Abstract
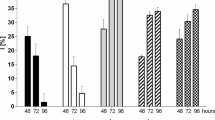
In aquatic ecosystems, arsenate (As(V)) and lead (Pb(II)) frequently coexist but their joint toxicity on microalgae remains unknown. In this study, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii was exposed to various levels of combined As(V) and Pb(II) treatments. The cell growth, respiration, pigment synthesis, polysaccharides and protein secretion as well as As speciation of C. reinhardtii were analyzed. The low-level coexistence of As(V) and Pb(II) had a stimulatory effect, as indicated by enhanced cell proliferation. In the middle-level coexistence, the cells resisted the toxicity by significant increasing protein secretion. Under high-level coexistence, the presence of Pb(II) inhibited the efflux of As and caused the decline of cell numbers and occurrence of cell lysis, indicating that the interaction mode between As(V) and Pb(II) switched to synergistic. Taken together, the above findings may deepen the understanding of detoxification mechanisms of algae upon exposure to combined metal(loid)s in aqueous environments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi JD, Arlen D, Webber CE, Chettle DR, Beaumont LF, Gordon CL (1998) Is there any association between the presence of bone disease and cumulative exposure to lead? Calcif Tissue Int 63:429–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002239900552
Ambade B, Sankar TK (2021) Source apportionment and health risks assessment of black carbon aerosols in an urban atmosphere in East India. J Atmos Chem 78:177–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10874-021-09418-9
Ambade B, Sethi SS (2021) Health Risk Assessment and characterization of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon from the Hydrosphere. J Hazard Toxic Radioactive Waste 25(2):5020008. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000586
Ashkenazy R, Gottlieb L, Yannai S (1997) Characterization of acetone-washed yeast biomass functional groups involved in lead biosorption. Biotechnol Bioeng 55(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290::AID-BIT1>3.0.CO;2-H
Bachate SP, Nandre VS, Ghatpande NS, Kodam KM (2012) Simultaneous reduction of cr(VI) and oxidation of as(III) by Bacillus firmus TE7 isolated from tannery effluent. Chemosphere 90(8):2273–2278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.081
Balaji S, Kalaivani T, Shalini M, Gopalakrishnan M, Muhammad M, Rajasekaran C (2016) Sorption sites of microalgae possess metal binding ability towards Cr(VI) from tannery effluents-a kinetic and characterization study. Desalin Water Treat 57(31):14518–14529. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1064032
Bentley R, Chasteen TG (2002) Microbial methylation of metalloids: arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66(2):250–271. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.66.2.250-271.2002
Byeon E, Kang HM, Yoon C, Lee JS (2021) Toxicity mechanisms of arsenic compounds in aquatic organisms. Aquat Toxicol 237:105901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2021.105901
Deng L, Su Y, Hua S, Wang X, Zhu X (2007) Sorption and desorption of lead (II) from wastewater by green algae Cladophora fascicularis. J Hazard Mater 143(1–2):220–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.09.009
Ge Y, Ning ZB, Wang Y, Zheng YH, Zhang CH, Figeys D (2016) Quantitative proteomic analysis of Dunaliella salina upon acute arsenate exposure. Chemosphere 145:112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.049
Hanikenne M (2003) Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as a eukaryotic photosynthetic model for studies of heavy metal homeostasis and tolerance. New Phytol 159(2):331–340. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00788.x
Hu XG, Ouyang SH, Mu L, An J, Zhou QX (2015) Effects of graphene oxide and oxidized carbon nanotubes on the cellular division, microstructure, uptake, oxidative stress, and metabolic profiles. Environ Sci Technol 49(18):10825–10833. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02102
Huang Z, Chen B, Zhang J, Yang C, Li S (2021) Absorption and speciation of arsenic by microalgae under arsenic-copper co-exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 213:112024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112024
Jiang HT, Islam MS, Sazawa K, Hata N, Taguchi S, Nakamura S, Sugawara K, Kuramitz H (2016) Development of an Electrochemical Bioassay based on the Alkaline phosphatase activity of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii to assess the toxicity of Heavy Metals. Int J Electrochem Sci 11(6):5090–5102. https://doi.org/10.20964/2016.06.65
Jiang ZQ, Sun YT, Guan HZ, Sun DQ, Fang S, Ma XN, Wang ZY, Li Z, Zhang CH, Ge Y (2022) Contributions of polysaccharides to arsenate resistance in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 229:113091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113091
Kumar B, Smita K, Flores LC (2017) Plant mediated detoxification of mercury and lead. Arab J Chem 10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.08.010. S2335-S2342
Kumar A, Kumar A, Cabral-Pinto MMS, Chaturvedi AK, Shabnam AA, Subrahmanyam G, Mondal R, Gupta DK, Malyan SK, Kumar SS, Khan SA, Yadav KK (2020) Lead toxicity: Health Hazards, influence on Food Chain, and sustainable remediation approaches. I Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(7):2179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072179
