Purpose:
To evaluate the feasibility and accuracy of daily B-mode acquisition and targeting ultrasound-based prostate localization (BAT™) and to compare it with computed tomography (CT) and electronic portal imaging (EPI) in 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3-D CRT) for prostate cancer.
Patients and Methods:
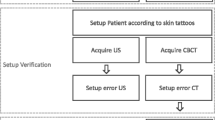
Ten patients were treated with 3-D CRT (72 Gy/30 fractions, 2.4 Gy/fraction, equivalent to 80 Gy/40 fractions, for α/β ratio of 1.5 Gy) and daily BAT-based prostate localization. For the first 5 fractions, CT and EPI were also performed in order to compare organ-motion and set-up error, respectively.
Results:
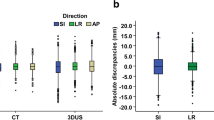
287 BAT-, 50 CT- and 46 EPI-alignments were performed. The average BAT-determined misalignments in latero-lateral, antero-posterior and cranio-caudal directions were –0.9 mm ± 3.3 mm, 1.0 mm ± 4.0 mm and –0.9 mm ± 3.8 mm, respectively. The differences between BAT- and CT-determined organ-motion in latero-lateral, antero-posterior and cranio-caudal directions were 2.7 mm ± 1.9 mm, 3.9 ± 2.8 mm and 3.4 ± 3.0 mm, respectively. Weak correlation was found between BAT- and CT-determined misalignments in antero-posterior direction, while no correlation was observed in latero-lateral and cranio-caudal directions. The correlation was more significant when only data of good image-quality patients were analyzed (8 patients).
Conclusion:
BAT ensures the relative positions of target are the same during treatment and in treatment plan, however, the reliability of alignment is patient-dependent. The average BAT-determined misalignments were small, confirming the prevalence of random errors in 3-D CRT. Further study is warranted in order to establish the clinical value of BAT.
Ziel:
Ziel dieser Studie ist es, die Möglichkeit und Genauigkeit der täglichen B-mode-Akquisition und zielgerichteten ultraschallbasierten Prostatapositionierung (BAT™) einzuschätzen und sie mit der Computertomographie (CT) und dem elektronischen Portal-Imaging (EPI) bei der 3D-konformalen Strahlentherapie (3D-CRT) des Prostatakrebses zu vergleichen.
Patienten und Methodik:
10 Patienten wurden mit 3D-CRT (72 Gy/30 Fraktionen, 2,4 Gy/Fraktion, äquivalent zu 80 Gy/40 Fraktionen, α/β-Verhältnis von 1,5 Gy ) und täglicher BAT behandelt. Für die ersten 5 Fraktionen wurden auch CT und EPI durchgeführt, um jeweils die Bewegung der Organe und die Set-up-Fehler zu vergleichen.
Ergebnisse:
287 BAT-, 50 CT- und 46 EPI-Positionierungen wurden durchgeführt. Der durchschnittliche BAT-Positionierungsfehler war jeweils –0,9 mm ± 3,3 mm, 1,0 mm ± 4,0 mm und –0,9 mm ± 3,8 mm in den latero-lateralen, anterior-posterioren und kraniokaudalen Richtungen. Die Unterschiede zwischen der BAT- und CT-Technik bei der Bestimmung der Organbewegung in den latero-lateralen, anterior-posterioren und kraniokaudalen Richtungen waren jeweils 2,7 mm ± 1,9 mm, 3,9 ± 2,8 mm und 3,4 ± 3,0 mm. Eine sehr geringe Korrelation zwischen BAT- und CT-Positionierungsungenauigkeit wurde nur für die anterior-posteriore Richtung gefunden (R = 0,29, p = 0,04). Die Korrelation war leicht besser, wenn nur die Patienten mit guter Bildqualität analysiert wurden (8 Patienten).
Schlussfolgerung:
BAT garantiert, dass die relative Position des Ziels dieselbe während der Behandlung und in dem Behandlungsplan ist, obwohl die Genauigkeit der Positionierung patientenabhängig ist. Die durchschnittlichen, mit BAT bestimmten, Positionierungsfehler waren klein und bestätigen, dass der statistische Fehler in 3D-CRT vorwiegend ist. Weitere Studien sind erforderlich, um den klinischen Wert von BAT festzustellen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jereczek-Fossa, B.A., Cattani, F., Garibaldi, C. et al. Transabdominal Ultrasonography, Computed Tomography and Electronic Portal Imaging for 3-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer. Strahlenther Onkol 183, 610–616 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-007-1702-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-007-1702-5
Key Words:
- Prostate cancer
- 3-D conformal radiotherapy
- Ultrasonography
- Electronic portal imaging
- Computed Tomography