Abstract
In the process of leukocyte migration from the circulation across the vascular wall, the crosstalk with endothelial cells that line the blood vessels is essential. It is now firmly established that in endothelial cells important signaling events are initiated upon leukocyte adhesion that impinge on the regulation of cell–cell contact and control the efficiency of transendothelial migration. In addition, several external factors such as shear force and vascular stiffness were recently identified as important regulators of endothelial signaling and, consequently, leukocyte transmigration. Here, I review recent insights into endothelial signaling events that are linked to leukocyte migration across the vessel wall. In this field, protein phosphorylation and Rho-mediated cytoskeletal dynamics are still widely studied using increasingly sophisticated mouse models. In addition, activation of tyrosine phosphatases, changes in endothelial cell stiffness as well as different vascular beds have all been established as important factors in endothelial signaling and leukocyte transmigration. Finally, I address less-well-studied but interesting components in the endothelium that also control transendothelial migration, such as the ephrins and their Eph receptors, that provide novel insights in the complexity associated with this process.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nourshargh S, Hordijk PL, Sixt M (2010) Breaching multiple barriers: leukocyte motility through venular walls and the interstitium. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:366–378
Nourshargh S, Alon R (2014) Leukocyte migration into inflamed tissues. Immunity 41:694–707
Muller WA (2015) The regulation of transendothelial migration: new knowledge and new questions. Cardiovasc Res 107:310–320
Vestweber D (2015) How leukocytes cross the vascular endothelium. Nat Rev Immunol 15:692–704
Scheiermann C, Frenette PS, Hidalgo A (2015) Regulation of leucocyte homeostasis in the circulation. Cardiovasc Res 107:340–351
Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI, Nourshargh S (2007) Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol 7:678–689
Springer TA (1994) Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell 76:301–314
Butcher EC (1991) Leukocyte–endothelial cell recognition: three (or more) steps to specificity and diversity. Cell 67:1033–1036
Fernandez-Borja M, van Buul JD, Hordijk PL (2010) The regulation of leucocyte transendothelial migration by endothelial signalling events. Cardiovasc Res 86:202–210
Muller WA (2011) Mechanisms of leukocyte transendothelial migration. Annu Rev Pathol 6:323–344
Heemskerk N, van Rijssel J, van Buul JD (2014) Rho-GTPase signaling in leukocyte extravasation: an endothelial point of view. Cell Adh Migr 8:67–75
Reymond N, d’Agua BB, Ridley AJ (2013) Crossing the endothelial barrier during metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 13:858–870
Chavakis E, Dimmeler S (2011) Homing of progenitor cells to ischemic tissues. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:967–980
Voermans C, van Hennik PB, van der Schoot CE (2001) Homing of human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells: new insights, new challenges? J Hematother Stem Cell Res 10:725–738
Aird WC (2007) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ. Res. 100:174–190
Aird WC (2007) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res 100:158–173
Schaefer A, Hordijk PL (2015) Cell-stiffness-induced mechanosignaling—a key driver of leukocyte transendothelial migration. J Cell Sci 128:2221–2230
Carman CV (2009) Mechanisms for transcellular diapedesis: probing and pathfinding by ‘invadosome-like protrusions’. J Cell Sci 122:3025–3035
Woodfin A, Voisin MB, Beyrau M, Colom B, Caille D, Diapouli FM, Nash GB, Chavakis T, Albelda SM, Rainger GE et al (2011) The junctional adhesion molecule JAM-C regulates polarized transendothelial migration of neutrophils in vivo. Nat Immunol 12:761–769
Voisin MB, Nourshargh S (2013) Neutrophil transmigration: emergence of an adhesive cascade within venular walls. J Innate Immun 5:336–347
Colom B, Bodkin JV, Beyrau M, Woodfin A, Ody C, Rourke C, Chavakis T, Brohi K, Imhof BA, Nourshargh S (2015) Leukotriene B4-neutrophil elastase axis drives neutrophil reverse transendothelial cell migration in vivo. Immunity 42:1075–1086
Proebstl D, Voisin MB, Woodfin A, Whiteford J, D’Acquisto F, Jones GE, Rowe D, Nourshargh S (2012) Pericytes support neutrophil subendothelial cell crawling and breaching of venular walls in vivo. J Exp Med 209:1219–1234
Phillipson M, Kaur J, Colarusso P, Ballantyne CM, Kubes P (2008) Endothelial domes encapsulate adherent neutrophils and minimize increases in vascular permeability in paracellular and transcellular emigration. PLoS One 3:e1649