Kurwadkar S, Sethi SS, Mishra P, Mishra P, Ambade B (2022) Unregulated discharge of wastewater in the Mahanadi River Basin: risk evaluation due to occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in surface water and sediments. Mar Pollut Bull 179:113686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113686
Leong YK, Chang JS (2020) Bioremediation of heavy metals using microalgae: recent advances and mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 303:122886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122886
Li C, Zheng C, Fu H, Zhai S, Ge Y (2021) Contrasting detoxification mechanisms of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii under cd and pb stress. Chemosphere 274(2):129771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129771
Liu D, Wong P, Dutka BJ (1973) Determination of carbohydrate in lake sediment by a modified phenol-sulfuric acid method. Water Res 7(5):741–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(73)90090-0
Milačič R, Zuliani T, Vidmar J, Oprčkal P, Ščančar J (2017) Potentially toxic elements in water and sediments of the Sava River under extremeflow events. Sci Total Environ 605–606:894–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.260
Minatel BC, Sage AP, Anderson C, Hubaux R, Marshall EA, Lam W, Martinez VD (2018) Environmental arsenic exposure: from genetic susceptibility to pathogenesis. Environ Int 112:183–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.017
Mirghaffari N, Moeini E, Farhadian O (2015) Biosorption of Cd and Pb ions from aqueous solutions by biomass of the green microalga, Scenedesmus quadricauda. J Appl Phycol 27(1):311–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0345-z
Mohapatra H, Gupta R (2005) Concurrent sorption of zn(II), Cu(II) and Co(II) by Oscillatoria angustissima as a function of pH in binary and ternary metal solutions. Bioresour Technol 96(12):1387–1398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.11.004
Phan NN, Wang CY, Lin YC (2014) The novel regulations of MEF2A, CAMKK2, CALM3, and TNNI3 in ventricular hypertrophy induced by arsenic exposure in rats. Toxicol 324(3):123–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2014.07.010
Priatni S, Ratnaningrum D, Warya S, Audina E (2018) Phycobiliproteins production and heavy metals reduction ability of Porphyridium sp. Earth Environ Sci 160:012006. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/160/1/012006
Samadani M, Perreault F, Oukarroum A, Dewez D (2018) Effect of cadmium accumulation on green algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and acid-tolerant Chlamydomonas CPCC 121. Chemosphere 191:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.017
Shan B, Hao RX, Zhang JM, Li JN, Ye YB, Lu AH (2023) Microbial remediation mechanisms and applications for lead-contaminated environments. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39(2):38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03484-1
Sulaymon AH, Mohammed AA, Al-Musawi TJ (2012) Competitive biosorption of lead, cadmium, copper, and arsenic ions using algae. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(5):3011–3023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1208-2
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the Environment. In: Luch A (ed) Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology. Springer, New York, pp 133–164
Wang NX, Li Y, Deng XH, Miao AJ, Ji R, Yang LY (2013) Toxicity and bioaccumulation kinetics of arsenate in two freshwater green algae under different phosphate regimes. Water Res 47(7):2497–2506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.02.034
Wang YZ, Yu J, Wang P, Deng SW, Chang JH, Ran ZX (2018) Response of energy microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii to nitrogen and phosphorus stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:5762–5770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0931-0
Yang WL, Luo LQ, Bostick BC, Wiita E, Cheng Y, Shen YT (2021) Effect of combined arsenic and lead exposure on their uptake and translocation in indian mustard. Environ Pollut 274:116549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116549
Zhang J, Zhou F, Liu Y, Huang F, Zhang CL (2019) Effect of extracellular polymeric substances on arsenic accumulation in Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Sci Total Environ 704(20):135368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135368
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31770548, 32171623), Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (No. KYCX21_0570) and Undergraduate Student Research Training Program in Nanjing Agricultural University (No. 202113YX21, 202013YX18). We also thank the support from Jiangsu Policy Guidance Program (BZ2020064) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYZ202123). We are grateful to Dr. Jiani Chen in Nanjing University for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, D., Jiang, Z., Yu, H. et al. Assessment of Joint Toxicity of Arsenate and Lead by Multiple Endpoints in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 111, 30 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03792-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03792-8