Abstract
Background
Coronary artery disease (CAD) seriously disturbs the life of people. LncRNA H19 is reported to promote the progression of CAD; Nevertheless, the detailed mechanism by which H19 modulates CAD development is unclear.
Methods
Clinical samples of CAD patients were collected, meanwhile we established in vitro and in vivo models of CAD by treating HCAECs with ox-LDL and feeding ApoE−/− mice with high fat diets (HFD). MTT assay was adopted to assess the cell viability. Transwell detection was applied to test the migration, and apoptosis was tested by flow cytometry. The levels of inflammatory cytokines were examined by ELISA. The relation among H19, miR-20a-5p and HDAC4 was explored by dual luciferase reporter and RIP assay.
Results
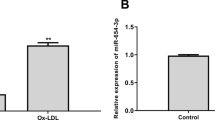
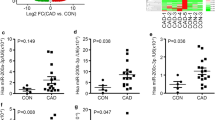
H19 and HDAC4 levels were elevated, while miR-20a-5p was reduced in plasma of CAD patients and ox-LDL-treated HCAECs. ox-LDL increased H19 level and induced apoptosis and inflammation in HCAECs, while silencing of H19 rescued this phenomenon. In addition, the level of H19 was negatively correlated with miR-20a-5p, and miR-20a-5p inhibitor restored the effect of H19 silencing on HCAECs function. HDAC4 was the downstream mRNA of miR-20a-5p, and miR-20a-5p upregulation reversed ox-LDL-induced HCAECs injury through targeting HDAC4. Furthermore, H19 silencing significantly alleviated the coronary atherosclerotic plaques and inhibited the inflammatory responses in vivo.
Conclusions
We proved that knockdown of H19 alleviated ox-LDL-induced HCAECs injury via miR-20a-5p/HDAC4 axis, which might provide a new tactics against CAD.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
18 February 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-023-01701-7
References
Kai H, Wu Q, Yin R, Tang X, Shi H, Wang T, et al. LncRNA NORAD promotes vascular endothelial cell injury and atherosclerosis through suppressing VEGF gene transcription via enhancing H3K9 deacetylation by recruiting HDAC6. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 701628.
Radecke CE, Warrick AE, Singh GD, Rogers JH, Simon SI, Armstrong EJ. Coronary artery endothelial cells and microparticles increase expression of VCAM-1 in myocardial infarction. Thromb Haemost. 2015;113(3):605–16.
Guo F, Tang C, Li Y, Liu Y, Lv P, Wang W, et al. The interplay of LncRNA ANRIL and miR-181b on the inflammation-relevant coronary artery disease through mediating NF-kappaB signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(10):5062–75.
Jin H, Zhu Y, Wang XD, Luo EF, Li YP, Wang BL, et al. BDNF corrects NLRP3 inflammasome-induced pyroptosis and glucose metabolism reprogramming through KLF2/HK1 pathway in vascular endothelial cells. Cell Signal. 2021;78: 109843.
Chen S, Sun Y, Neoh KH, Chen A, Li W, Yang X, et al. Microfluidic assay of circulating endothelial cells in coronary artery disease patients with angina pectoris. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(7): e0181249.
Zeng M, Yan X, Wu W. Risk factors for revascularization and in-stent restenosis in patients with triple-vessel disease after second-generation drug-eluting stent implantation: a retrospective analysis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021;21(1):446.
Wang J, Su Z, Lu S, Fu W, Liu Z, Jiang X, et al. LncRNA HOXA-AS2 and its molecular mechanisms in human cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;485:229–33.
Li L, Wang L, Li H, Han X, Chen S, Yang B, et al. Characterization of LncRNA expression profile and identification of novel LncRNA biomarkers to diagnose coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2018;275:359–67.
Chen J, Dang J. LncRNA CASC11 was downregulated in coronary artery disease and inhibits transforming growth factor-beta1. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(3):300060519889187.
