Abstract
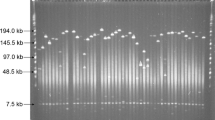
The cultivated sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) is one of the most important oil crops in the world. The importance of sunflower oil in human nutrition and in the chemical industry makes the sunflower a major research interest. An essential element for genomic libraries is the preparation of high molecular weight (HMW) DNA. We developed 2 methods for isolating HMW sunflower DNA. We prepared the DNA from nuclei and from protoplasts isolated from mesophyll tissue with the enzymes cellulase RS and pectolyase Y23. The HMW DNA was digested with restriction endonucleases. The ethidium bromide-stained gel suggested the DNA to be completely digested. These results were confirmed by Southern analysis using a radiolabeled RFLP marker. Both methods made it possible to generate sufficient quantities of megabase-size sunflower DNA suitable for bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) cloning.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAC:
-
bacterial artificial chromosome
- HMW:
-
high molecular weight
- PFGE:
-
pulsed-field gel electrophoresis
- YAC:
-
yeast artificial chromosome
References
Arumuganathan K and Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9: 208–218.
Birren B, Green ED, Klapholz S, Myers RM, Riethman H, and Roskams J (1997) Bacterial Artificial Chromosomes. In: Genome Analysis: A laboratory manual. Vol. 3 Cloning Systems (ed B. Birren et al.), pp.242–295. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Burke DT, Carle GF, and Olson MV (1987) Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science 236: 806–811.
Carle GF, Frank M, and Olson MV (1986) Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science 232: 65–68.
Chu G, Vollrath D, and Davis RW (1986) Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science 234: 1582–1585.
Collins J and Hohn B (1978) Cosmids: a type of plasmid gene-cloning vector that is packageablein vitro in bacteriophage lambda heads. Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA 75: 4242.
Daelen RAJ, Jonkers JJ, and Zabel P (1989) Preparation of megabase-sized tomato DNA and separation of large restriction fragments by field inversion gel electrophoresis (FIGE). Plant Mol Biol 12: 341–342.
Ganal MW and Tanksley SD (1989) Analysis of tomato DNA by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 7: 17–27.
Ganal MW (1996) Isolation and analysis of high-molecular-weight DNA from plants. In: Nonmammalian Genomic Analysis: A Practical Guide. Academic Press Inc. San Diego, 61–73.
Kleine M, Cai D, Hermann RG, and Jung C (1995) Physical mapping and cloning of a translocation in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) carrying a gene for nematode (Heterodera schachtii) resistance fromB procumbens. Theor Appl Genet 90: 399–406.
Martin GB, Ganal MW, and Tanksley SD (1992) Construction of a yeast artificial chromosome library of tomato and identification of cloned segments linked to two disease resistance loci. Mol Gen Genet 233: 25–32.
Mösges G (1994) Molekulargenetische und isoenzymatische Untersuchungen an Sonnenblumen (Helianthus annuus L.) unter dem Aspekt der Markerselektion und Charakterisierung von Linien and Hybriden. Ph.D. Dissertation, Justus-Liebig-Universität Geißen.
Nakamura S, Asakawa S, Ohmido N, Fukui K, Shimizu N, and Kawasaki S (1997) Construction of an 800-Kbp contig in the near-centromeric region of the rice blast resistance genePi-ta 2 using a highly representative rice BAC library. MolGen Genet 254: 611–620.
Schwartz DC and Cantor CR (1984) Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed-field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell 37: 67–75.
Sheng Y, Mancino V, and Birren B (1995) Transformation ofEscherichia coli with large DNA molecules by electroporation. Nucl Acids Res 23: 1990–1996.
Shizuya H, Birren B, Kim UJ, Mancino V, Slepak T, Tachiiri Y, and Simon M (1992) Cloning and stable maintenance of 300-kilobase-pair fragments of human DNA inEscherichia coli using an F-factor-based vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 8794–8797.
Sossey-Alaoui K, Serieys H, Tersac M, Lambert P, and Berville (1996) Phylogenetic relationship of Helianthus species based upon RAPD fragments: Amphiploid origin of the genus. In: Compositae: Biology & Utilization. Proc Intern Comp Conference. Kew. 1994, Calgari PDS & Hind DJN (eds). Vol 2: 9–21.
Timmis JN and Scott NS (1983) Sequence homology between spinach nuclear and chloroplast genomes. Nature 305: 65–67.
Wing RA, Rastogi VK, Zhang HB, Paterson AH, and Tanksley SD (1993) An improved method of plant megabase DNA isolation in agarose microbeads suitable for physical mapping and YAC cloning. Plant J 4: 893–898.
Wing RA, Zhang HB, and Tanskley SD (1994) Map-based cloning in crop plants: Tomato as a model system I. Genetic and Physical mapping ofjointless. Mol Gen Genet 242: 681–688.
Wing RA and Choi S (1997) Cloning and analysis of large DNA molecules. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory manual.
Woo SS, Jiang J, Gill BS, Paterson AH, and Wing RA (1994) Construction and characterisation of a bacterial artificial chromosomes library ofSorghum bicolor. Nucl Acid Res 22: 4922–4931.
Woo SS, Rastogi VK, Zhang HB, Paterson AH, Schertz KF, and Wing R (1995) Isolation of megabase-size DNA fromsorghum sand applications for physical mapping and bacterial and yeast artificial chromosome library construction. Plant Mol Biol Rep 13: 82–94.
Zhang H, Zhao X, Ding X, Paterson AH, and Wing RA (1995) Preparation of megabasesize DNA from plant nuclei. Plant J 7: 175–184.
Zhang HB, Choi S, Woo SS, Li Z, and Wing RA (1996) Construction and characterisation of two rice bacterial artificial chromosome libraries from the parents of a permanent recombinant inbred mapping population. Mol Breeding 2: 11–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özdemir, N., Horn, R. & Friedt, W. Isolation of HMW DNA from sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) for BAC cloning. Plant Mol Biol Rep 20, 239–249 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02782459
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02782459