Abstract
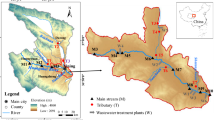
The occurrence and distribution of five selected fluoroquinolones (FQs) were studied in the Dongjiang River and the Beijiang River, South China. Ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and enoxacin, used as human and veterinary medicines, were detected with detection frequencies of 75%–100% and average concentrations of 9.5–18.8 ng L−1 in the two rivers. Meanwhile, enrofloxacin, which is only used as veterinary medicine, was detected at lower levels (2.9–4.0 ng L−1) than those of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and enoxacin. The spatial distribution of the five FQs exhibited a close relationship with the intensity of local human activity. Certain antibiotics were detected in industrial wastewater and domestic sewage at considerably higher concentrations than those measured in the river water, indicating important sources of antibiotic contamination. Finally, an ecological risk assessment based on the calculated risk quotient showed that ciprofloxacin could pose high risk to Microcystis aeruginosa (M. aeruginosa). The two rivers are important sources of drinking water and should arouse the attention of relevant departments. Effective measures must be taken to strengthen the protection of the two rivers.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Leung SY, Wong WC, Selvam A (2013) Preliminary occurrence studies of antibiotic residues in Hong Kong and Pearl River Delta. Environ Monit Assess 185:745–754. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2589-x
Eguchi K, Nagase H, Ozawa M, Endoh YS, Goto K, Hirata K (2004) Evaluation of antimicrobial agents for veterinary use in the ecotoxicity test using microalgae. Chemosphere 57:1733–1738. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.07.017
European Commission (2003) European commission technical guidance document in support of commission directive 93//67/EEC on risk assessment for new notified substances and commission regulation (EC) no. 1488/94 on risk assessment for existing substance, Part II. European Commission, pp 100–103
Gao L, Yang XM, Zhen SF, Liu Y (2010) Remote sensing analysis of gravity-center migration of the aquaculture in the Zhujiang River Estuary. J Tropical Oceanogra 29:35–40 (in Chinese)
Halling-Sorensen B, Lutzhoft HCH, Andersen HR, Ingerslev F (2000) Environmental risk assessment of antibiotics: comparison of mecillinam, trimethoprim and ciprofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemoth 46:53–58. doi:10.1093/jac/46.suppl_1.53
Hartmann A, Alder AC, Koller T, Widmer RM (1998) Identification of fluoroquinolone antibiotics as the main source of umuC genotoxicity in native hospital wastewater. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:377–382. doi:10.1002/etc.5620170305
Hernando MD, Mezcua M, Fernandez-Alba AR, Barcelo D (2006) Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 69:334–342. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2005.09.037
Isidori M, Lavorgna M, Nardelli A, Pascarella L, Parrella A (2005) Toxic and genotoxic evaluation of six antibiotics on non-target organisms. Sci Total Environ 346:87–98. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.11.017
Jjemba PK (2002) The potential impact of veterinary and human therapeutic agents in manure and biosolids on plants grown on arable land: a review. Agric Ecosyst Environ 93:267–278. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(01)00350-4
Kemper N (2008) Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Eco Indic 8:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2007.06.002
Kools SAE, Moltmann JF, Knacker T (2008) Estimating the use of veterinary medicines in the European Union. Regul Toxicol Pharm 50:59–65. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2007.06.003
Luo Y, Xu L, Rysz M, Wang Y, Zhang H, Alvarez PJJ (2011) Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ Sci Technol 45:1827–1833. doi:10.1021/es104009s
Peng X, Zhang K, Tang C, Huang Q, Yu Y, Cui J (2011) Distribution pattern, behavior, and fate of antibacterials in urban aquatic environments in South China. J Environ Monitor 13:446–454. doi:10.1039/c0em00394h
Robinson AA, Belden JB, Lydy MJ (2005) Toxicity of fluoroquinolone antibiotics to aquatic organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:423–430. doi:10.1897/04-210r.1
Saling P, Maisch R, Silvani M, König N (2005) Assessing the environmental-hazard potential for life cycle assessment, ecoefficiency and SEE balance®. Int J Life Cycle Assess 10:364–371. doi:10.1065/lca2005.08.220
Thiele-Bruhn S (2003) Pharmaceutical antibiotic compounds in soils: a review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 166:145–167. doi:10.1002/jpln.200390023
Wang L (2006) The current situation of antibiotics pollution and the effect on environmental microcosm. Pharm Biotechnol 1:265–288. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-8915.2006.02.016 (in Chinese)
Wang G, Cheng J (2009) Utilization of quinolones antibacterials in our hospital between 2006 and 2008. Eval Anal Drug Use Hosp China 9:354–357. doi:10.14009/j.issn.1672-2124.2009.05.029 (in Chinese).