Tan J, Liu S, Jiang Q, Yu T, Huang K. LncRNA-MIAT increased in patients with coronary atherosclerotic heart disease. Cardiol Res Pract. 2019;2019:6280194.
Wang H, Zhang N, Li G, Xu B. Proinflammatory cytokine IFN-gamma, lncRNA BANCR and the occurrence of coronary artery disease. Life Sci. 2019;231: 116510.
Zhang Z, Gao W, Long QQ, Zhang J, Li YF, Liu DC, et al. Increased plasma levels of lncRNA H19 and LIPCAR are associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease in a Chinese population. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):7491.
Bernardo BC, Ooi JY, Lin RC, McMullen JR. miRNA therapeutics: a new class of drugs with potential therapeutic applications in the heart. Future Med Chem. 2015;7(13):1771–92.
Agiannitopoulos K, Samara P, Papadopoulou M, Efthymiadou A, Papadopoulou E, Tsaousis GN, et al. miRNA polymorphisms and risk of premature coronary artery disease. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2021;62(4):278–84.
Schulte C, Karakas M, Zeller T. microRNAs in cardiovascular disease—clinical application. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017;55(5):687–704.
Zhu Y, Yang T, Duan J, Mu N, Zhang T. MALAT1/miR-15b-5p/MAPK1 mediates endothelial progenitor cells autophagy and affects coronary atherosclerotic heart disease via mTOR signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(4):1089–109.
Yin Z, Zhou Y, Ma T, Chen S, Shi N, Zou Y, et al. Down-regulated lncRNA SBF2-AS1 in M2 macrophage-derived exosomes elevates miR-122-5p to restrict XIAP, thereby limiting pancreatic cancer development. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(9):5028–38.
Wang D, Wang Y, Ma J, Wang W, Sun B, Zheng T, et al. MicroRNA-20a participates in the aerobic exercise-based prevention of coronary artery disease by targeting PTEN. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;95:756–63.
Luo L, Martin SC, Parkington J, Cadena SM, Zhu J, Ibebunjo C, et al. HDAC4 controls muscle homeostasis through deacetylation of myosin heavy chain, PGC-1alpha, and Hsc70. Cell Rep. 2019;29(3):749-63 e12.
Zhang B, Dong Y, Liu M, Yang L, Zhao Z. miR-149-5p inhibits vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation, invasion, and migration by targeting histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4). Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:7581–90.
Gordon JW, Pagiatakis C, Salma J, Du M, Andreucci JJ, Zhao J, et al. Protein kinase a-regulated assembly of a MEF2{middle dot}HDAC4 repressor complex controls c-Jun expression in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(28):19027–42.
Li X, Hou L, Cheng Z, Zhou S, Qi J, Cheng J. Overexpression of GAS5 inhibits abnormal activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in myocardial tissues of rats with coronary artery disease. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(7):11348–59.
Ma S, Wang S, Li M, Zhang Y, Zhu P. The effects of pigment epithelium-derived factor on atherosclerosis: putative mechanisms of the process. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17(1):240.
Zheng Q, Li XX, Xiao L, Shao S, Jiang H, Zhang XL, et al. MicroRNA-365 functions as a mechanosensitive microRNA to inhibit end plate chondrocyte degeneration by targeting histone deacetylase 4. Bone. 2019;128: 115052.
Cheleschi S, De Palma A, Pecorelli A, Pascarelli NA, Valacchi G, Belmonte G, et al. Hydrostatic pressure regulates MicroRNA expression levels in osteoarthritic chondrocyte cultures via the wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(1):133–5.
Yang TC, Chen YJ, Chang SF, Chen CH, Chang PY, Lu SC. Malondialdehyde mediates oxidized LDL-induced coronary toxicity through the Akt-FGF2 pathway via DNA methylation. J Biomed Sci. 2014;21:11.
Tang Y, Zhao J, Shen L, Jin Y, Zhang Z, Xu G, et al. ox-LDL induces endothelial dysfunction by promoting Arp2/3 complex expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;475(2):182–8.
