Abstract
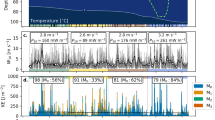
Persistent weak temperature stratification characterizes the epilimnion of Lake Opeongo, Ontario, Canada, and reduces the magnitude of turbulent mixing. Throughout July and August 2009, the epilimnion was isothermal for only 34 % of the record, while for 28 % of the record there was at least a 2 °C temperature difference across the 5 m deep epilimnion. During these stratified periods, there were increases in gradient Richardson numbers (Ri g ), and decreases in rates of dissipation of turbulent kinetic energy (\(\varepsilon\)), the turbulence activity parameter (I = ε/νN 2), an indicator of active mixing, and vertical eddy diffusivity (K z ) inferred from temperature microstructure profiles. During periods of shear induced mixing, values of ε approached 10−6 m2 s−3 and decreased during periods of increasing Ri g . For 0 < Ri g < 1, average values of I were ~1,000 and values of K z were slightly higher than 10−4 m2 s−1. For Ri g >1, average values of I were ~300 and K z was reduced by one to three orders of magnitude. Mixing during cold fronts occurred over time scales of minutes to hours, which worked to erode diurnal thermoclines. However, during periods of persistent secondary thermoclines, mixing was suppressed throughout the epilimnion.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberg J, Jansson M, Jonsson A (2010) The importance of water temperature and thermal stratification dynamics for temporal variation of surface water CO2 in a boreal lake. J Geophys Res 115:G02024. doi:10.1029/2009JG001085
Anis A, Singhal G (2006) Mixing in the surface boundary layer of a tropical freshwater lake. J Mar Syst 63:225–243
Arhonditsis GB, Brett MT (2005) Eutrophication model for Lake Washington (USA) part I. Model description and sensitivity analysis. Ecol Model 187:140–178
Boegman L, Loewen MR, Hamblin PF, Culver DA (2008) Vertical mixing and weak stratification over zebra mussel colonies in western Lake Erie. Limnol Oceanogr 53(3):1093–1111
Bonnet MP, Wessen K (2001) ELMO, a 3D water quality model for nutrients and chlorophyll: first application on a lacustrine ecosystem. Ecol Model 141:19–33
Bouffard D, Boegman L (2013) A diapycnal diffusivity model for stratified environmental flows. Dynam Atmos Oceans 61:14–34
Brainerd K, Gregg M (1993) Diurnal restratification and turbulence in the oceanic surface mixed layer. J Geophys Res 98(C12):22645–22656
Chen CT, Millero FJ (1977) The use and misuse of pure water PVT properties for lake waters. Nature 266:707–708
Dillon TM, Caldwell DR (1980) The Batchelor spectrum and dissipation in the upper ocean. J Geophys Res 85:1910–1916
Dunckley JF, Koseff JR, Steinbuck JV, Monismith SG, Genin A (2012) Comparison of mixing efficiency and vertical diffusivity models from temperature microstructure. J Geophys Res 117:C10008
Finlay KP, Cyr H, Shuter BJ (2001) Spatial and temporal variability in water temperatures in the littoral zone of a multibasin lake. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 58:609–619
Gargett AE (1985) Evolution of scalar spectra with the decay of turbulence in a stratified fluid. J Fluid Mech 159:379–401
Gregg MC (1999) Uncertainties and limitations in measuring ε and χT. J Atmos Ocean Tech 16(1483):1490
Hutchinson GE (1957) A treatise on limnology. Volume 1. Geography, physics and chemistry. Wiley, New York, p 1015
Imberger J (1985) The diurnal mixed layer. Limnol Oceanogr 30(4):737–770
Ivey GN, Imberger J (1991) On the nature of turbulence in a stratified fluid. Part 1: the efficiency of mixing. J Phys Oceanogr 21:650–658
Ivey GN, Imberger J, Koseff JR (1998) Buoyancy fluxes in a stratified fluid. In: Imberger J (ed) Physical processes in lakes and oceans. Coastal and estuarine studies. AGU, Washington, pp 377–388. doi:10.1029/CE054p0377
Ivey GN, Winters KB, Koseff JR (2008) Density stratification, turbulence, but how much mixing? Ann Rev Fluid Mech 40:169–184
Jonas T, Stips A, Eugster W, Wüest A (2003) Observations of a quasi-free lacustrine convective boundary layer: stratification and its implication on turbulence. J Geophys Res 108(C10):3328. doi:10.1029/2002JC001440
