Abstract
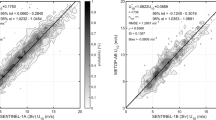
Two wind algorithms of ENVISAT advanced synthetic aperture radar (ASAR), i. e. CMOD4 model from the European Space Agency (ESA) and CMOD_IFR2 model from Quilfen et al., are compared in this paper. The wind direction is estimated from orientation of low and linear signatures in the ASAR imagery. The wind direction has inherently a 1801 ambiguity since only a single ASAR image is used. The 1801 ambiguity is eliminated by using the buoy data from the NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) buoys moored in the Pacific. Wind speed is obtained with the two wind algorithms using both estimated wind direction and normalized radar cross section (NRCS). The retrieved wind results agree well with the data from Quikscat. The root mean square error (RMSE) of wind direction is 2.801. The RMSEs of wind speed from CMOD4 model and CMOD_IFR2 model are 1.09 m/s and 0.60 m/s respectively. The results indicate that the CMOD_IFR2 model is slight better than CMOD4 model at high wind.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpers, W. and B. Brummer, 1994. Atmospheric boundary layer rills observed by the synthetic aperture radar aboard the ERS-1 satellite.J. Geophys. Res. 99(C6): 12 613–12 621.
Bentamy, A., Y. Quilfen, P. Queuffeulou and A. Cavanie, 1994. Calibration of the ERS-1 scatterometer C-band mode. Tech. Rep. RSMAS p. 1:72.
Fetterer, F., D. Gineris and C. S. Wackerman, 1998. Validating a scatterometer wind algorithm for ERS-1 SAR.IEEE Trans. Geophys. Remote Sensing 36(2): 479–492.
Gerling, T. W., 1986. Structure of the surface wind field from the Seasat SAR.J. Geophys. Res. 91(C2): 2 308–2 320.
Johannessen, J. A., P. W. Vachon and O. M. Johannessen, 1994. ERS-1 SAR imaging of marine boundary layer processes. ESA EOQ 46, Eur. Space Agency, p. 1–256, Paris, France.
Quilfen, Y. and A. Bentamy, 1994. Calibration/validation of ERS-1 scatterometer precision products. Proceedings of IGARSS'94. IEEE press, Piscataway, USA, p. 945–947.
Quilfen, Y., B. Chapron, T. Elfouhaily, K. Katsaros and J. Tournadre, 1998. Observation of tropical cyclones by high-resolution scatterometry.J. Geophys. Res. 103(c4): 7 767–7 786.
Stoffelen, A. and D. L. Anderson, 1997. ERS-1 scatterometer data characteristic and wind retrieval skill. Proc. First ERS-1 Symp., Noordwijk. ESA, The Netherlands. p. 1–359.
Valwnzuela, G. R., 1978. Theories for interaction of electromagnetic and oceanic waves: A review.Boundary Layer Meteorol. 13: 61–85.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the High-Tech Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, No. 2001AA633070; 2003AA604040), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40476015).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guiting, S., Yijun, H. & Yijun, H. Comparison of two wind algorithms of ENVISAT ASAR at high wind. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 24, 92–96 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842781
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842781