Abstract
Purpose
Childhood trauma may increase vulnerability to numerous specific psychiatric disorders, or a generalised liability to experience dimensions of internalising or externalising psychopathology. We use a nationally representative sample (N = 34,653) to examine the long-term consequences of childhood trauma and their combined effect as predictors of subsequent psychopathology.
Methods
Data from the US National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions were used. Latent class analysis was used to identify childhood trauma profiles and multinomial logistic regression to validate and explore these profiles with a range of associated demographic and household characteristics. We used Structural Equation Modelling to substantiate initial latent class analysis findings by investigating a range of mental health diagnoses. Internalising and externalising domains of psychopathology were regressed on trauma profiles and associated demographic and household characteristics. We used Differential Item Functioning to examine associations between the trauma groups and a number of psychiatric disorders within internalising and externalising dimensions of mental health.
Results
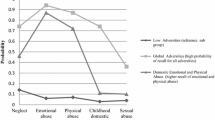
We found a 3-class model of childhood trauma in which 85% of participants were allocated to a low trauma class; 6% to a multi-type victimization class (reporting exposures for all the child maltreatment criteria); and 9% to a situational trauma class (exposed to a range of traumas). Confirmatory Factor Analysis revealed an internalising–externalising spectrum was used to represent lifetime reporting patterns of mental health disorders. Both trauma groups showed specific gender and race/ethnicity differences, related family discord and increased psychopathology. Additionally, we found significant associations between the trauma groups and specific diagnoses within the internalising–externalising spectrum of mental health.
Conclusions
The underlying patterns in the exposure to types of interpersonal and non-interpersonal traumas and associated mental health highlight the need to screen for particular types of childhood traumas when individuals present with symptoms of psychiatric disorders.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McLaughlin KA, Koenen KC, Hill ED, Petukhova M, Sampson NA, Zaslavsky AM, Kessler RC (2013) Trauma exposure and posttraumatic stress disorder in a national sample of adolescents. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 52:815–830 (e14)
Cloitre M, Stolbach BC, Herman JL, Kolk BVD, Pynoos R, Wang J, Petkova E (2009) A developmental approach to complex PTSD: childhood and adult cumulative trauma as predictors of symptom complexity. J Trauma Stress 22:399–408
Briggs-Gowan MJ, Carter AS, Ford JD (2011) Parsing the effects violence exposure in early childhood: Modeling developmental pathways. J Pediatr Psychol 37:11–22
Mongillo EA, Briggs-Gowan M, Ford JD, Carter AS (2009) Impact of traumatic life events in a community sample of toddlers. J Abnorm Child Psychol 37:455–468
Cook A, Spinazzola J, Ford J, Lanktree C, Blaustein M, Cloitre M, DeRosa R, Hubbard R, Kagan R, Liautaud J (2017) Complex trauma in children and adolescents. Psychiatric annals 35:390–398
Grasso DJ, Ford JD, Briggs-Gowan MJ (2012) Early life trauma exposure and stress sensitivity in young children. J Pediatr Psychol 38:94–103
D’Andrea W, Ford J, Stolbach B, Spinazzola J, BA van der Kolk (2012) Understanding interpersonal trauma in children: why we need a developmentally appropriate trauma diagnosis. Am J Orthopsychiatry 82:187–200
Teicher MH, Samson JA (2013) Childhood maltreatment and psychopathology: a case for ecophenotypic variants as clinically and neurobiologically distinct subtypes. Am J Psychiatry 170:1114–1133
Finkelhor D, Ormrod RK, Turner HA (2007) Poly-victimization: a neglected component in child victimization. Child Abuse Negl 31:7–26
Raissian KM, Dierkhising CB, Geiger JM, Schelbe L (2014) Child maltreatment reporting patterns and predictors of substantiation: comparing adolescents and younger children. Child Maltreat 19:3–16
Teicher MH, Rabi K, Sheu Y, Seraphin SB, Andersen SL, Anderson CM, Tomoda A (2010) Neurobiology of childhood trauma and adversity. The impact of early life trauma on health and disease: the hidden epidemic. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 112–122
Higgins DJ (2004) Differentiating between child maltreatment experiences. Fam Mat (69):50
Finkelhor D, Ormrod R, Turner H, Holt M (2009) Pathways to poly-victimization. Child Maltreat 14:316–329
Sesar K, Živčić-Bećirević I, Sesar D (2008) Multi-type maltreatment in childhood and psychological adjustment in adolescence: questionnaire study among adolescents in Western Herzegovina Canton. Croat Med J 49:243–256