Petri B, Kaur J, Long EM, Li H, Parsons SA, Butz S, Phillipson M, Vestweber D, Patel KD, Robbins SM et al (2011) Endothelial LSP1 is involved in endothelial dome formation, minimizing vascular permeability changes during neutrophil transmigration in vivo. Blood 117:942–952
Sanz MJ, Kubes P (2012) Neutrophil-active chemokines in in vivo imaging of neutrophil trafficking. Eur J Immunol 42:278–283
Zheng Y, Chen J, Craven M, Choi NW, Totorica S, Diaz-Santana A, Kermani P, Hempstead B, Fischbach-Teschl C, Lopez JA et al (2012) In vitro microvessels for the study of angiogenesis and thrombosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:9342–9347
Zheng Y, Chen J, Lopez JA (2015) Flow-driven assembly of VWF fibres and webs in in vitro microvessels. Nat Commun 6:7858
van Geemen D, Smeets MW, van Stalborch AM, Woerdeman LA, Daemen MJ, Hordijk PL, Huveneers S (2014) F-actin-anchored focal adhesions distinguish endothelial phenotypes of human arteries and veins. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34:2059–2067
Seok J, Warren HS, Cuenca AG, Mindrinos MN, Baker HV, Xu W, Richards DR, McDonald-Smith GP, Gao H, Hennessy L et al (2013) Genomic responses in mouse models poorly mimic human inflammatory diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:3507–3512
Takao K, Miyakawa T (2015) Genomic responses in mouse models greatly mimic human inflammatory diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:1167–1172
Wittchen ES (2009) Endothelial signaling in paracellular and transcellular leukocyte transmigration. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 14:2522–2545
Muller WA, Gimbrone MA Jr (1986) Plasmalemmal proteins of cultured vascular endothelial cells exhibit apical–basal polarity: analysis by surface-selective iodination. J Cell Biol 103:2389–2402
Parat MO, Anand-Apte B, Fox PL (2003) Differential caveolin-1 polarization in endothelial cells during migration in two and three dimensions. Mol Biol Cell 14:3156–3168
Giampietro C, Deflorian G, Gallo S, Di MA, Pradella D, Bonomi S, Belloni E, Nyqvist D, Quaranta V, Confalonieri S et al (2015) The alternative splicing factor Nova2 regulates vascular development and lumen formation. Nat Commun 6:8479
Huang AJ, Manning JE, Bandak TM, Ratau MC, Hanser KR, Silverstein SC (1993) Endothelial cell cytosolic free calcium regulates neutrophil migration across monolayers of endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 120:1371–1380
Etienne S, Adamson P, Greenwood J, Strosberg AD, Cazaubon S, Couraud PO (1998) ICAM-1 signaling pathways associated with Rho activation in microvascular brain endothelial cells. J Immunol 161:5755–5761
Etienne-Manneville S, Manneville JB, Adamson P, Wilbourn B, Greenwood J, Couraud PO (2000) ICAM-1-coupled cytoskeletal rearrangements and transendothelial lymphocyte migration involve intracellular calcium signaling in brain endothelial cell lines. J Immunol 165:3375–3383
Walters CE, Pryce G, Hankey DJ, Sebti SM, Hamilton AD, Baker D, Greenwood J, Adamson P (2002) Inhibition of Rho GTPases with protein prenyltransferase inhibitors prevents leukocyte recruitment to the central nervous system and attenuates clinical signs of disease in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 168:4087–4094
Wojciak-Stothard B, Williams L, Ridley AJ (1999) Monocyte adhesion and spreading on human endothelial cells is dependent on Rho-regulated receptor clustering. J Cell Biol 145:1293–1307
Thompson PW, Randi AM, Ridley AJ (2002) Intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1, but not ICAM-2, activates RhoA and stimulates c-fos and rhoA transcription in endothelial cells. J Immunol 169:1007–1013
Nieuw Amerongen GP, van Delft S, Vermeer MA, Collard JG, van Hinsbergh VW (2000) Activation of RhoA by thrombin in endothelial hyperpermeability: role of Rho kinase and protein tyrosine kinases. Circ Res 87:335–340
Nieuw Amerongen GP, Beckers CM, Achekar ID, Zeeman S, Musters RJ, van Hinsbergh VW (2007) Involvement of Rho kinase in endothelial barrier maintenance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:2332–2339
van Buul JD, Hordijk PL (2004) Signaling in leukocyte transendothelial migration. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:824–833
van Buul JD, Kanters E, Hordijk PL (2007) Endothelial signaling by Ig-like cell adhesion molecules. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1870–1876
Muller WA, Weigl SA, Deng X, Phillips DM (1993) PECAM-1 is required for transendothelial migration of leukocytes. J Exp Med 178:449–460
Schenkel AR, Chew TW, Muller WA (2004) Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule deficiency or blockade significantly reduces leukocyte emigration in a majority of mouse strains. J Immunol 173:6403–6408
