Abstract
Background
Some studies have indicated that glucose metabolism plays an important role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study aimed to find the novel genes affecting glucose metabolism in RA.
Materials/methods
Synovial tissues of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) were analyzed with Rat Glucose Metabolism RT2 Profiler™ PCR Array to screen those genes with special expressions in glucose metabolism. Real-time PCR, western blotting, and ELISA were used to confirm the result in synovial tissues and blood of human RA. Culture synovial fibroblast cells (RASF) was treated with siRNA to suppress expressions of the target genes. CCK-8 cell proliferation assay and two-compartment transwell system were performed to examine cell proliferation and cell migration of the treated RASF.
Results
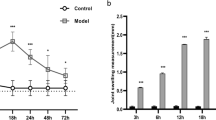
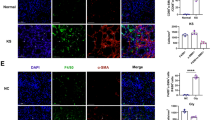
Both PCR array and real-time PCR detected the up-regulation of ENO1, HK2, and PGK1 and the down-regulation of PCK1 and PDK4 in synovial tissues of CIA rats. Real-time PCR and western blotting detected the increased expression of ENO1 and PGK1 in RA synovial tissues. ELISA detected a high level of PGK1 in the blood of RA patients. Decreased cell proliferation and cell migration capabilities were significantly detected in RASF following treatment of anti-PGK1 siRNA. IL-1β and IFN-γ rather than TNF-α and IL-1α levels were significantly declined in supernatants of the treated RASF.
Conclusions
PGK1, a glycolytic enzyme catalyzing the conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate into 2-phosphoglycerate, has increased expression in synovial tissues and blood of RA, which may be involved in pro-inflammation and synovial hyperplasia of the disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henderson B, Bitensky L, Chayen J. Glycolytic activity in human synovial lining cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1979;38(1):63–7.
Ciurtin C, Cojocaru V, Miron I. Correlation between different components of synovial fluid and pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases. Rom J Intern Med. 2006;44(2):171–81.
Naughton D, Whelan M, Smith EC, Williams R, Blake DR, Grootveld M. An investigation of the abnormal metabolic status of synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis by high field proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1993;317(1–2):135–8.
Tak PP, Zvaifler NJ, Green DR, Firestein GS. Rheumatoid arthritis and p53: how oxidative stress might alter the course of inflammatory diseases. Immunol Today. 2000;21(2):78–82.
Okamoto H, Hoshi D, Kiire A, Yamanaka H, Kamatani N. Molecular targets of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2008;7(1):53–66.
Zhu T, Feng L. Comparison of anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides, anti-glucose-6-phosphate isomerase and anti-keratin antibodies and rheumatoid factor in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese patients. Int J Rheum Dis. 2013;16(2):157–61.
Umeda N, Matsumoto I, Ito I, Kawasaki A, Tanaka Y, Inoue A, et al. Anti-citrullinated glucose-6-phosphate isomerase peptide antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis are associated with HLA-DRB1 shared epitope alleles and disease activity. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013;172(1):44–53.
Dai L, Zhu LJ, Zheng DH, Mo YQ, Wei XN, Su JH, et al. Elevated serum glucose-6-phosphate isomerase correlates with histological disease activity and clinical improvement after initiation of therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2010;37(12):2452–61.
Mandik-Nayak L, Allen PM. Initiation of an autoimmune response: insights from a transgenic model of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Res. 2005;32(1–3):5–13.
Chang X, Cui Y, Zong M, Zhao Y, Yan X, Chen Y, et al. Identification of proteins with increased expression in synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(5):872–80.
Yang Z, Fujii H, Mohan SV, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Phosphofructokinase deficiency impairs ATP generation, autophagy, and redox balance in rheumatoid arthritis T cells. J Exp Med. 2013;210(10):2119–34.
Yang Z, Matteson EL, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. T-cell metabolism in autoimmune disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:29.
Tsokos GC. Metabolic control of arthritis: switch pathways to treat. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(331):331fs8.