King JR, Shuter BJ, Zimmerman AP (1999) Signals of climate trends and extreme events in the thermal stratification pattern of multibasin Lake Opeongo, Ontario. Can J Fish and Aquat Sci 56:847–852
Knauer K, Nepf HM, Hemond HF (2000) The production of chemical heterogeneity in upper Mystic Lake. Limnol Oceanogr 45(7):1647–1654
Lewis WM (1973) The thermal regime of Lake Lanao (Philippines) and its theoretical implications for tropical lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 18(2):200–217
Lewis M, Horne EP, Cullen JJ, Oakey N, Platt T (1984) Turbulent motions may control phytoplankton photosynthesis in the upper ocean. Nature 311:49–50
Loewen M, Ackerman J, Hamblin P (2007) Environmental implications of stratification and turbulent mixing in a shallow lake basin. Can J Fish and Aquat Sci 64(1):43–57
Lombardo CP, Gregg MC (1989) Similarity scaling of viscous and thermal dissipation in a convective surface boundary layer. J Geophys Res 94:6273–6284
Lorke A, Wüest A (2002) Probability density of displacement and overturning length scales under diverse stratification. J Geophys Res 107(C12):3214. doi:10.1029/2001JC001154
MacIntyre S (1993) Vertical mixing in a shallow, eutrophic lake: possible consequences for the light climate of phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 38(4):798–817
MacIntyre S (1996) Turbulent eddies and their implications for phytoplankton within the euphotic zone of Lake Biwa, Japan. Jpn J Limnol 57(4):395–410
MacIntyre S, Romero JR, Kling GW (2002) Spatial-temporal variability in surface layer deepening and lateral advection in an embayment of Lake Victoria, East Africa. Limnol Oceanogr 47(3):656–671
MacIntyre S, Fram JP, Kushner PJ, Bettez ND, O’Brien WJ, Hobbie JE, Kling GW (2009) Climate-related variations in mixing dynamics in an Alaskan arctic lake. Limnol Oceanogr 54:2401–2417
MacIntyre S, Jonsson A, Jansson M, Aberg J, Turney DE, Miller SD (2010) Buoyancy flux, turbulence, and the gas transfer coefficient in a stratified lake. Geophys Res Lett 37:L24604. doi:10.1029/2010GL044164
MacKinnon JA, Gregg MC (2003) Mixing on the late-summer New England shelf––solibores, shear, and stratification. J Phys Oceanogr 33(7):1476–1492
MacKinnon JA, Gregg MC (2005) Near-inertial waves on the New England shelf: the role of evolving stratification, turbulent dissipation, and bottom drag. J Phys Oceanogr 35(12):2408–2424
McManus MA, Alldredge AL, Barnard A et al (2003) Changes in characteristics, distribution and persistence of thin layers over a 48 h period. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 261:1–19
Miles JW (1961) On the stability of heterogeneous shear flows. J Fluid Mech 10(4):496–508
Miles JW, Howard LN (1964) Note on a heterogeneous shear flow. J Fluid Mech 20(2):331–336
Monismith SG, MacIntyre S (2009) The surface mixed layer in lakes and reservoirs. Encyclopedia Inland Waters 1:636–650
Munk WH, Anderson ER (1948) Notes on the theory of a thermocline. J Mar Res 7(3):276–295
Münnich M, Wüest A, Imboden DM (1992) Observations of the second vertical mode of internal seiche in an alpine lake. Limnol Oceanogr 37(8):1705–1719
O’Brien KR, Ivey GN, Hamilton DP, Waite AM, Visser PM (2003) Simple mixing criteria for the growth of negatively buoyant phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 48(3):1326–1337
Oakey NS (1982) Determination of the rate of dissipation of turbulent energy from simultaneous temperature and velocity shear microstructure measurements. J Phys Oceanogr 12(3):256–271
Osborn TR (1980) Estimates of the local-rate of vertical diffusion from dissipation measurements. J Phys Oceanogr 10(1):83–89
Patterson JC, Hamblin P, Imberger J (1984) Classification and dynamic simulation of the vertical density structure of lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 29(4):845–861
Peters H, Gregg MC, Toole JM (1988) On the parameterization of equatorial turbulence. J Geophys Res 93(C2):1199–1218
Polzin K (1996) Statistics of the Richardson number: mixing models and fine structure. J Phys Oceanogr 26(8):1409–1425
Polzin K, Kunze E, Hummon J, Firing E (2002) The finescale response of lowered ADCP velocity profiles. J Atmos Ocean Tech 19(2):205–224
