Abstract
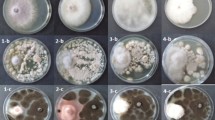
Phytopathogenic effect ofGeosmithia pallida, G. langdonii, Ophiostoma grandicarpum, O. querci, two isolates ofO. piceae, and two isolates ofFusarium solani was compared using plant growth test (stem and root length of garden cress plants seeded on mycelium-covered potato carrot agar);Ophiostoma spp. andF. solani were isolated from oak,Geosmithia spp. from galleries ofScolytus intricatus on beech. All fungi inhibited more the root elongation than that of stems.F. solani led to plant collapse after briefly stimulating the growth of stem and in one case also root.G. langdonii inhibited stem and root growth to 20 % and led to plant collapse.G. pallida inhibited root growth to 25 % whereas stem growth was almost unimpaired.Ophiostoma spp. reduced stem growth to ∼60–80 % and root growth to 25–60 %O. piceae andO. querci caused plant collapse after 15–20 d.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Čapek M., Finďo S., Brutovský D.: Biological control of global oak decline, pp. 169–182 inVedecké práce VÚLH 36 (M. Čapek, Ed.). Priroda Publishers, Bratislava (Slovakia) 1987.
Farrell B.D., Sequeira A.S., O’Meara B.C., Normark B.B., Chung J.H., Jordal B.H.: The evolution of agriculture in beetles (Curculionidae:Scolytinae andPlatypodinae).Evolution 55, 2011–2027 (2001).
Führer E.: Oak decline in Central Europe: a synopsis of hypotheses, pp. 7–24 in M.L. McManus, A.M. Liebhold (Eds):Proc. Population Dynamics, Impacts, and Integrated Management of Forest Defoliating Insects. USDA Forest Service General Technical Report NE-247. USDA, Washington (DC) 1998.
Igmandy Z.: Die Welkeepidemic vonQuercus petraea (Matt.)Lieb. in Ungarn (1978 bis 1986).Österr.Forstz. 98, 48–50 (1987).
Iwamoto S., Tokumasu S., Suyama Y., Kakishima M.: Molecular phylogeny of four selected species of the strictly anamorphic genusThysanophora using nuclear ribosomal DNA sequences.Mycoscience 43, 169–180 (2002).
Jung T., Blaschke H., Neumann P.: Isolation, identification and pathogenicity ofPhytophthora species from declining oak stands.Eur.J.Forest Pathol. 26, 253–272 (1996).
Kolařík M., Kubátová A., Pažoutová S., Šrůtka P.: Morphological and molecular characterization ofG. putterillii, G. pallida comb.nov. andG. flava sp.nov., associated with subcorticolous insects.Mycol.Res. 108, 1053–1069 (2004).
Kubátová A.: NeglectedPenicillium spp. associated with declining trees, pp. 299–307 in R.A. Samson, J.I. Pitt (Eds):Integration of Modern Taxonomic Methods for Penicilliumand AspergillusClassification. Harwood Academic Publishers, Newark (USA) 2000.
Kubátová A., Kolařik M., Prašil K., Novotny D.: Bark beetles and their galleries: well-known niches for little known fungi on the example ofGeosmithia.Czech Mycol. 56, 1–18 (2004).
Leontovyč R., Čapek M.: Eichenwelken in der Slowakei.Österr.Forstz. 98, 51–52 (1987).
Marcu G.: Ursachen des Eichensterbens in Rumänien und Gegenmaßnahmen.Österr.Forstz. 98, 53–54 (1987).
Novotny D., Šrůtka P.:Ophiostoma stenoceras andO. grandicarpum (Ophiostomatales) first records in the Czech Republic.Czech Mycol. 56, 19–32 (2004).
Ogawa H., Yoshimura A., Sugiyama J.: Polyphyletic origins of species of the anamorphic genusGeosmithia and the relationships of the cleistothecial genera: evidence from 18S, 5S and 28S rDNA sequence analyses.Mycologia 89, 756–771 (1997).
Oszako T.: Contribution ofOphiostomatales in oak decline (Q. robur).Proc. Internat. Symp., Kornik (Poland) 1990.
Oszako T.: Relationship between tree vitality and fungal infections, inProc. Internat. Congr. Recent Advances in Studies on Oak Decline (N. Luisi, P. Lerario, A. Vanini, Eds). Brindisi (Italy) 1992.
Peterson S.W.: Phylogenetic analysis ofPenicillium species based on ITS and LSU rDNA nucleotide sequences. pp. 163–178 inIntegration of Modern Taxonomic Methods for Penicilliumand AspergillusClassification (R.A. Samson, J.I. Pitt, Eds). Harwood Academic Publishers, Newark (USA) 2000.
Ragazzi A., Mugnai L., Moricca S., Vagniluca S., Dellavalle I.: Requirements and biological aspects ofFusarium eumartii and its possible role in oak decline in north-eastern Italian oak forests.Eur.J.Forest Pathol. 23, 171–177 (1993).
Riziero T., Ragazzi A., Marianelli L., Sabbatini P., Roversi P.F.: Insects and fungi involved in oak decline in Italy, p. 67 inIOBC/WPRS Bull. 25. Working Group “Integrated Protection in Oak Forests” (Proc Meet. Oeiras) (C. Villemant. E. Sousa, Eds). Lisbon (Portugal) 2002.
Salemink C., Rebel H., Kerling L.C.P., Tchernoff V.: Phytotoxin isolated from liquid cultures ofCeratocystis ulmi.Science 149, 202–203 (1965).
Takai S., Richards W.C.: Cerato-ulmin, a wilting toxin ofCeratocystis ulmi: isolation and some properties of cerato-ulmin from the culture ofC. ulmi.Phytopath.Z. 91, 129–146 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The study was supported by theGrant Agency of the Czech Republic (projects no. 203/00/0219 and 522/02/1206), theInstitutional Research Concept no. AV 0Z 502 0903, and theMinistry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic (MSM 021 620 828).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Čížková, D., Šrůtka, P., Kolařík, M. et al. Assessing the pathogenic effect ofFusarium, Geosmithia andOphiostoma fungi from broad-leaved trees. Folia Microbiol 50, 59–62 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931294
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931294