Iwanami K, Matsumoto I, Tanaka-Watanabe Y, Inoue A, Mihara M, Ohsugi Y, Mamura M, Goto D, Ito S, Tsutsumi A, Kishimoto T, Sumida T. Crucial role of the interleukin-6/interleukin-17 cytokine axis in the induction of arthritis by glucose-6-phosphate isomerase. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(3):754–63.
Chang X, Wei C. Glycolysis and rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2011;14(3):217–22.
Goëb V, Thomas-L’Otellier M, Daveau R, Charlionet R, Fardellone P, Le Loët X, et al. Candidate autoantigens identified by mass spectrometry in early rheumatoid arthritis are chaperones and citrullinated glycolytic enzymes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(2):R38.
Wang TY, Zhou H, Wong YF, Wu PK, Hsiao WL, Leung EL, et al. The predicted proteomic network associated with the antiarthritic action of Qingfu Guanjieshu in collagen-II-induced arthritis in rats. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. 2013;2013:582493.
Krause ML, Davis JM 3rd, Knutson KL, Strausbauch MA, Crowson CS, Therneau TM, et al. Assessing immune function by profiling cytokine release from stimulated blood leukocytes and the risk of infection in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol. 2011;141(1):67–72.
Roy K, Kanwar RK, Kanwar JR. Molecular targets in arthritis and recent trends in nanotherapy. Int J Nanomed. 2015;10:5407–20.
Moltó A, Olivé A. Anti-IL-1 molecules: new comers and new indications. Joint Bone Spine. 2010;77(2):102–7.
Skurkovich B, Skurkovich S. Inhibition of IFN-gamma as a method of treatment of various autoimmune diseases, including skin diseases. Ernst Scher Res Found Workshop. 2006;56:1–27.
Taranto E, Leech M. Expression and function of cell cycle proteins in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Histol Histopathol. 2006;21(2):205–11.
Ahmad SS, Glatzle J, Bajaeifer K, Bühler S, Lehmann T, Königsrainer I, et al. Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 as a promoter of metastasis in colon cancer. Int J Oncol. 2013;43(2):586–90.
Zieker D, Königsrainer I, Weinreich J, Beckert S, Glatzle J, Nieselt K, et al. Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 promoting tumor progression and metastasis in gastric cancer-detected in a tumor mouse model using positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010;26(2):147–54.
Zieker D, Königsrainer I, Traub F, Nieselt K, Knapp B, Schillinger C, et al. PGK1 a potential marker for peritoneal dissemination in gastric cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2008;21(5–6):429–36.
Wang J, Wang J, Dai J, Jung Y, Wei CL, Wang Y, et al. A glycolytic mechanism regulating an angiogenic switch in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67(1):149–59.
Szekanecz Z, Besenyei T, Paragh G, Koch AE. New insights in synovial angiogenesis. Joint Bone Spine. 2010;77(1):13–9.
Vermam Dutta S. DNA sequences encoding enolase are remarkably conserved from yeast to mammals. Life Sci. 1994;5:893–9.
Saulot V, Vittecoq O, Charlionet R, Fardellone P, Lange C, Marvin L, et al. Presence of autoantibodies to the glycolytic enzyme α-enolase in sera from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(5):1196–201.
Montes A, Perez-Pampin E, Calaza M, Gomez-Reino JJ, Gonzalez A. Association of anti-citrullinated vimentin and anti-citrullinated α-enolase with subsets of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(10):3102–10.
Bae S, Kim H, Lee N, Won C, Kim HR, Hwang YI. α-Enolase expressed on the surfaces of monocytes and macrophages induces robust synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 2012;189(1):365–72.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NTFC) (81171990 and 81373218), and the Shandong Science and Technology Promotion Program (2014GSF118135 and 2014XGA01011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Yoshiya Tanaka.
Y. Zhao and X. Yan have equal contribution to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Yan, X., Li, X. et al. PGK1, a glucose metabolism enzyme, may play an important role in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm. Res. 65, 815–825 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-0965-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-0965-7