Holt MK, Finkelhor D, Kantor GK (2007) Multiple victimization experiences of urban elementary school students: Associations with psychosocial functioning and academic performance. Child Abuse Negl 31:503–515
Scott J, Varghese D, McGrath J (2010) As the twig is bent, the tree inclines: adult mental health consequences of childhood adversity. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67:111–112
Arata CM, Langhinrichsen-Rohling J, Bowers D, O’Brien N (2007) Differential correlates of multi-type maltreatment among urban youth. Child Abuse Negl 31:393–415
Sesar K, Šimić N, Barišić M (2010) Multi-type childhood abuse, strategies of coping, and psychological adaptations in young adults. Croat Med J 51:406–416
Higgins DJ, McCabe MP (2000) Relationships between different types of maltreatment during childhood and adjustment in adulthood. Child Maltreat 5:261–272
Saunders BE, Adams ZW (2014) Epidemiology of traumatic experiences in childhood. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am 23:167–184
Ford JD, Courtois CA (2013) Treating complex traumatic stress disorders in children and adolescents: Scientific foundations and therapeutic models. Guilford Press, New York
Kilpatrick DG, Ruggiero KJ, Acierno R, Saunders BE, Resnick HS, Best CL (2003) Violence and risk of PTSD, major depression, substance abuse/dependence, and comorbidity: results from the National Survey of Adolescents. J Consult Clin Psychol 71:692
Hooven C, Nurius PS, Logan-Greene P, Thompson EA (2012) Childhood violence exposure: cumulative and specific effects on adult mental health. J Fam Violence 27:511–522
Charak R, Byllesby BM, Roley ME, Claycomb MA, Durham TA, Ross J, Armour C, Elhai JD (2016) Latent classes of childhood poly-victimization and associations with suicidal behavior among adult trauma victims: moderating role of anger. Child Abuse Negl 62:19–28
Curran E, Adamson G, Stringer M, Rosato M, Leavey G (2016) Severity of mental illness as a result of multiple childhood adversities: US National Epidemiologic Survey. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 51:647–657
Rutter M (2000) Psychosocial influences: critiques, findings, and research needs. Dev Psychopathol 12:375–405
Kessler RC, Ormel J, Petukhova M, McLaughlin KA, Green JG, Russo LJ, Stein DJ, Zaslavsky AM, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, Alonso J (2011) Development of lifetime comorbidity in the World Health Organization world mental health surveys. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:90–100
Benjet C, Borges G, Medina-Mora ME (2010) Chronic childhood adversity and onset of psychopathology during three life stages: childhood, adolescence and adulthood. J Psychiatr Res 44:732–740
Oladeji BD, Makanjuola VA, Gureje O (2010) Family-related adverse childhood experiences as risk factors for psychiatric disorders in Nigeria. Br J Psychiatry 196:186–191
Lee AC, Maheswaran R (2011) The health benefits of urban green spaces: a review of the evidence. J Public Health 33:212–222
Fujiwara T, Okuyama M, Izumi M (2012) The impact of childhood abuse history, domestic violence and mental health symptoms on parenting behaviour among mothers in Japan. Child Care Health Dev 38:530–537
Slopen N, Fitzmaurice G, Williams DR, Gilman SE (2010) Poverty, food insecurity, and the behavior for childhood internalizing and externalizing disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 49:444–452
Read JP, Griffin MJ, Wardell JD, Ouimette P (2014) Coping, PTSD symptoms, and alcohol involvement in trauma-exposed college students in the first three years of college. Psychol Addict Behav 28:1052
Vreeburg SA, Hoogendijk WJ, van Pelt J, DeRijk RH, Verhagen JC, van Dyck R, Smit JH, Zitman FG, Penninx BW (2009) Major depressive disorder and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity: results from a large cohort study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:617–626
Elzinga BM, Spinhoven P, Berretty E, de Jong P, Roelofs K (2010) The role of childhood abuse in HPA-axis reactivity in social anxiety disorder: a pilot study. Biol Psychol 83:1–6
Valiengo LL, Soeiro-de-Souza MG, Marques AH, Moreno DH, Juruena MF, Andreazza AC, Gattaz WF, Machado-Vieira R (2012) Plasma cortisol in first episode drug-naïve mania: differential levels in euphoric versus irritable mood. J Affect Disord 138:149–152
Van Winkel R, Esquivel G, Kenis G, Wichers M, Collip D, Peerbooms O, Rutten B, Myin-Germeys I, Van Os J (2010) Genome-wide findings in schizophrenia and the role of gene–environment interplay. CNS Neurosci Ther 16(5):e185–192
Trickett PK, Negriff S, Ji J, Peckins M (2011) Child maltreatment and adolescent development. J Res Adolesc 21:3–20
Ehring T, Quack D (2010) Emotion regulation difficulties in trauma survivors: the role of trauma type and PTSD symptom severity. Behav Therapy 41:587–598
