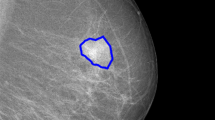
Abstract
In this paper, an effective method is proposed for breast mass segmentation using a superpixel generation and curve evolution method. The simple linear iterative clustering method and density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise method are applied to generate superpixels in mammograms at first. Thereafter, a region of interesting (ROI) that contains the breast mass is built on the superpixel generation results. Finally, the image patch and the position of the manual labeled seed are used to build the prior knowledge for the level set method driven by the local Gaussian distribution fitting energy and evolve the curve to capture the edge of breast mass in ROI. Experimental results on mammogram data set demonstrate that the proposed method shows superior performance in contrast to some well-known methods in breast mass segmentation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeSantis, C., Ma, J., Bryan, L., et al.: Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J. Clin. 64(1), 52–62 (2014)
Harbeck, N., Gnant, M.: Breast cancer. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 21(1), 51–65 (2016)
Murkies, A., Dalais, F.S., Briganti, E.M., et al.: Phytoestrogens and breast cancer in postmenopausal women: a case control study. Menopause-the J. North Am. Menopause Soc. 7(5), 289 (2016)
Veronese, S.M., Gambacorta, M., Gottardi, O., et al.: Proliferation index as a prognostic marker in breast cancer. Cancer 71(12), 3926–3931 (2015)
Klemm, M., Craddock, I.J., Preece, A., et al.: Evaluation of a hemi-spherical wideband antenna array for breast cancer imaging. Radio Sci. 43(6), 1–15 (2016)
Bower, J.E., Ganz, P.N.: Altered cortisol response to psychologic stress in breast cancer survivors with persistent fatigue. Psychosom. Med. 67(2), 277–280 (2016)
Song, H., Ramus, S.J., Kjaer, S.K., et al.: Association between invasive ovarian cancer susceptibility and 11 best candidate SNPs from breast cancer genome-wide association study. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18(12), 2297–2304 (2016)
Brown, R.S., Wahl, R.L.: Overexpression of Glut-1 glucose transporter in human breast cancer. An Immunohistochem. Study. Cancer 72(10), 2979–2985 (2015)
Rouhi, R., Jafari, M., Kasaei, S., et al.: Benign and malignant breast tumors classification based on region growing and CNN segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(3), 990–1002 (2015)
Dong, Z., Yu, L., Yan, Y., et al.: A region-based segmentation method for ultrasound images in HIFU therapy. Med. Phys. 43(6), 2975–2989 (2016)
Shi, C., Cheng, Y., Liu, F., et al.: A hierarchical local region-based sparse shape composition for liver segmentation in CT scans. Pattern Recognit. 50(C), 88–106 (2016)
Li, D., Zang, P., Chai, X., et al.: Automatic multiorgan segmentation in CT images of the male pelvis using region-specific hierarchical appearance cluster models. Med. Phys. 43(10), 5426 (2016)
Hao, L., Zhang, S., Rui, M., et al.: Ultrasound intima-media thickness measurement of the carotid artery using ant colony optimization combined with a curvelet-based orientation-selective filter. Med. Phys. 43(4), 1795 (2016)
Javaid, Z., Boocock, M.G., Mcnair, P.J., et al.: Contour interpolated radial basis functions with spline boundary correction for fast 3D reconstruction of the human articular cartilage from MR images. Med. Phys. 43(3), 1187 (2016)
Phellan, R., Falcão, A.X., Udupa, J.K.: Medical image segmentation via atlases and fuzzy object models: improving efficacy through optimum object search and fewer models. Med. Phys. 43(1), 401 (2016)
Namías, R., D’Amato, J.P., Del, F.M., et al.: Multi-object segmentation framework using deformable models for medical imaging analysis. Med. Biol. Eng. Compu. 54(8), 1181–1192 (2016)
Wang, S., Lan, D.I., Liang, J.: Multi-dimensional fuzzy clustering image segmentation algorithm based on kernel metric and local information. Electron. Lett. 51(9), 693–695 (2015)
Dong, L., Smyl, D., Du, J.: A parametric level set based approach to difference imaging in electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(1), 145–155 (2018)
Feng, Y., Dong, F., Xia, X., et al.: An adaptive Fuzzy C-means method utilizing neighboring information for breast tumor segmentation in ultrasound images. Med. Phys. 44(7), 3752 (2017)