Lou O, Alcaide P, Luscinskas FW, Muller WA (2007) CD99 is a key mediator of the transendothelial migration of neutrophils. J Immunol 178:1136–1143
Wegmann F, Petri B, Khandoga AG, Moser C, Khandoga A, Volkery S, Li H, Nasdala I, Brandau O, Fassler R et al (2006) ESAM supports neutrophil extravasation, activation of Rho, and VEGF-induced vascular permeability. J Exp Med 203:1671–1677
Del Maschio A, De Luigi A, Martin-Padura I, Brockhaus M, Bartfai T, Fruscella P, Adorini L, Martino G, Furlan R, De Simoni MG et al (1999) Leukocyte recruitment in the cerebrospinal fluid of mice with experimental meningitis is inhibited by an antibody to junctional adhesion molecule (JAM). J Exp Med 190:1351–1356
Ostermann G, Weber KS, Zernecke A, Schroder A, Weber C (2002) JAM-1 is a ligand of the beta(2) integrin LFA-1 involved in transendothelial migration of leukocytes. Nat Immunol 3:151–158
Durieu-Trautmann O, Chaverot N, Cazaubon S, Strosberg AD, Couraud PO (1994) Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 activation induces tyrosine phosphorylation of the cytoskeleton-associated protein cortactin in brain microvessel endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 269:12536–12540
Minshall RD, Tiruppathi C, Vogel SM, Niles WD, Gilchrist A, Hamm HE, Malik AB (2000) Endothelial cell-surface gp60 activates vesicle formation and trafficking via G(i)-coupled Src kinase signaling pathway. J Cell Biol 150:1057–1070
Tilghman RW, Hoover RL (2002) The Src-cortactin pathway is required for clustering of E-selectin and ICAM-1 in endothelial cells. FASEB J 16:1257–1259
Wang Q, Pfeiffer GR, Gaarde WA (2003) Activation of SRC tyrosine kinases in response to ICAM-1 ligation in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 278:47731–47743
Potter MD, Barbero S, Cheresh DA (2005) Tyrosine phosphorylation of VE-cadherin prevents binding of p120- and beta-catenin and maintains the cellular mesenchymal state. J Biol Chem 280:31906–31912
Yang L, Kowalski JR, Zhan X, Thomas SM, Luscinskas FW (2006) Endothelial cell cortactin phosphorylation by Src contributes to polymorphonuclear leukocyte transmigration in vitro. Circ Res 98:394–402
Allingham MJ, van Buul JD, Burridge K (2007) ICAM-1-mediated, Src- and Pyk2-dependent vascular endothelial cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation is required for leukocyte transendothelial migration. J Immunol 179:4053–4064
Dasgupta B, Muller WA (2008) Endothelial Src kinase regulates membrane recycling from the lateral border recycling compartment during leukocyte transendothelial migration. Eur J Immunol 38:3499–3507
van Wetering S, van den Berk N, van Buul JD, Mul FP, Lommerse I, Mous R, ten Klooster JP, Zwaginga JJ, Hordijk PL (2003) VCAM-1-mediated Rac signaling controls endothelial cell–cell contacts and leukocyte transmigration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285:C343–C352
Matheny HE, Deem TL, Cook-Mills JM (2000) Lymphocyte migration through monolayers of endothelial cell lines involves VCAM-1 signaling via endothelial cell NADPH oxidase. J Immunol 164:6550–6559
Deem TL, Cook-Mills JM (2004) Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) activation of endothelial cell matrix metalloproteinases: role of reactive oxygen species. Blood 104:2385–2393
Vockel M, Vestweber D (2013) How T cells trigger the dissociation of the endothelial receptor phosphatase VE-PTP from VE-cadherin. Blood 122:2512–2522
van Wetering S, van Buul JD, Quik S, Mul FP, Anthony EC, ten Klooster JP, Collard JG, Hordijk PL (2002) Reactive oxygen species mediate Rac-induced loss of cell–cell adhesion in primary human endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 115:1837–1846
Cook-Mills JM, Marchese ME, Abdala-Valencia H (2011) Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression and signaling during disease: regulation by reactive oxygen species and antioxidants. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:1607–1638
Schulte D, Kuppers V, Dartsch N, Broermann A, Li H, Zarbock A, Kamenyeva O, Kiefer F, Khandoga A, Massberg S et al (2011) Stabilizing the VE-cadherin-catenin complex blocks leukocyte extravasation and vascular permeability. EMBO J 30:4157–4170
Kanters E, van Rijssel J, Hensbergen PJ, Hondius D, Mul FP, Deelder AM, Sonnenberg A, van Buul JD, Hordijk PL (2008) Filamin B mediates ICAM-1-driven leukocyte transendothelial migration. J Biol Chem 283:31830–31839
van Buul JD, van Rijssel J, Van Alphen FP, van Stalborch AM, Mul EP, Hordijk PL (2010) ICAM-1 clustering on endothelial cells recruits VCAM-1. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:120328
van Buul JD, Allingham MJ, Samson T, Meller J, Boulter E, Garcia-Mata R, Burridge K (2007) RhoG regulates endothelial apical cup assembly downstream from ICAM1 engagement and is involved in leukocyte trans-endothelial migration. J Cell Biol 178:1279–1293
