Abstract
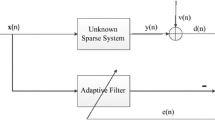
It is well known that the zero-attracting least mean square (ZA-LMS) algorithm and reweighted zero-attracting LMS (RZA-LMS) algorithm outperform the standard LMS algorithm in sparse systems. However, because the ZA-LMS algorithm does not distinguish the size of the tap coefficients, its performance in low-sparse or non-sparse systems declines rapidly. Although RZA-LMS selectively attracts taps with small magnitudes, there is extra attraction to large tap coefficients, which can increase the steady-state mean square error (MSE). In this paper, a Cauchy distribution function-penalized LMS (C-LMS) algorithm is proposed. The proposed algorithm changed the penalty term of the cost function into Cauchy distribution function, which can decrease the attraction to large tap coefficients and enhances the force to the small tap coefficients. The simulation results indicate that the C-LMS can achieve lower steady-state MSE than other algorithms in sparse systems and demonstrates similar performance to the conventional LMS algorithm in non-sparse system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Baraniuk, A lecture on compressive sensing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 24, 118–120 (2007)
E.J. Candes, M. Wakin, S. Boyd, Enhancing sparsity by reweighted l 1 minimization. J. Fourier Anal. Appl. 14(5–6), 877–905 (2008)
Y. Chen, Y. Gu, A.O. Hero, Sparse LMS for system identification, in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech & Signal Processing (2009), pp. 3125–3128
H.B. Chen, Y.S. Xiao, F. Ding, Hierarchical gradient parameter estimation algorithm for Hammerstein nonlinear systems using the key term separation principle. Appl. Math. Comput. 247, 1202–1210 (2014)
J.L. Ding, Recursive and iterative least squares parameter estimation algorithms for multiple-input-output-error systems with autoregressive noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37(5), 1884–1906 (2018)
F. Ding, X. Wang, Hierarchical stochastic gradient algorithm and its performance analysis for a class of bilinear-in-parameter systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(4), 1393–1405 (2017)
F. Ding, X.H. Wang, Q.J. Chen, Y.S. Xiao, Recursive least squares parameter estimation for a class of output nonlinear systems based on the model decomposition. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(9), 3323–3338 (2016)
F. Ding, L. Xu, F.E. Alsaadi, T. Hayat, Iterative parameter identification for pseudo-linear systems with ARMA noise using the filtering technique. IET Control Theory Appl. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cta.2017.0821
F. Ding, H.B. Chen, L. Xu et al., A hierarchical least squares identification algorithm for Hammerstein nonlinear systems using the key term separation. J. Franklin Inst. 355(6), 3737–3752 (2018)
B. Farhang-Boroujeny, Adaptive Filters: Theory and Applications, 2nd edn. (Wiley, Chichester, 2013)
P.C. Gong, W.Q. Wang, F.C. Li, H.C. So, Sparsity-aware transmit beamspace design for FDA-MIMO radar. Sig. Process. 144, 99–103 (2018)
Y. Gu, J. Jin, S. Mei, l 0 norm constraint LMS algorithm for sparse system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 16(9), 774–777 (2009)
M.H. Li, X.M. Liu, The least squares based iterative algorithms for parameter estimation of a bilinear system with autoregressive noise using the data filtering technique. Sig. Process. 147, 23–34 (2018)
C.G. Li, P. Liu, C. Zou et al., Spectral-efficient cellular communications with coexistent one- and two-hop transmissions. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 65(8), 6765–6772 (2016)
W.L. Li, Y.M. Jia, J.P. Du, Distributed filtering for discrete-time linear systems with fading measurements and time-correlated noise. Digit. Signal Proc. 60, 211–219 (2017)
M.H. Li, X.M. Liu, F. Ding, The maximum likelihood least squares based iterative estimation algorithm for bilinear systems with autoregressive noise. J. Franklin Inst. 354(12), 4861–4881 (2017)
M.H. Li, X.M. Liu, F. Ding, The gradient based iterative estimation algorithms for bilinear systems with autoregressive noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(11), 4541–4568 (2017)
M.H. Li, X.M. Liu, F. Ding, Least-squares-based iterative and gradient-based iterative estimation algorithms for bilinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(1), 1–15 (2017)
C.G. Li, K. Song, L.X. Yang, Low computational complexity design over sparse channel estimator in underwater acoustic OFDM communication system. IET Commun. 11(7), 1143–1151 (2017)
J. Maheshwari, N.V. George, Polynomial sparse adaptive algorithm. Electron. Lett. 52(25), 2063–2065 (2016)
C. Paleologu, J. Benesty, S. Ciochina, Sparse Adaptive Filters for Echo Cancellation (Morgan & Claypool, San Rafael, 2010)
Z.H. Rao, C.Y. Zeng, M.H. Wu et al., Research on a handwritten character recognition algorithm based on an extended nonlinear kernel residual network. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 12(1), 413–435 (2018)
G. Su, J. Jin, Y. Gu, J. Wang, Performance analysis of l 0 norm constraint least mean square algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(5), 2223–2235 (2012)
R. Tibshirani, Regression shrinkage and selection via the LASSO. J. Roy. Stat. Soc.: Ser. B (Methodol.) 58(1), 267–288 (1996)
L.R. Vega, H. Rey, A Rapid Introduction to Adaptive Filtering (Springer, New York, 2013)
Y. Wang, F. Ding, Recursive parameter estimation algorithms and convergence for a class of nonlinear systems with colored noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(10), 3461–3481 (2016)
Y. Wang, F. Ding, L. Xu, Some new results of designing an IIR filter with colored noise for signal processing. Digit. Signal Proc. 72, 44–58 (2018)
L. Xu, F. Ding, Recursive least squares and multi-innovation stochastic gradient parameter estimation methods for signal modeling. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(4), 1735–1753 (2017)
Z. Yang, Y.R. Zheng, S.L. Grant, Proportionate affine projection sign algorithms for network echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(8), 2273–2284 (2011)
X. Zhang, K. Song, C.G. Li, L.X. Yang, Parameter estimation for multi-scale multi-lag underwater acoustic channels based on modified particle swarm optimization algorithm. IEEE Access 5(99), 4808–4820 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, S., Lin, Y. Cauchy Distribution Function-Penalized LMS for Sparse System Identification. Circuits Syst Signal Process 38, 470–480 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0870-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0870-0