Abstract
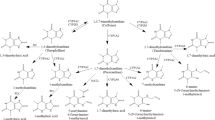
Grapefruit-mediated fruit–drug interaction has been well discussed in clinical practice. However, the biochemical mechanisms for such interaction are far beyond our understanding. The objectives of the present study aimed at the interaction between bergaptol (BGT) and CYP2C9. BGT, one of the major furanocoumarin constituents in grapefruit, has been reported to inhibit the activity of CYP2C9. And a number of furan-containing compounds are known to act as mechanism-based inactivators of CYP2C9. In this study, BGT was found to induce time-, concentration-, and NADPH-dependent irreversible inhibition of CYP2C9. A GSH conjugate was detected in an incubation mixture containing CYP2C9, BGT, NADPH, and GSH. Further mechanistic investigation revealed that a γ-ketoenal metabolite was responsible for the enzyme inactivation. The obtained data indicate that BGT was a mechanism-based inactivator of CYP2C9. The study would facilitate the understanding of the mechanistic insight into fruit–drug interactions mediated by grapefruits.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourgaud F et al. (2006) Biosynthesis of coumarins in plants: a major pathway still to be unravelled for cytochrome P450 enzymes. Phytochemistry Rev 5:293–308
Chavez ML, Jordan MA, Chavez PI (2006) Evidence-based drug–herbal interactions. Life Sci 78:2146–2157
Chudnovskiy R, Thompson A, Tharp K, Hellerstein M, Napoli JL, Stahl A (2014) Consumption of clarified grapefruit juice ameliorates high-fat diet induced insulin resistance and weight gain in mice. PLoS ONE 9:e108408
Doull J, Klaassen CD, Amdur MO, Casarett LJ (1986) Casarett and Doull’s toxicology:the basic science of poisons. 3rd edn. Macmillan, New York, NY, p 974
Galbraith RA, Michnovicz JJ (1989) The oxidative metabolism of estradiol: inhibition by cimetidine. Trans Assoc Am Physicians 102:44–54
Girennavar B, Jayaprakasha GK, Patil BS (2007) Potent inhibition of human cytochrome P450 3A4, 2D6, and 2C9 isoenzymes by grapefruit juice and its furocoumarins. J Food Sci 72:C417–C421
Guo LQ, Fukuda K, Ohta T, Yamazoe Y (2000) Role of furanocoumarin derivatives on grapefruit juice-mediated inhibition of human CYP3A activity. Drug Metab Dispos 28:766–771
Ho HK, Chan JC, Hardy KD, Chan EC (2015) Mechanism-based inactivation of CYP450 enzymes: a case study of lapatinib. Drug Metab Rev 47:21–28
Hutzler JM, Balogh LM, Zientek M, Kumar V, Tracy TS (2009) Mechanism-based inactivation of cytochrome P450 2C9 by tienilic acid and (+/−)-suprofen: a comparison of kinetics and probe substrate selection. Drug Metab Dispos 37:59–65
Ji L, Lu D, Cao J, Zheng L, Peng Y, Zheng J (2015) Psoralen, a mechanism-based inactivator of CYP2B6. Chem Biol Interact 240:346–352
Lin HL, Kenaan C, Hollenberg PF (2012) Identification of the residue in human CYP3A4 that is covalently modified by bergamottin and the reactive intermediate that contributes to the grapefruit juice effect. Drug Metab Dispos 40:998–1006
Lopez-Garcia MP, Dansette PM, Mansuy D (1994) Thiophene derivatives as new mechanism-based inhibitors of cytochromes P-450: inactivation of yeast-expressed human liver cytochrome P-450 2C9 by tienilic acid. Biochemistry 33:166–175
Lu D, Ji L, Zheng L, Cao J, Peng Y, Zheng J (2016) Mechanism-based inactivation of cytochrome P450 2B6 by isopsoralen. Xenobiotica 46:335–341
Madrigal-Bujaidar E, Martino RL, Garcia-Aguirre K, Garcia-Medina S, Alvarez-Gonzalez I (2013) Grapefruit juice suppresses azoxymethane-induced colon aberrant crypt formation and induces antioxidant capacity in mice. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:6851–6856
Marks GS, McCluskey SA, Mackie JE, Riddick DS, James CA (1988) Disruption of hepatic heme biosynthesis after interaction of xenobiotics with cytochrome P-450. FASEB J 2:2774–2783
Masubuchi Y, Horie T (2007) Toxicological significance of mechanism-based inactivation of cytochrome p450 enzymes by drugs. Crit Rev Toxicol 37:389–412
Murray M (2006) Altered CYP expression and function in response to dietary factors: potential roles in disease pathogenesis. Curr Drug Metab 7:67–81
Nagata M et al. (2007) Effects of pomegranate juice on human cytochrome P450 2C9 and tolbutamide pharmacokinetics in rats. Drug Metab Dispos 35:302–305
Silverman RB (1995) Mechanism-based enzyme inactivators. Methods Enzymol 249:240–283
Wang H et al. (2015) Mechanism-based inactivation of CYP2C9 by linderane. Xenobiotica 45:1037–1046
Zhang HF et al. (2016) Physiological Content and Intrinsic Activities of 10 Cytochrome P450 Isoforms in Human Normal Liver Microsomes. J Pharm Exp Ther 358:83–93
Zheng L, Cao J, Lu D, Ji L, Peng Y, Zheng J (2015) Imperatorin is a mechanism-based inactivator of CYP2B6. Drug Metab Dispos 43:82–88
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [81960754, U1812403, and 81803623].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, T., Cheng, T., Li, J. et al. Bergaptol, a mechanism-based inactivator of CYP2C9. Med Chem Res 29, 1230–1237 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02564-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02564-x