Barreiro O, Yanez-Mo M, Serrador JM, Montoya MC, Vicente-Manzanares M, Tejedor R, Furthmayr H, Sanchez-Madrid F (2002) Dynamic interaction of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 with moesin and ezrin in a novel endothelial docking structure for adherent leukocytes. J Cell Biol 157:1233–1245
Barreiro O, Yanez-Mo M, Sala-Valdes M, Gutierrez-Lopez MD, Ovalle S, Higginbottom A, Monk PN, Cabanas C, Sanchez-Madrid F (2005) Endothelial tetraspanin microdomains regulate leukocyte firm adhesion during extravasation. Blood 105:2852–2861
Yang L, Kowalski JR, Yacono P, Bajmoczi M, Shaw SK, Froio RM, Golan DE, Thomas SM, Luscinskas FW (2006) Endothelial cell cortactin coordinates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 clustering and actin cytoskeleton remodeling during polymorphonuclear leukocyte adhesion and transmigration. J Immunol 177:6440–6449
van Buul JD, Hordijk PL (2009) Endothelial adapter proteins in leukocyte transmigration. Thromb Haemost 101:649–655
Schnoor M, Lai FP, Zarbock A, Klaver R, Polaschegg C, Schulte D, Weich HA, Oelkers JM, Rottner K, Vestweber D (2011) Cortactin deficiency is associated with reduced neutrophil recruitment but increased vascular permeability in vivo. J Exp Med 208:1721–1735
Schaefer A, Te RJ, Ritz K, Hoogenboezem M, Anthony EC, Mul FP, de Vries CJ, Daemen MJ, Figdor CG, van Buul JD et al (2014) Actin-binding proteins differentially regulate endothelial cell stiffness, ICAM-1 function and neutrophil transmigration. J Cell Sci 127:4470–4482
Celli L, Ryckewaert JJ, Delachanal E, Duperray A (2006) Evidence of a functional role for interaction between ICAM-1 and nonmuscle alpha-actinins in leukocyte diapedesis. J Immunol 177:4113–4121
Schnoor M (2015) Endothelial actin-binding proteins and actin dynamics in leukocyte transendothelial migration. J Immunol 194:3535–3541
Yang L, Froio RM, Sciuto TE, Dvorak AM, Alon R, Luscinskas FW (2005) ICAM-1 regulates neutrophil adhesion and transcellular migration of TNF-alpha-activated vascular endothelium under flow. Blood 106:584–592
Millan J, Hewlett L, Glyn M, Toomre D, Clark P, Ridley AJ (2006) Lymphocyte transcellular migration occurs through recruitment of endothelial ICAM-1 to caveola- and F-actin-rich domains. Nat Cell Biol 8:113–123
Carman CV, Sage PT, Sciuto TE, de la Fuente MA, Geha RS, Ochs HD, Dvorak HF, Dvorak AM, Springer TA (2007) Transcellular diapedesis is initiated by invasive podosomes. Immunity 26:784–797
Carman CV, Springer TA (2004) A transmigratory cup in leukocyte diapedesis both through individual vascular endothelial cells and between them. J Cell Biol 167:377–388
Martinelli R, Zeiger AS, Whitfield M, Sciuto TE, Dvorak A, Van Vliet KJ, Greenwood J, Carman CV (2014) Probing the biomechanical contribution of the endothelium to lymphocyte migration: diapedesis by the path of least resistance. J Cell Sci 127:3720–3734
Kalra VK, Shen Y, Sultana C, Rattan V (1996) Hypoxia induces PECAM-1 phosphorylation and transendothelial migration of monocytes. Am J Physiol 271:H2025–H2034
Deem TL, Abdala-Valencia H, Cook-Mills JM (2007) VCAM-1 activation of endothelial cell protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. J Immunol 178:3865–3873
Berdnikovs S, Pavlov VI, Abdala-Valencia H, McCary CA, Klumpp DJ, Tremblay ML, Cook-Mills JM (2012) PTP1B deficiency exacerbates inflammation and accelerates leukocyte trafficking in vivo. J Immunol 188:874–884
Berdnikovs S, Abdala-Valencia H, Cook-Mills JM (2013) Endothelial cell PTP1B regulates leukocyte recruitment during allergic inflammation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 304:L240–L249
Lanz TV, Becker S, Osswald M, Bittner S, Schuhmann MK, Opitz CA, Gaikwad S, Wiestler B, Litzenburger UM, Sahm F et al (2013) Protein kinase Cbeta as a therapeutic target stabilizing blood–brain barrier disruption in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:14735–14740
Watson RL, Buck J, Levin LR, Winger RC, Wang J, Arase H, Muller WA (2015) Endothelial CD99 signals through soluble adenylyl cyclase and PKA to regulate leukocyte transendothelial migration. J Exp Med 212:1021–1041
Nakhaei-Nejad M, Hussain AM, Zhang QX, Murray AG (2007) Endothelial PI 3-kinase activity regulates lymphocyte diapedesis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H3608–H3616
Cain RJ, Vanhaesebroeck B, Ridley AJ (2012) Different PI 3-kinase inhibitors have distinct effects on endothelial permeability and leukocyte transmigration. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:1929–1936
Cain RJ, Vanhaesebroeck B, Ridley AJ (2010) The PI3K p110alpha isoform regulates endothelial adherens junctions via Pyk2 and Rac1. J Cell Biol 188:863–876