Linscott R, Van Os J (2013) An updated and conservative systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological evidence on psychotic experiences in children and adults: on the pathway from proneness to persistence to dimensional expression across mental disorders. Psychol Med 43:1133–1149
Krueger RF, Markon KE, Patrick CJ, Iacono WG (2005) Externalizing psychopathology in adulthood: a dimensional-spectrum conceptualization and its implications for DSM-V. J Abnorm Psychol 114:537
Kendler KS, Prescott CA, Myers J, Neale MC (2003) The structure of genetic and environmental risk factors for common psychiatric and substance use disorders in men and women. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:929–937
Wright AG, Krueger RF, Hobbs MJ, Markon KE, Eaton NR, Slade T (2013) The structure of psychopathology: toward an expanded quantitative empirical model. J Abnorm Psychol 122:281
Wilson S, Sponheim SR (2014) Dimensions underlying psychotic and manic symptomatology: extending normal-range personality traits to schizophrenia and bipolar spectra. Compr Psychiatry 55:1809–1819
Kotov R, Ruggero CJ, Krueger RF, Watson D, Yuan Q, Zimmerman M (2011) New dimensions in the quantitative classification of mental illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:1003–1011
Keyes KM, Eaton NR, Krueger RF, McLaughlin KA, Wall MM, Grant BF, Hasin DS (2012) Childhood maltreatment and the structure of common psychiatric disorders. Br J Psychiatry 200:107–115
Read J, Os JV, Morrison AP, Ross CA (2005) Childhood trauma, psychosis and schizophrenia: a literature review with theoretical and clinical implications. Acta Psychiatr Scand 112:330–350
Myin-Germeys I, van Os J (2007) Stress-reactivity in psychosis: evidence for an affective pathway to psychosis. Clin Psychol Rev 27:409–424
Kessler RC, Angermeyer M, Anthony JC, DE Graaf R, Demyttenaere K, Gasquet I, DE Girolamo G, Gluzman S, Gureje O, Haro JM, Kawakami N, Karam A, Levinson D, Medina Mora ME, Oakley Browne MA, Posada-Villa J, Stein DJ, Adley Tsang CH, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, Alonso J, Lee S, Heeringa S, Pennell BE, Berglund P, Gruber MJ, Petukhova M, Chatterji S, Ustun TB (2007) Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of mental disorders in the World Health Organization’s World Mental Health Survey Initiative. World Psychiatry 6:168–176
Link BG, Struening EL, Neese-Todd S, Asmussen S, Phelan JC (2001) Stigma as a barrier to recovery: the consequences of stigma for the self-esteem of people with mental illnesses. Psychiatr Serv 52:1621–1626
Grant B, Kaplan K, Moore T, Kimball J (2007) 2004–2005 wave 2 National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions: source and accuracy statement. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, Bethesda
Grant B, Dawson D, Hasin D (2001) The alcohol use disorders and associated disabilities interview schedule—Version for DSM-IV (AUDADIS-IV). National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, Bethesda
Grant BF, Harford TC, Dawson DA, Chou PS, Pickering RP (1995) The alcohol use disorder and associated disabilities Interview Schedule (AUDADIS): reliability of alcohol and drug modules in a general population sample. Drug Alcohol Depend 39:37–44
Hasin D, Carpenter KM, McCloud S, Smith M, Grant BF (1997) The alcohol use disorder and associated disabilities interview schedule (AUDADIS): reliability of alcohol and drug modules in a clinical sample. Drug Alcohol Depend 44:133–141
Üstün B, Compton W, Mager D, Babor T, Baiyewu O, Chatterji S, Cottler L, Gögüs A, Mavreas V, Peters L et al (1997) WHO Study on the reliability and validity of the alcohol and drug use disorder instruments: overview of methods and results. Drug Alcohol Depend 47:161–169
Vrasti R, Grant BF, Chatterji S, Üstün B, Mager D, Olteanu I, Badoi M (1998) Reliability of the Romanian version of the alcohol module of the WHO alcohol use disorder and associated disabilities: interview schedule–alcohol/drug-revised. Eur Addict Res 4:144–149
Breslau N, Bohnert KM, Koenen KC (2010) The 9/11 terrorist attack and posttraumatic stress disorder revisited. J Nerv Ment Dis 198:539–543
American Psychiatric Association (2000) diagnostic criteria from dsM-iV-tr. American Psychiatric Pub, Arlington
Walsh K, Fortier MA, DiLillo D (2010) Adult coping with childhood sexual abuse: a theoretical and empirical review. Aggress Violent Behav 15:1–13
Muthen B (2001) Latent variable mixture modeling. New developments and techniques in structural equation modeling. In: Marcoulides GA, Schumacker (eds) Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, New Jersey, pp 1–33
Woods CM (2009) Empirical selection of anchors for tests of differential item functioning. Appl Psychol Meas 33:42–57
Hu L, Bentler PM (1995) Evaluating model fit