Water Resource Department of Guangdong (2009) Guangdong water resource bulletin of the year 2008. http://www.gdsw.gov.cn (in Chinese)
Wu Y, Liao X, Wang Z, Chen Z, Zhou Y (2006a) Hydrolysis characteristics of enrofloxacin. Chin J Appl Ecol 17:1086–1090. doi:10.13287/j.1001-9332.2006.0216 (in Chinese)
Wu Y, Wang Z, Liao X, Chen Z (2006b) Effects of enrofloxacin on microorganisms in wetlands. Acta Ecol Sinica 26:2640–2645. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2006.08.029 (in Chinese)
Xu WH, Zhang G, Zou SC, Li XD, Liu YC (2006) Occurrence and seasonal changes of antibiotics in the Victoria Harbour and the Pearl River, South China. Environ Sci 27:2458–2462. doi:10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.12.016 (in Chinese)
Xu WH, Zhang G, Zou SC, Li XD, Liu YC (2007) Determination of selected antibiotics in the Victoria Harbour and the Pearl River, South China using high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Environ Pollut 145:672–679. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.05.038
Xu WH, Yan W, Li X, Zou Y, Chen X, Huang W (2013) Antibiotics in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta and Pearl River Estuary, China: concentrations, mass loading and ecological risks. Environ Pollut 182:402–407. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2013.08.004
Yan C, Yang Y, Zhou J, Liu M, Nie M, Shi H, Gu L (2013) Antibiotics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary: occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Environ Pollut 175:22–29. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2012.12.008
Ying GG, Peng PA, Zhao JL, Ren MZ, Chen HM, Wei DB, Li BG, Song JZ (2012) The ecological risk evaluation of chemicals from Rivers: take of the Dongjiang River for example. Science Press, Beijing, pp 128–139
Zhang B, Liu YH (2010) Utilization of quinolones antibacterials in our hospital between 2007 and 2009. Guide Chin Med 8:112–113. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-8194.2010.26.075 (in Chinese)
Zhang RJ, Zhang G, Tang JH, Xu WH, Li J, Liu X (2012a) Levels, spatial distribution and sources of selected antibiotics in the East River (Dongjiang), South China. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manage 15:210–218. doi:10.1080/14634988.2012.689576
Zhang RJ, Zhang G, Zheng Q, Tang JH, Chen YJ, Xu WH (2012b) Occurrence and risks of antibiotics in the Laizhou Bay, China: impacts of river discharge. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 80:208–215. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.03.002
Zhou LJ, Wu QL, Zhang BB, Zhao YG, Zhao BY (2016) Occurrence, spatiotemporal distribution, mass balance and ecological risks of antibiotics in subtropical shallow Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Proc Impacts 18:500–513. doi:10.1039/c6em00062b
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Knowledge Innovative Programme of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-YW-Q02-01), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NOs. 41463011 and 41473118), the National Key Basic Research Programme of China (2013CB956102), and the BaGui Fellowship from Guangxi Province of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Zhang, R., Zou, S. et al. Occurrence, Distribution and Ecological Risks of Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics in the Dongjiang River and the Beijiang River, Pearl River Delta, South China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 99, 46–53 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2107-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2107-5