van Buul JD, Anthony EC, Fernandez-Borja M, Burridge K, Hordijk PL (2005) Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2) mediates vascular endothelial-cadherin-based cell–cell adhesion by regulating beta-catenin tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 280:21129–21136
Huveneers S, Oldenburg J, Spanjaard E, VanDerKrogt G, Grigoriev I, Akhmanova A, Rehmann H, de Rooij J (2012) Vinculin associates with endothelial VE-cadherin junctions to control force-dependent remodeling. J Cell Biol 196:641–652
Timmerman I, Heemskerk N, Kroon J, Schaefer A, van Rijssel J, Hoogenboezem M, van UJ, Goedhart J, Gadella TW, Jr, Yin T et al (2015) A local VE-cadherin/Trio-based signaling complex stabilizes endothelial junctions through Rac1. J Cell Sci
Fruman DA, Rommel C (2014) PI3K and cancer: lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13:140–156
Di LA, Fernandez-Hernando C, Cirino G, Sessa WC (2009) Akt1 is critical for acute inflammation and histamine-mediated vascular leakage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:14552–14557
Martinelli R, Gegg M, Longbottom R, Adamson P, Turowski P, Greenwood J (2009) ICAM-1-mediated endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation via calcium and AMP-activated protein kinase is required for transendothelial lymphocyte migration. Mol Biol Cell 20:995–1005
Liu G, Place AT, Chen Z, Brovkovych VM, Vogel SM, Muller WA, Skidgel RA, Malik AB, Minshall RD (2012) ICAM-1-activated Src and eNOS signaling increase endothelial cell surface PECAM-1 adhesivity and neutrophil transmigration. Blood 120:1942–1952
Lampugnani MG, Corada M, Andriopoulou P, Esser S, Risau W, Dejana E (1997) Cell confluence regulates tyrosine phosphorylation of adherens junction components in endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 110(Pt 17):2065–2077
Esser S, Lampugnani MG, Corada M, Dejana E, Risau W (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor induces VE-cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation in endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 111(Pt 13):1853–1865
Andriopoulou P, Navarro P, Zanetti A, Lampugnani MG, Dejana E (1999) Histamine induces tyrosine phosphorylation of endothelial cell-to-cell adherens junctions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:2286–2297
Tinsley JH, Wu MH, Ma W, Taulman AC, Yuan SY (1999) Activated neutrophils induce hyperpermeability and phosphorylation of adherens junction proteins in coronary venular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 274:24930–24934
Wessel F, Winderlich M, Holm M, Frye M, Rivera-Galdos R, Vockel M, Linnepe R, Ipe U, Stadtmann A, Zarbock A et al (2014) Leukocyte extravasation and vascular permeability are each controlled in vivo by different tyrosine residues of VE-cadherin. Nat Immunol 15:223–230
Orsenigo F, Giampietro C, Ferrari A, Corada M, Galaup A, Sigismund S, Ristagno G, Maddaluno L, Koh GY, Franco D et al (2012) Phosphorylation of VE-cadherin is modulated by haemodynamic forces and contributes to the regulation of vascular permeability in vivo. Nat Commun 3:1208
Turowski P, Martinelli R, Crawford R, Wateridge D, Papageorgiou AP, Lampugnani MG, Gamp AC, Vestweber D, Adamson P, Dejana E et al (2008) Phosphorylation of vascular endothelial cadherin controls lymphocyte emigration. J Cell Sci 121:29–37
Wallez Y, Cand F, Cruzalegui F, Wernstedt C, Souchelnytskyi S, Vilgrain I, Huber P (2007) Src kinase phosphorylates vascular endothelial-cadherin in response to vascular endothelial growth factor: identification of tyrosine 685 as the unique target site. Oncogene 26:1067–1077
Earley S, Plopper GE (2006) Disruption of focal adhesion kinase slows transendothelial migration of AU-565 breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 350:405–412
Parsons SA, Sharma R, Roccamatisi DL, Zhang H, Petri B, Kubes P, Colarusso P, Patel KD (2012) Endothelial paxillin and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) play a critical role in neutrophil transmigration. Eur J Immunol 42:436–446
Jean C, Chen XL, Nam JO, Tancioni I, Uryu S, Lawson C, Ward KK, Walsh CT, Miller NL, Ghassemian M et al (2014) Inhibition of endothelial FAK activity prevents tumor metastasis by enhancing barrier function. J Cell Biol 204:247–263
Jouve N, Bachelier R, Despoix N, Blin MG, Matinzadeh MK, Poitevin S, Aurrand-Lions M, Fallague K, Bardin N, Blot-Chabaud M et al (2015) CD146 mediates VEGF-induced melanoma cell extravasation through FAK activation. Int J Cancer 137:50–60
Adam AP (2015) Regulation of endothelial adherens junctions by tyrosine phosphorylation. Mediators Inflamm 2015:272858
Naikawadi RP, Cheng N, Vogel SM, Qian F, Wu D, Malik AB, Ye RD (2012) A critical role for phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate-dependent Rac exchanger 1 in endothelial junction disruption and vascular hyperpermeability. Circ Res 111:1517–1527