Chen, Y., Zhang, H., Zheng, Y., et al.: An improved anisotropic hierarchical fuzzy c-means method based on multivariate student t-distribution for brain MRI segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 60(C), 778–792 (2016)
Dong, X., Shen, J., Shao, L., et al.: Sub-Markov random walk for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(2), 516–527 (2016)
Zhang, Y.D., Muhammad, K., Tang, C.: Twelve-layer deep convolutional neural network with stochastic pooling for tea category classification on GPU platform. Multimedia Tools Appl. 77(17), 22821–22839 (2018)
Zhang, Y.D., Zhang, Y., Hou, X.X., et al.: Seven-layer deep neural network based on sparse autoencoder for voxelwise detection of cerebral microbleed. Multimedia Tools Appl. 77(9), 10521–10538 (2017)
Wang, G., Li, W., Zuluaga, M.A., et al.: Interactive medical image segmentation using deep learning with image-specific fine-tuning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 37(7), 1562–1573 (2018)
Zhang, Y.D., Pan, C.C., Sun, J.D., et al.: Multiple sclerosis identification by convolutional neural network with dropout and parametric ReLU. J. Comput. Sci. 28, 1–10 (2018)
Zhan, T., Yu, R., Zheng, Y., et al.: Multimodal spatial-based segmentation framework for white matter lesions in multi-sequence magnetic resonance images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 31, 52–62 (2017)
Annegreet, V.O., Achterberg, H.C., Vernooij, M.W., et al.: Transfer learning for image segmentation by combining image weighting and kernel learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(1), 213–224 (2019)
Sun, Z., Qiao, Y., Lelieveldt, B.P.F., et al.: Integrating spatial-anatomical regularization and structure sparsity into SVM: improving interpretation of Alzheimer’s disease classification. Neuroimage 178, 445 (2014)
Zhang, Y.D., Zhao, G., Sun, J., et al.: Smart pathological brain detection by synthetic minority oversampling technique, extreme learning machine, and Jaya algorithm. Multimedia Tools Appl. 77(17), 22629–22648 (2018)
Tao, Y., Lo, S.C.B., Freedman, M.T., et al.: Multilevel learning-based segmentation of ill-defined and spiculated masses in mammograms. Med. Phys. 37(11), 5993–6002 (2010)
Berber, T., Alpkocak, A., Balci, P., et al.: Breast mass contour segmentation algorithm in digital mammograms. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 110(2), 150–159 (2013)
Song, E., Jiang, L., Jin, R., et al.: Breast mass segmentation in mammography using plane fitting and dynamic programming. Acad. Radiol. 16(7), 826–835 (2009)
Wang, X., Guo, Y., Wang, Y., et al.: Automatic breast tumor detection in ABVS images based on convolutional neural network and superpixel patterns. Neural Comput. Appl. 1–13 (2017)
Kallenberg, M., Petersen, K., Nielsen, M., et al.: Unsupervised deep learning applied to breast density segmentation and mammographic risk scoring. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(5), 1322–1331 (2016)
Achanta, R., Shaji, A., Smith, K., et al.: SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(11), 2274–2282 (2012)
Ester, M., Kriegel, H.P., Sander, J., et al.: A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. Kdd 96(34), 226–231 (1996)
Wang, L., He, L., Mishra, A., et al.: Active contours driven by local Gaussian distribution fitting energy. Sig. Process. 89(12), 2435–2447 (2009)
Buades, A., Coll, B., Morel, J.M.: A non-local algorithm for image denoising. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2005. CVPR IEEE, vol. 2, 60–65 (2005)
Nguyen, T.M., Wu, Q.M.J.: Fast and robust spatially constrained gaussian mixture model for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 23(4), 621–635 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of High Education Institutions of Jiangsu Province, China (Nos. 18KJB50030, 18KJB520042 and 17KJB520033), the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grants (Nos. 61502206, 61772277, and 61672291), the Nature Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under grants (Nos. BK20150523 and BK20171494). The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, S., Chen, Y., Sheng, F. et al. A novel method for breast mass segmentation: from superpixel to subpixel segmentation. Machine Vision and Applications 30, 1111–1122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-019-01020-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-019-01020-0