Abstract
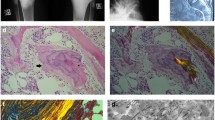
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a rare, heterogeneous, inherited connective tissue disorder frequently caused by abnormalities of type I collagen. It is characterized by bone fragility, osteopenia, and progressive skeletal deformities. Electron microscopy of three OI type II fetal bone samples revealed numerous large osteocyte lacunae. In addition, there was a perilacunar osteoid-like band of collagen surrounding the osteocytes, which was unmineralized and morphologically unusual. Furthermore, large osteocyte lacunae contained fine particles and filamentous material similar to the expected ultrastructural appearance of proteoglycans. More detailed examination was carried out using histochemical and immunogold localization of proteoglycans at light and ultrastructural levels. These tests and the use of electron probe X-ray microanalysis confirmed that the material in the osteocyte lacunae was proteoglycan. In contrast, in the age- and site-matched normal fetal bone, all the osteocyte lacunae appeared negative for proteoglycan. Proteoglycans are regarded as inhibitors of calcification. Our observation of substantial amounts of proteoglycan in abnormally enlarged osteocytic lacunae of some OI fetal bone suggests association with the abnormal bone of this particular subtype of OI type II.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith R (1994) Osteogenesis imperfecta: from phenotype to genotype and back again. Int J Exper Pathol 75:233–241
Rowe DW, Shapiro JR (1990) Osteogenesis imperfecta. In: Avioli LV, Krane SM (eds) Metabolic bone diseases and clinically related disorders. W.B. Saunders Co, Philadelphia, p 659
Sillence DO, Senn A Danks DM (1979) Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet 16:101–116
Sillence DO (1981) Osteogenesis imperfecta: an expanding panorama of variants. Clin Orthop Rel Res 159;11–25
Cole W (1992) Collagen genes: mutations affecting structure and expression. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 47:29–80
Cassella JP, Ali SY (1992) Abnormal collagen and mineral formation in osteogenesis imperfecta. Bone. Miner 17:123–128
Cassella JP, Barber P, Catterall AC, Ali SY (1994) A morphometric analysis of osteoid collagen fibril diameter in osteogenesis imperfecta. Bone 15:329–334
Cassella JP, Pereira R, Khillan JS, Prockop DJ, Garrington N, Ali SY (1994) An ultrastructural, microanalytical, and spectroscopic study of bone from a transgenic mouse with a COL1.A1 Pro-Alpha-1 mutation. Bone 15:611–619
Cassella JP, Garrington N, Stamp TCB, Ali SY (1994) An electron probe X-ray microanalytical study of bone mineral in osteogenesis imperfecta. Calcif Tissue Int 56:118–122
Stoss H, Freisinger P (1990) The collagen fibrils of the osteoid in osteogenesis imperfecta: morphometric analysis of the fibril diameter. IV Intl Conf Osteogenesis Imperfecta, p 1236
Bleckmaan H, Kresse H, Wollensak J, Buddecke E (1972) Glykosaminoglykan und kollagenanalysen bei Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Z Kinderhelik 110:74–84
Engfeldt B, Hjerpe A (1976) Glycosaminoglycans of cartilage and bone tissue in two cases of osteogenesis imperfecta congenita. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Sect. A84:488–494
Brown DM, Sauk JJ, Corbin KW, Witkop CJ (1975) Glycosaminoglycans (GAG) of EDTA soluble and insoluble soluble dentin in autosomal dominant osteogenesis imperfecta. Pediatr Res 9:312
Spencer AL (1962) Histochemical study of long bones in osteogenesis imperfecta congenita. J Pathol Bacteriol 83:423–427
Blumenthal NC, Posner AS, Silverman LD, Rosenburg LC (1979) Effect of proteoglycan on in vitro hydroxyapatite formation. Calcif Tissue Int 27:75–82
Ali SY (1992) Matrix formation and mineralisation in bone. In: Whitehead CC (ed) Bone biology and skeletal disorders. Carfax Pub Co., Abingdon, UK, p 19–38
Posner AS, Betts F, Blumenthal NC (1978) Properties of nucleating systems. Metab Bone Dis Rel Res 1:179–183
Richardson KC, Jarett L, Finke EH (1960) Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol 35:313–323
Humphrey CD, Pittman FE (1974) A simple methylene blueazure II- basic fuchsin stain for epoxy-embedded tissue sections. Stain Technol 42:9–14
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 71:208–212