Ellerbroek SM, Wennerberg K, Arthur WT, Dunty JM, Bowman DR, Demali KA, Der C, Burridge K (2004) SGEF, a RhoG guanine nucleotide exchange factor that stimulates macropinocytosis. Mol Biol Cell 15:3309–3319
van Rijssel J, Kroon J, Hoogenboezem M, Van Alphen FP, de Jong RJ, Kostadinova E, Geerts D, Hordijk PL, van Buul JD (2012) The Rho-guanine nucleotide exchange factor Trio controls leukocyte transendothelial migration by promoting docking structure formation. Mol Biol Cell 23:2831–2844
Samson T, van Buul JD, Kroon J, Welch C, Bakker EN, Matlung HL, van den Berg TK, Sharek L, Doerschuk C, Hahn K et al (2013) The guanine-nucleotide exchange factor SGEF plays a crucial role in the formation of atherosclerosis. PLoS One 8:e55202
Bellanger JM, Lazaro JB, Diriong S, Fernandez A, Lamb N, Debant A (1998) The two guanine nucleotide exchange factor domains of Trio link the Rac1 and the RhoA pathways in vivo. Oncogene 16:147–152
van Rijssel J, Timmerman I, Van Alphen FP, Hoogenboezem M, Korchynskyi O, Geerts D, Geissler J, Reedquist KA, Niessen HW, van Buul JD (2013) The Rho-GEF Trio regulates a novel pro-inflammatory pathway through the transcription factor Ets2. Biol Open 2:569–579
van Rijssel J, Hoogenboezem M, Wester L, Hordijk PL, van Buul JD (2012) The N-terminal DH-PH domain of Trio induces cell spreading and migration by regulating lamellipodia dynamics in a Rac1-dependent fashion. PLoS One 7:e29912
Bellanger JM, Astier C, Sardet C, Ohta Y, Stossel TP, Debant A (2000) The Rac1- and RhoG-specific GEF domain of Trio targets filamin to remodel cytoskeletal actin. Nat Cell Biol 2:888–892
Stossel TP, Condeelis J, Cooley L, Hartwig JH, Noegel A, Schleicher M, Shapiro SS (2001) Filamins as integrators of cell mechanics and signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:138–145
Lessey-Morillon EC, Osborne LD, Monaghan-Benson E, Guilluy C, O’Brien ET, Superfine R, Burridge K (2014) The RhoA guanine nucleotide exchange factor, LARG, mediates ICAM-1-dependent mechanotransduction in endothelial cells to stimulate transendothelial migration. J Immunol 192:3390–3398
Stroka KM, Aranda-Espinoza H (2009) Neutrophils display biphasic relationship between migration and substrate stiffness. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 66:328–341
Stroka KM, Aranda-Espinoza H (2011) Endothelial cell substrate stiffness influences neutrophil transmigration via myosin light chain kinase-dependent cell contraction. Blood 118:1632–1640
Stroka KM, Hayenga HN, Aranda-Espinoza H (2013) Human neutrophil cytoskeletal dynamics and contractility actively contribute to trans-endothelial migration. PLoS One 8:e61377
Huveneers S, de Rooij J (2013) Mechanosensitive systems at the cadherin-F-actin interface. J Cell Sci 126:403–413
Cinamon G, Shinder V, Alon R (2001) Shear forces promote lymphocyte migration across vascular endothelium bearing apical chemokines. Nat Immunol 2:515–522
Huveneers S, Daemen MJ, Hordijk PL (2015) Between Rho(k) and a hard place: the relation between vessel wall stiffness, endothelial contractility, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 116:895–908
Abadier M, Haghayegh JN, Cardoso AL, Boscacci R, Vestweber D, Barnum S, Deutsch U, Engelhardt B, Lyck R (2015) Cell surface levels of endothelial ICAM-1 influence the transcellular or paracellular T-cell diapedesis across the blood–brain barrier. Eur J Immunol 45:1043–1058
Gerard A, van der Kammen RA, Janssen H, Ellenbroek SI, Collard JG (2009) The Rac activator Tiam1 controls efficient T-cell trafficking and route of trans-endothelial migration. Blood 113:6138–6147
Kumar S, Xu J, Kumar RS, Lakshmikanthan S, Kapur R, Kofron M, Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M, Filippi MD (2014) The small GTPase Rap1b negatively regulates neutrophil chemotaxis and transcellular diapedesis by inhibiting Akt activation. J Exp Med 211:1741–1758
Liu L, Cara DC, Kaur J, Raharjo E, Mullaly SC, Jongstra-Bilen J, Jongstra J, Kubes P (2005) LSP1 is an endothelial gatekeeper of leukocyte transendothelial migration. J Exp Med 201:409–418
Hossain M, Qadri SM, Xu N, Su Y, Cayabyab FS, Heit B, Liu L (2015) Endothelial LSP1 modulates extravascular neutrophil chemotaxis by regulating nonhematopoietic vascular PECAM-1 expression. J Immunol 195:2408–2416
Kullander K, Klein R (2002) Mechanisms and functions of Eph and ephrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:475–486
Pasquale EB (2010) Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 10:165–180
Hafner C, Schmitz G, Meyer S, Bataille F, Hau P, Langmann T, Dietmaier W, Landthaler M, Vogt T (2004) Differential gene expression of Eph receptors and ephrins in benign human tissues and cancers. Clin Chem 50:490–499
Pfaff D, Heroult M, Riedel M, Reiss Y, Kirmse R, Ludwig T, Korff T, Hecker M, Augustin HG (2008) Involvement of endothelial ephrin-B2 in adhesion and transmigration of EphB-receptor-expressing monocytes. J Cell Sci 121:3842–3850
