Lett. 90, 72–75 (2013)
Chen X., Moumni Z., He Y.J., Zhang W.H.: A three-dimensional model of magneto-mechanical behaviors of martensite reorientation in ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 64, 249–286 (2014)
LaMaster D.H., Feigenbaum H.P., Nelson I.D., Ciocanel C.: A full two-dimensional thermodynamic-based model for magnetic shape memory alloys. J. Appl. Mech. 81, 061003 (2014)
Chen Q., Konrad A.: A review of finite element open boundary techniques for static and quasi-static electromagnetic field problems. IEEE Trans. Mag. 33, 663–676 (1997)
Eshelby J.D.: The elastic energy-momentum tensor. J. Elast. 5, 321–335 (1975)
Suorsa, I.: Performance and modeling of magnetic shape memory actuators and sensors. Doctoral dissertation, Helsinki University of Technology (2005)
Straka L., Hänninen H., Soroka A., Sozinov A.: Ni–Mn–Ga single crystals with very low twinning stress. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 303, 012079 (2011)
Abeyaratne R.: An admissibility condition for equilibrium shocks in finite elasticity. J. Elast. 13, 175–184 (1983)
Landis C.M.: A continuum thermodynamics formulation for micro-magneto-mechanics with applications to ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56, 3059–3076 (2008)
Wu P.P., Ma X.Q., Zhang J.X., Chen L.Q.: Phase-field simulations of stress–strain behaviour in ferromagnetic shape memory alloy NiMnGa. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 073906 (2008)
Jin Y.M.: Effects of twin boundary mobility on domain microstructure evolution in magnetic shape memory alloys: phase field simulation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 062508 (2009)
Li L.J., Lei C.H., Shu Y.C., Li J.Y.: Phase-field simulation of magnetoelastic couplings in ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Acta. Mater. 59, 2648–2655 (2011)
Mennerich C., Wendler F., Jainta M., Nestler B.: A phase-field model for the magnetic shape memory effect. Arch. Mech. 63, 549–571 (2011)
Peng Q., He Y.J., Moumni Z.: A phase-field model on the hysteretic magneto-mechanical behaviors of ferromagnetic shape memory alloy. Acta. Mater. 88, 13–24 (2015)
Lai, Y.W.: Magnetic microstructure and actuation dynamics of NiMnGa magnetic shape memory materials. Ph.D. thesis, Technical University of Dresden (2009)
Straka L., Hänninen H., Lanska N., Sozinov A.: Twin interaction and large magnetoelasticity in Ni–Mn–Ga single crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 063504 (2011)
Ball J.M., James R.D.: Fine phase mixtures as minimizers of energy. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 100, 13–52 (1987)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Andreas Öchsner.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Steinmann, P. On the modeling of equilibrium twin interfaces in a single-crystalline magnetic shape-memory alloy sample—III: Magneto-mechanical behaviors. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 28, 885–913 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-015-0452-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-015-0452-3