Preusse M, Peeters F, Lorke A (2010) Internal waves and the generation of turbulence in the thermocline of a large lake. Limnol Oceanogr 55(6):2353–2365
Read JS, Hamilton DP, Jones ID, Muraoka K et al (2011) Derivation of lake mixing and stratification indices from high-resolution lake buoy data. Environ Modell Softw 26:1325–1336
Reynolds CS (1984) The ecology of freshwater phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 396
Reynolds CS, Oliver RL, Walsby AE (1987) Cyanobacterial dominance: the role of buoyancy regulation in dynamic lake environments. N Z J Mar Fresh Res 21:379–390
Rothschild BJ, Osborn TR (1988) Small-scale turbulence and plankton contact rates. J Plankton Res 10(3):465–474
Ruddick B, Anis A, Thompson KL (2000) Maximum likelihood spectral fitting: the batchelor spectrum. J Atmos Ocean Tech 17(11):1541–1555
Shih LH, Koseff JR, Ivey GN, Ferziger JH (2005) Parameterization of turbulent fluxes and scales using homogeneous sheared stably stratified turbulence simulations. J Fluid Mech 525:193–214
Smith S (1988) Coefficients for sea surface wind stress, heat flux and wind profiles as a function of wind speed and temperature. J Geophys Res 93(C12):15467–15472
Smyth RL (2010) Stratification and turbulent mixing in small strongly stratified lakes with implications for planktonic disease dynamics. Ph.D. Thesis. University of California, Santa Barbara
Steinbuck JV, Stacey MT, Monismith SG (2009) An evaluation of χT estimation techniques: implications for batchelor fitting and ε. J Atmos Ocean Tech 26(8):1652–1662
Thorpe SA (1977) Turbulence and mixing in a Scottish Loch. Philos T R Soc A 286(1334):125–181
Turner JS (1973) Buoyancy effects in fluids. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 368
van der Lee EM, Umlauf L (2011) Internal wave mixing in the Baltic Sea: near-inertial waves in the absence of tides. J Geophys Res 116:C10016. doi:10.1029/2011JC007072
Van Gastel P, Pelegri JL (2004) Estimates of gradient Richardson numbers from vertically smoothed data in the Gulf Stream region. Sci Mar 68(4):459–482
Vidal J, MacIntyre S, McPhee-Shaw EE, Shaw WJ, Monismith SG (2013) Temporal and spatial variability of the internal wave field in a lake with complex morphometry. Limnol Oceanogr 58:1557–1580
Vincent W, Neale P, Richerson P (1984) Photoinhibition-algal response to bright light during diel stratification and mixing in a tropical alpine lake. J Phycol 20(2):201–211
Wain DJ, Rehmann CR (2005) Evaluation of oceanographic microstructure methods for hydraulics problems, paper presented at world water and environmental resources congress. Anchorage, Alaska
Walter RK, Woodson CB, Arthur RS, Fringer OB, Monismith SG (2012) Nearshore internal bores and turbulent mixing in southern Monterey Bay. J Geophys Res 117:C07017. doi:10.1029/2012JC008115
Wu J (1973) Wind-induced turbulent entrainment across a stable density interface. J Fluid Mech 61:275–287
Wüest A, Lorke A (2003) Small-scale hydrodynamics in lakes. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 35:373–412
Xenopoulos M, Schindler DW (2001) The environmental control of near-surface thermoclines in boreal lakes. Ecosystems 4(7):699–701
Zhao J, Ramin M, Cheng V, Arhonditsis GB (2008) Plankton community patterns across a trophic gradient: the role of zooplankton functional groups. Ecol Model 213:417–436
Acknowledgments
The field work was conducted at the OMNR Harkness field station, and we thank Mark Ridgway for his help and support. Funding was provided by the US National Science Foundation Grants DEB0640953, DEB0919603, and ARC0714085 to SM. MGW was supported by the Canadian Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council, the Canadian Foundation for Innovation and the Ontario Research Fund. PP was supported by an OGSST award and a University of Toronto CGCS travel award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pernica, P., Wells, M.G. & MacIntyre, S. Persistent weak thermal stratification inhibits mixing in the epilimnion of north-temperate Lake Opeongo, Canada. Aquat Sci 76, 187–201 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-013-0328-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-013-0328-1