Abstract
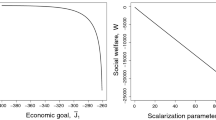
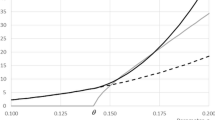
It is often claimed that there is a trade-off between economic goals and the quality of the environment. For this reason, an environmental input-output optimization model with multiple objectives is formulated. The criteria are the minimization of factor costs to produce the Gross National Product and the minimization of net pollution for a given level of final demand. Using the LeChatelier-Samuelson principle, we analyze the changes in the production of the sectors and in the prices of the goods (described by the dual model) due to the change in the preferences of the decision makers. It can be shown that higher weights for the environmental objectives imply — in tendency —non-decreasing production of the sectors andnon-decreasing abatement activities. The changes of prices are ambiguous. The condition for increasing prices is given. To some degree, the opposite results can be achieved, if maximization of the value of final demand (or of private consumption) and minimization of net pollution under the constraints for primary input are taken as objective functions. In this case, increasing weights for environmental goals will leadin tendency tonon-increasing final demand and tonon-increasing net pollution. Under given conditions, higher environmental quality will be achieved bynon-increasing gross production and abatement activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Leontief, Environmental repercussions and the economic structure: An input-output approach, Rev. Econ. Statist. 52(1970)262–271.
P.D. Lowe, Pricing problems in an input-output approach to environment protection, Rev. Econ. Statist. 56(1979)110–117.
M. Luptáčik and B. Böhm, A reconsideration of non-negative solutions for the augmented Leontief model, Research Report, Institute of Econometrics, Operations Research and Systems Theory, University of Technology, Vienna (1993).
R.E. Miller and P.D. Blair,Input-Output Analysis: Foundations and Extension (Prentice-Hall, 1985).
K. Miyazawa, Foreign trade multipler, input-output analysis, and the consumption function, Quart. J. Econ. 74(1960)53–64.
Y. Murata,Mathematics for Stability and Optimization of Economic Systems (Academic Press, New York/San Francisco/London, 1977).
J.J. Rhee and J.A. Miranowski, Determination of income, production, and employment under pollution control: An input-output approach, Rev. Econ. Statist. 66(1984)146–150.
Umweltbundesamt,Umwelt in Österreich (1991).
W. Wolfsberger, Quotation from: Die Presse, 2. Sept. 1983, p. 16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luptáčik, M., Böhm, B. An environmental input-output model with multiple criteria. Ann Oper Res 54, 119–127 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02031730
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02031730