Bancroft JD, Stevens A (eds) (1990) Theory and practice of histological techniques, 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone. Edinburgh, UK
Roth J, Bendayan M, Orci L (1978) Ultrastructural localization of intracellular antigens by the use of protein A-gold complex. J Histochem Cytochem 26:1074–1081
Couchman JR, Caterson B, Christner JE, Barker JR (1984) Mapping by monoclonal antibody detection of glycosaminoglycans in connective tissue. Nature 307:650
Flavo KA, Bullough PG (1973) Osteogenesis imperfecta: a histometric analysis. J Bone Joint Surg 55A:275–286
Currey JD (1984) Effects of differences in mineralisation on the mechanical properties of bone. Philos Trans R Soc Lond [Biol] 304:509–518
Usui Y, Kawai K, Hirohata K (1989) An electron microscopic study of the changes observed in osteocytes under ischemic conditions. J Orthop Res 7:12–21
Solheim K (1969) Osteogenesis imperfecta: micrographic and biochemical studies with special reference, to the mucopolysaccharides (glycosaminoglycans). J Oslo City Hosp 19:193–199
Goldberg H (1978) A study of the urinary mucopolysaccharides in osteogenesis imperfecta and other skeletal disorders. M. Phil thesis, University of London, UK
Bosse A, Schwarz K, Vollmer E, Kresse H (1993) Divergent and co-localization of the two small proteoglycans decorin and proteoglycan-100 in human skeletal tissues and tumours. J Histochem Cytochem 41:13–19
Bianco P, Fisher LW, Young MF, Termine JD (1990) Expression and localization of the two small proteoglycans biglycan and decorin in developing skeletal and nonskeletal tissue. J Histochem Cytochem 38:1549–1559
Takagi M, Maeno M, Kagami A, Takahashi Y, Otsuka K (1991) Biochemical and immunocytochemical characterization of mineral-binding proteoglycans in rat bone. J Histochem Cytochem 39:41–50
Fisher LW (1985) The nature of proteoglycans in bone. In: Butler TW (ed) The chemistry and biology of mineralised tissue. EBSCO Media Inc, Birmingham, AL, pp 188–196
Sauren YMHF, Mieremet RHP, Groot CG, Scherft JP (1992) An electron microscopic study on the presence of proteoglycans in the mineralised matrix of rat and human compact lamellar bone. Anat Red 232:36–44
Sauren YMHF, Mieremet RHP, Groot CG, Scherft JP (1989) An electron microscopical study on the presence of proteoglycans in the calcified bone matrix by the use of cuprolinic blue. Bone 10:287–294
Vetter U, Fisher LW, Mintz KP, Kopp JB, Tuross N, Termine JD, Gehron Robey P (1991) Ostogenesis imperfecta: changes in noncollagenous proteins in bone. J Bone Miner Res 6:501–505
Fedarko NS, Moerike M, Brenner R, Gehron Robey P, Vetter U (1992) Extracellular matrix formation by osteoblasts from patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Bone Miner 7:921–930
Sillence DO, Barlow KK, Garber AP, Hall JG, Rimoin DL (1984) Osteogenesis imperfecta type II. Delineation of the phenotype with reference to genetic heterogeneity. Am J Med Genet 17:407–423
Fedarko NS, Gehron Robey P, Vetter U (1995) Extracellular matrix stoichiometry in osteoblasts from patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Bone and Miner Res 10:1122–1129
Bowness JM, Lee KH (1966) Effects of chondroitin sulphates on mineralisation in vitro. Biochem J 103:382–390
Cuervo LA, Pita JC, Howell DS (1973) Inhibition of calcium phosphate mineral growth by proteoglycan aggregate fractions in synthetic lymph. Calcif Tissue Res 13:1–10
Chung CC, Boskey AL (1985) Mechanisms of proteoglycan inhibition of hydroxyapatite growth. Calcif Tissue Int 37:395–400
Dopping-Hepenstal PJC, Ali SY, Stamp TCB (1981) Matrix vesicles in the osteoid of human bone. In: Acenzi A, Bonucci E, Bernard B (eds) Matrix vesicles. Proc 3rd Int Conf matrix vesicles. Wichtig Editore, srl. Milano, pp 229–234
Ralphs JR, Stamp TCB, Dopping-Hepenstal P, Ali SY (1985) Ultrastructural features of osteoid of patients with fibrogenesis imperfecta ossium. Bone 10:243–249
Ali SY (1983) Calcification of cartilage. In: Hall BK (ed) Cartilage, vol 1, structure, function, and biochemistry. Academic Press, London, UK, p 343–378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarathchandra, P., Michael Pope, F. & Yousuf Ali, S. An ultrastructural and immunogold localization study of proteoglycans associated with the osteocytes of fetal bone in osteogenesis imperfecta. Calcif Tissue Int 58, 435–442 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02509444
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02509444