Collins LM, Lanza ST (2010) Latent class analysis with covariates. Latent class and latent transition analysis: with applications in the social, behavioral, and health sciences, vol 718. Wiley
Dziak JJ, Coffman DL, Lanza ST, Li R (2017) Sensitivity and specificity of information criteria. PeerJ PrePrints, Corte Madera
Chaffin M (2006) The changing focus of child maltreatment research and practice within psychology. J Soc Iss 62:663–684
Walsh F (2002) A family resilience framework: innovative practice applications. Fam Relat 51:130–137
Verona E, Sachs-Ericsson N (2005) The intergenerational transmission of externalizing behaviors in adult participants: the mediating role of childhood abuse. J Consult Clin Psychol 73:1135
Green JG, McLaughlin KA, Berglund PA, Gruber MJ, Sampson NA, Zaslavsky AM, Kessler RC (2010) Childhood adversities and adult psychiatric disorders in the national comorbidity survey replication I: associations with first onset of DSM-IV disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67:113–123
Breslau N, Davis GC, Peterson EL, Schultz LR (2000) A second look at comorbidity in victims of trauma: the posttraumatic stress disorder–major depression connection. Biol Psychiatry 48:902–909
Hamby S, McDonald R, Grych J (2014) Trends in violence research: an update through 2013. An update through 2013. Psychol Violence 4(1):1–7
Villodas MT, Litrownik AJ, Thompson R, Jones D, Roesch SC, Hussey JM, Block S, English DJ, Dubowitz H (2015) Developmental transitions in presentations of externalizing problems among boys and girls at risk for child maltreatment. Dev Psychopathol 27:205–219
Sanders MR, Cann W, Markie-Dadds C (2003) The triple P-positive parenting programme: a universal population-level approach to the prevention of child abuse. Child abuse review 12:155–171
Gilbert R, Kemp A, Thoburn J, Sidebotham P, Radford L, Glaser D, MacMillan HL (2009) Recognising and responding to child maltreatment. Lancet 373:167–180
Finkelhor D, Browne A (1985) The traumatic impact of child sexual abuse: a conceptualization. Am J Orthopsychiatry 55:530
Debowska A, Boduszek D (2017) Child abuse and neglect profiles and their psychosocial consequences in a large sample of incarcerated males. Child Abuse Negl 65:266–277
Krueger RF, Markon KE (2011) A dimensional-spectrum model of psychopathology: progress and opportunities. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:10–11
Liberzon I, King AP, Ressler KJ, Almli LM, Zhang P, Ma ST, Cohen GH, Tamburrino MB, Calabrese JR, Galea S (2014) Interaction of the ADRB2 gene polymorphism with childhood trauma in predicting adult symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder. JAMA psychiatry 71:1174–1182
Leverich GS, McElroy SL, Suppes T, Keck PE, Denicoff KD, Nolen WA, Altshuler LL, Rush AJ, Kupka R, Frye MA (2002) Early physical and sexual abuse associated with an adverse course of bipolar illness. Biol Psychiatry 51:288–297
Ford JD (2015) Complex PTSD: Research directions for nosology/assessment, treatment, and public health. Eur J Psychotraumatol 6:27584
Houston JE, Shevlin M, Adamson G, Murphy J (2011) A person-centred approach to modelling population experiences of trauma and mental illness. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 46:149–157
Khantzian EJ (2013) Addiction as a self-regulation disorder and the role of self-medication. Addiction 108:668–669
Mann NC, MacKenzie E, Teitelbaum SD, Wright D, Anderson C (2005) Trauma system structure and viability in the current healthcare environment: a state-by-state assessment. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 58:136–147
Della Femina D, Yeager CA, Lewis DO (1990) Child abuse: adolescent records vs. adult recall. Child Abuse Negl 14:227–231
Haro JM, Arbabzadeh-Bouchez S, Brugha TS, De Girolamo G, Guyer ME, Jin R, Lepine JP, Mazzi F, Reneses B, Vilagut G (2006) Concordance of the Composite International Diagnostic Interview Version 3.0 (CIDI 3.0) with standardized clinical assessments in the WHO World Mental Health surveys. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 15:167–180
Dong M, Anda RF, Felitti VJ, Dube SR, Williamson DF, Thompson TJ, Loo CM, Giles WH (2004) The interrelatedness of multiple forms of childhood abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction. Child Abuse Negl 28:771–784
Acknowledgements
This study was part funded by a PhD a Department of Education and Learning (DEL) Northern Ireland award to the corresponding author. DEL had no further role in producing this paper for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curran, E., Adamson, G., Rosato, M. et al. Profiles of childhood trauma and psychopathology: US National Epidemiologic Survey. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 53, 1207–1219 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-018-1525-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-018-1525-y