Liu H, Devraj K, Moller K, Liebner S, Hecker M, Korff T (2014) EphrinB-mediated reverse signalling controls junctional integrity and pro-inflammatory differentiation of endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost 112:151–163
Korff T, Dandekar G, Pfaff D, Fuller T, Goettsch W, Morawietz H, Schaffner F, Augustin HG (2006) Endothelial ephrinB2 is controlled by microenvironmental determinants and associates context-dependently with CD31. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:468–474
van Gils JM, Ramkhelawon B, Fernandes L, Stewart MC, Guo L, Seibert T, Menezes GB, Cara DC, Chow C, Kinane TB et al (2013) Endothelial expression of guidance cues in vessel wall homeostasis dysregulation under proatherosclerotic conditions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33:911–919
Funk SD, Yurdagul A Jr, Albert P, Traylor JG Jr, Jin L, Chen J, Orr AW (2012) EphA2 activation promotes the endothelial cell inflammatory response: a potential role in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32:686–695
Trinidad EM, Ballesteros M, Zuloaga J, Zapata A, Alonso-Colmenar LM (2009) An impaired transendothelial migration potential of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells can be linked to ephrin-A4 expression. Blood 114:5081–5090
Tawadros T, Brown MD, Hart CA, Clarke NW (2012) Ligand-independent activation of EphA2 by arachidonic acid induces metastasis-like behaviour in prostate cancer cells. Br J Cancer 107:1737–1744
Boyd AW, Bartlett PF, Lackmann M (2014) Therapeutic targeting of EPH receptors and their ligands. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13:39–62
Funk SD, Orr AW (2013) Ephs and ephrins resurface in inflammation, immunity, and atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Res 67:42–52
Weber EW, Han F, Tauseef M, Birnbaumer L, Mehta D, Muller WA (2015) TRPC6 is the endothelial calcium channel that regulates leukocyte transendothelial migration during the inflammatory response. J Exp Med 212:1883–1899
Kusche-Vihrog K, Jeggle P, Oberleithner H (2014) The role of ENaC in vascular endothelium. Pflugers Arch 466:851–859
Bittner S, Ruck T, Schuhmann MK, Herrmann AM, Moha ou MH, Bobak N, Gobel K, Langhauser F, Stegner D, Ehling P et al (2013) Endothelial TWIK-related potassium channel-1 (TREK1) regulates immune-cell trafficking into the CNS. Nat Med 19:1161–1165
Lohman AW, Leskov IL, Butcher JT, Johnstone SR, Stokes TA, Begandt D, DeLalio LJ, Best AK, Penuela S, Leitinger N et al (2015) Pannexin 1 channels regulate leukocyte emigration through the venous endothelium during acute inflammation. Nat Commun 6:7965
Bao Y, Chen Y, Ledderose C, Li L, Junger WG (2013) Pannexin 1 channels link chemoattractant receptor signaling to local excitation and global inhibition responses at the front and back of polarized neutrophils. J Biol Chem 288:22650–22657
Barletta KE, Ley K, Mehrad B (2012) Regulation of neutrophil function by adenosine. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32:856–864
Schwab ME (2010) Functions of Nogo proteins and their receptors in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:799–811
Harrison KD, Park EJ, Gao N, Kuo A, Rush JS, Waechter CJ, Lehrman MA, Sessa WC (2011) Nogo-B receptor is necessary for cellular dolichol biosynthesis and protein N-glycosylation. EMBO J 30:2490–2500
Di LA, Manes TD, Davalos A, Wright PL, Sessa WC (2011) Endothelial reticulon-4B (Nogo-B) regulates ICAM-1-mediated leukocyte transmigration and acute inflammation. Blood 117:2284–2295
Johnsson AK, Dai Y, Nobis M, Baker MJ, McGhee EJ, Walker S, Schwarz JP, Kadir S, Morton JP, Myant KB et al (2014) The Rac-FRET mouse reveals tight spatiotemporal control of Rac activity in primary cells and tissues. Cell Rep 6:1153–1164
Mizuno R, Kamioka Y, Kabashima K, Imajo M, Sumiyama K, Nakasho E, Ito T, Hamazaki Y, Okuchi Y, Sakai Y et al (2014) In vivo imaging reveals PKA regulation of ERK activity during neutrophil recruitment to inflamed intestines. J Exp Med 211:1123–1136
Krishnan R, Klumpers DD, Park CY, Rajendran K, Trepat X, van Bezu J, van Hinsbergh VW, Carman CV, Brain JD, Fredberg JJ et al (2011) Substrate stiffening promotes endothelial monolayer disruption through enhanced physical forces. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 300:C146–C154
Huynh J, Nishimura N, Rana K, Peloquin JM, Califano JP, Montague CR, King MR, Schaffer CB, Reinhart-King CA (2011) Age-related intimal stiffening enhances endothelial permeability and leukocyte transmigration. Sci Transl Med 3:112ra122