Li P, Xing J, Zhang J, Jiang J, Liu X, Zhao D, et al. Inhibition of long noncoding RNA HIF1A-AS2 confers protection against atherosclerosis via ATF2 downregulation. J Adv Res. 2020;26:123–35.
Song J, Zhu XM, Wei QY. MSCs reduce airway remodeling in the lungs of asthmatic rats through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(21):11199–211.
Zhou Y, Zhang S, Ji W, Gan X, Hua L, Hou C, et al. LncRNA landscape of coronary atherosclerosis reveals differentially expressed LncRNAs in proliferation and migration of coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 656636.
Kong C, Lyu D, He C, Li R, Lu Q. Dioscin elevates lncRNA MANTIS in therapeutic angiogenesis for heart diseases. Aging Cell. 2021;20(7): e13392.
Kim IJ, Lee JY, Park HW, Park HS, Ko EJ, Sung JH, et al. Association between HOTAIR lncRNA polymorphisms and coronary artery disease susceptibility. J Pers Med. 2021;11(5):375–9.
Zou B, Huang T, Wu D, Hu X, Xiao L, Wang C, et al. Knockdown of ZFAS1 improved the cardiac function of myocardial infarction rats via regulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(9):12919–28.
Huang J, Li M, Li J, Liang B, Chen Z, Yang J, et al. LncRNA H19 rs4929984 variant is associated with coronary artery disease susceptibility in han Chinese female population. Biochem Genet. 2021;59(6):1959–80.
Hu WN, Ding HX, Xu Q, Zhang XY, Yang DT, Jin YZ. Relationship between long noncoding RNA H19 polymorphisms and risk of coronary artery disease in a chinese population: a case-control study. Dis Markers. 2020;2020:9839612.
Si Y, Liu F, Wang D, Fang C, Tang X, Guo B, et al. Exosomal transfer of miR-185 is controlled by hnRNPA2B1 and impairs Re-endothelialization after vascular injury. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 619444.
Zhang F, Cheng N, Du J, Zhang H, Zhang C. MicroRNA-200b-3p promotes endothelial cell apoptosis by targeting HDAC4 in atherosclerosis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021;21(1):172.
Tian D, Xiang Y, Tang Y, Ge Z, Li Q, Zhang Y. Circ-ADAM9 targeting PTEN and ATG7 promotes autophagy and apoptosis of diabetic endothelial progenitor cells by sponging mir-20a-5p. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(7):526.
Gao J, Chen X, Shan C, Wang Y, Li P, Shao K. Autophagy in cardiovascular diseases: role of noncoding RNAs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;23:101–18.
Miao J, Wang B, Shao R, Wang Y. CircUSP36 knockdown alleviates oxidized lowdensity lipoproteininduced cell injury and inflammatory responses in human umbilical vein endothelial cells via the Mir20a5p/ROCK2 axis. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(4):260–4.
Wei W, Chen W, He N. HDAC4 induces the development of asthma by increasing Slug-upregulated CXCL12 expression through KLF5 deacetylation. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):258.
Zhang L, Cheng H, Yue Y, Li S, Zhang D, He R. H19 knockdown suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis by regulating miR-148b/WNT/beta-catenin in ox-LDL -stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biomed Sci. 2018;25(1):11.
Li H, Zhao Q, Chang L, Wei C, Bei H, Yin Y, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 modulates ox-LDL induced EndMT through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Lipids Health Dis. 2019;18(1):62.
Funding
This work was supported by Scientific Research Project of Health Commission of Hunan Province (No. 20201270).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
These authors declared no competing interests in this research.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The human participants and animal research involved in this study has reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Changsha Third Hospital. The individual’s written informed consent has been obtained for the release of any potentially identifiable images or data contained herein.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised. Author affiliations and Funding section have been corrected.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Wang, Z., Xu, Y. et al. Knockdown of lncRNA H19 alleviates ox-LDL-induced HCAECs inflammation and injury by mediating miR-20a-5p/HDAC4 axis. Inflamm. Res. 71, 1109–1121 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01604-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01604-z