Abstract
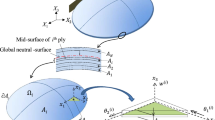
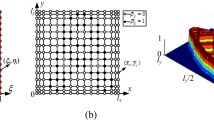
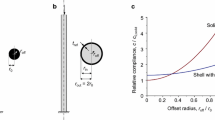
Topology stiffness (compliance) design of linear and geometrically nonlinear shell structures is solved using the SIMP approach together with a filtering scheme. A general anisotropic multi-layer shell model is employed to allow the formation of through-the-thickness holes or stiffening zones. The finite element analysis is performed using nine-node Mindlin-type shell elements based on the degenerated shell approach, which are capable of modeling both single and multi-layered structures exhibiting anisotropic or isotropic behavior. The optimization problem is solved using analytical compliance and constraint sensitivities together with the Method of Moving Asymptotes (MMA). Geometrically nonlinear problems are solved using iterative Newton–Raphson methods and an adjoint variable approach is used for the sensitivity analysis. Several benchmark tests are presented in order to illustrate the difference in optimal topologies between linear and geometrically nonlinear shell structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1996Bathe-1996 Bathe, K.J. 1996: Finite element procedures. New Jersey: Prentice Hall
2002belblidia-bulman-2002 Belblidia, F.; Bulman, S. 2002: A hybrid topology optimization algorithm for static and vibrating shell structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng54, 835–852
2001Belblidia-etal-2001 Belblidia, F.; Lee, J.E.B.; Rechak, S.; Hinton, E. 2001: Topology optimization of plate structures using a single- or three-layered artificial material model. Adv Eng Softw32(2), 159–168
1989Bendsoe-1989 Bendsøe, M.P. 1989: Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Optim1, 193–203
1988Bendsoe-kikuchi-1988 Bendsøe, M.P.; Kikuchi, N. 1988: Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng71(2), 197–224
2003Bendsoe-Sigmund-2003 Bendsøe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. 2003: Topology optimization – theory, methods and applications. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer, 2nd edn.
2002Bruns-etal-2002 Bruns, T.E.; Sigmund, O.; Tortorelli, D.A. 2002: Numerical methods for the topology optimization of structures that exhibit snap-through. Int J Numer Methods Eng55, 1215–1237
2001Bruns-Tortorelli-2001 Bruns, T.E.; Tortorelli, D.A. 2001: Topology optimization of non-linear elastic structures and compliant mechanisms. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng190, 3443–3459
2000Buhl-etal-2000 Buhl, T.; Pedersen, C.B.W.; Sigmund, O. 2000: Stiffness design of geometrically nonlinear structures using topology optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim19, 93–104
1995Diaz-etal-1995 Diaz, A.R.; Lipton, R.; Soto, C.A. 1995: A new formulation of the problem of optimum reinforcement of reissner-mindlin plates. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng123, 121–139
2001Eschenauer-Olhoff-2001 Eschenauer, H.A.; Olhoff, N. 2001: Topology optimization of continuum structures: A review. Appl Mech Rev54(4); 331–389
2001Gea-Luo-2001 Gea, H.C.; Luo, J. 2001: Topology optimization of structures with geometrical nonlinearities. Comput Struct79, 1977–1985
1986Haug-etal-1986 Haug, E.J.; Choi, K.K.; Komkov, V. 1986: Design sensitivity analysis of structural systems. Amsterdam: Academic
1996Jog-1996 Jog, C. 1996: Distributed-parameter optimization and topology design for non-linear thermoelasticity. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng132, 117–134
1998Jones-1998 Jones, R.M. 1998: Mechanics of composite materials. London: Taylor and Francis, 2nd edn.
1999Krog-Olhoff-1999 Krog, L.A.; Olhoff, N. 1999: Optimum topology and reinforcement design of disk and plate structures with multiple stiffness and eigenfrequency objectives. Comput Struct72, 535–563
1997Kumar-Palaninathan-1997 Prema Kumar, W.P.; Palaninathan, R. 1997: Finite element analysis of laminated shells with exact through-thickness integration. Comput Struct63, 173–184
2000Lee-etal-2000 Lee, S.J.; Bae, J.E.; Hinton, E. 2000: Shell topology optimization using the layered artificial material model. Int J Numer Methods Eng47, 843–867
1997Maute-Ramm-1997 Maute, K.; Ramm, E. 1997: Adaptive topology optimization of shell structures. AIAA J35(11), 1767–1773
2004Must-2004 MUST 2004: Institute of Mechanical Engineering, Aalborg University, Denmark. www.ime.auc.dk/must, June 2004
1992Rozvany-etal-1992 Rozvany, G.I.N.; Zhou, M.; Birker, T. 1992: Generalized shape optimization without homogenization. Struct Optim4, 250–252
2001Stegmann-etal-2001b Stegmann, J.; Jensen, L.R.; Rauhe, J.M.; Lund, E. 2001: Shell element for geometrically non-linear analysis of composite laminates and sandwich structures. In: Beldia, L. et al. (eds.), 14th Nordic Seminar on Computational Mechanics (NSCM14), pp. 83–86. Division of Structural Mechanics, LTH, Sweden
1987Svanberg-1987 Svanberg, K. 1987: The method of moving asymptotes – a new method for structural optimization. Numer Methods Eng24, 359–373
1999Yuge-etal-1999 Yuge, K.; Iwai, N.; Kikuchi, N. 1999: Optimization of 2-d structures subjected to nonlinear deformations using the homogenization method. Struct Optim17(4), 286–299
1991Zhou-Rozvany-1991 Zhou, M; Rozvany, G.I.N. 1991: The COC algorithm – Part II. Topological, geometrical and generalized shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng89, 309–336
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stegmann, J., Lund, E. Nonlinear topology optimization of layered shell structures. Struct Multidisc Optim 29, 349–360 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-004-0468-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-004-0468-y