Reijerkerk A, Lopez-Ramirez MA, van Het HB, Drexhage JA, Kamphuis WW, Kooij G, Vos JB, van der Pouw Kraan TC, van Zonneveld AJ, Horrevoets AJ et al (2013) MicroRNAs regulate human brain endothelial cell-barrier function in inflammation: implications for multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci 33:6857–6863
Poissonnier L, Villain G, Soncin F, Mattot V (2014) miR126-5p repression of ALCAM and SetD5 in endothelial cells regulates leucocyte adhesion and transmigration. Cardiovasc Res 102:436–447
Boon RA, Iekushi K, Lechner S, Seeger T, Fischer A, Heydt S, Kaluza D, Treguer K, Carmona G, Bonauer A et al (2013) MicroRNA-34a regulates cardiac ageing and function. Nature 495:107–110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Box 1: The classical transmigration paradigm for acute inflammation
Box 1: The classical transmigration paradigm for acute inflammation
The swift response of our bodies’ defense mechanism to foreign invaders, such as bacteria on a sharp kitchen knife, requires that circulating leukocytes such as neutrophils deploy to the area of infestation a.s.a.p. While so doing, however, these cells (our ‘first line of defense’) encounter a number of problems to which an adequate response is mandatory. This response requires the leukocytes, following their recruitment to the inflamed site, to initiate a now well-established standard operating protocol for their approach (see schematic and text below).
The first phase of this multi-step process is the rolling along and adhesion to the inner wall of the blood vessel. This wall is paved with a monolayer of endothelial cells (EC) which can be locally activated by inflammatory cytokines. Upregulated by these cytokines, carbohydrate-conjugated endothelial cell surface proteins known as selectins (mainly E-selectin) orchestrate the ‘first contact’; their low-affinity interactions with cognate receptors such as PSGL-1 (P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1) are key to the rolling behavior of leukocytes under flow. The flow in itself can induce leukocyte to initiate the TEM program, a response known as chemorheotaxis. Despite the continuous contact with large numbers of red blood cells, many rolling leukocytes remain associated with the vessel wall. Locally accumulated chemokines instruct the leukocytes to transform their circular shape into a spread-out, polarized and motile form, imitating directional motility (chemotaxis). This transformation is not possible without the rapid activation of special adhesion molecules, the β1 and β2 integrins, that allow the cells to further resist the external forces imposed by the blood plasma and its constituents. Activated integrins will lock on to their endothelial ligands ICAM-1 and VCAM-1, securing firm leukocyte adhesion. These ligands may also present as a gradient on the endothelial cells’ surface, driving haptotaxis, migration along a gradient of adhesion molecules.
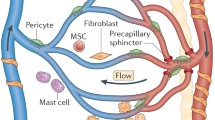
The crawling along the vessel wall is next, directing the cells to optimal sites for TEM that are marked by largely unknown markers. Some of these may involve local differences in EC stiffness, leading to durotaxis. Next is the key process of TEM: the cells’ reversion to a round shape, possibly driven by regions of low stiffness, a phenomenon recently coined ‘tenertaxis’. Subsequently, the cells will protrude and cross the endothelial barrier. Once on the other side, the turbulence of the blood is no more but now the cells need to crawl in a novel way through dense, 3-dimensional networks of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins and along other types of cell, such as pericytes and smooth muscle cells, in search for the inflammatory culprit.
The inflamed vascular endothelium, in the meantime, has been anything but oblivious to the spectacle and has welcomed the leukocytes not only by presenting sufficient adhesion sites in the shape of upregulated ICAM-1 and VCAM-1, but also by forming ‘docking structures’ or ‘transmigratory cups’ that promote the entrance into the inflamed tissue. These endothelial responses are driven by complicated intracellular signaling machinery, of which new components and interactions are still being discovered.
To conclude, be it by crossing the endothelial barrier through the seemingly obvious way of passage, i.e. through the intercellular junction, or by penetration of an endothelial cell’s body while aiming for an as yet unknown target, this incursion of inflamed tissue results in a rapid resolution of the original problem through the tracking down and killing of invader pathogens.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hordijk, P.L. Recent insights into endothelial control of leukocyte extravasation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 73, 1591–1608 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2136-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2136-y