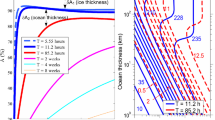
Abstract
In reviewing seafloor induction studies conducted over the last seven years, we observe a decline in single-station magnetotelluric (MT) experiments in favour of large, multinational, array experiments with a strong oceanographic component. However, better instrumentation, processing techniques and interpretational tools are improving the quality of MT experiments in spite of the physical limitations of the band limited seafloor environment, and oceanographic array deployments are allowing geomagnetic depth sounding studies to be conducted. Oceanographic objectives are met by the sensitivity of the horizontal electric field to vertically averaged motional currents, providing the same information, at much greater reliability and much lower cost, as an array of continuously operating current meter moorings.
The seafloor controlled source method has now become, if not routine, at least viable. Prior to 1982, only one seafloor controlled source experiment has been conducted; now at least three groups are involved in the experimental aspects of this field. The horizontal dipole-dipole configuration is favoured, although a variant of the magnetometric resistivity method utilising a vertical electric transmitter has been developed and deployed. By exploiting the characteristics of the seafloor environment, source receiver spacings unimaginable on land can be achieved; on a recent deployment dipole spacings of 90 km were used with a clear 24 Hz signal transmitted through the seafloor. This, and prior experiments, show that the oceanic upper mantle is characteristically very resistive, 105 Ω m at least. This resistive zone is becoming apparent from other experiments as well, such as studies of the MT response in coastal areas on land.
Mid-ocean ridge environments are likely to be the target of many future electromagnetic studies. By taking available laboratory data on mineral, melt and water conductivity we predict to first order the kinds of structures the EM method will help us explore.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahr, K. and Filloux, J. H.: 1989, ‘Local Sq Response Functions from EMSLAB data’,J. Geophys. Res. 94, 14195–14200.
Baines, P. G. and Bell, R. C.: 1987, ‘The Relationship between Ocean Current Transports and Electric Potential Differences across the Tasman Sea, Measured Using an Ocean Cable’,Deep-Sea Res. 34, 531–546.
Becker, K. and 13 others.: 1982, ‘In situ Electrical Resistivity and Bulk Porosity of the Oceanic Crust Costa Rica Rift’,Nature 300, 594–598.
Berdichevsky, M. N., Zhdanova, O. N., and Yakovlev, A. G.: 1984, ‘Anomalous Electromagnetic Fields and Electromagnetic Sounding on the Bottom of the Ocean’,Geomag. Aeronomy 24, 542–547.
Bindoff, N. L., Filloux, J. H., Mulhearn, P. J., Lilley, F. E. M., and Ferguson, I. J.: 1986, ‘Vertical Electric Field Fluctuations at the Floor of the Tasman Abyssal Plain’,Deep-Sea Res. 33, 587–600.
Caress, D. W.: 1989,Some Aspects of the Structure and Evolution of Oceanic Spreading Centers, Unpublished Thesis, Univ. Calif., San Diego.
Chan, E., Dosso, H. W., Law, L. K., Auld, D. R., Nienaber, W.: 1983, ‘Electromagnetic Induction in the Queen Charlotte Islands Region: Analogue Model and Field Station Results’,J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 35, 501–516.
Chave, A. D.: 1983a, ‘Numerical Integration of Related Hankel Transforms by Quadrature and Continued Fraction Expansion’,Geophysics 48, 1671–1686.
Chave, A. D.: 1983b, ‘On the Theory of Electromagnetic Induction in the Earth by Ocean Currents’,J. Geophys. Res. 88, 3531–3542.
Chave, A. D. and Cox, C. S.: 1982, ‘Controlled Electromagnetic Sources for Measuring Electrical Conductivity Beneath the Oceans, 1, Forward Problem and Model Study’,J. Geophys. Res. 87, 5327–5338.
Chave, A. D. and Cox, C. S.: 1983, ‘Electromagnetic Induction by Ocean Currents and the Conductivity of the Oceanic Lithosphere’,J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 35, 491–499.
Chave, A. D. and Filloux, J. H.: 1984, ‘Electromagnetic Induction Fields in the Deep Ocean off California: Oceanic and Ionospheric Sources’,Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 77, 143–171.
Chave, A. D., Filloux, J. H., Luther, D. S., Law, L. K., and White, A.: 1989, ‘Observations of Motional Electromagnetic Fields During EMSLAB’,J. Geophys. Res. 94, 14153–14166.
Chave, A. D., Constable, S. C., and Edwards, R. N.: 1990, ‘Electrical Exploration Methods for the Seafloor’, in Nabighian M. N. (ed.), SEGElectromagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics, (in press).
Chave, A. D. Filloux, J. H. and Luther, D. S.: 1989, ‘Electromagnetic Induction by Ocean Currents: BEMPEX’,Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 53, 350–359.
Cheesman, S. R., Edwards, R. N., and Chave, A. D.: 1987, ‘On the Theory of Sea-Floor Conductivity Mapping Using Transient Electromagnetic Systems’,Geophysics 52, 204–217.
Cheesman S. J., Edwards, R. N., and Law, L. K.: 1988, ‘First Results of a New Short Baseline Sea Floor Transient EM System’, Presented at the 58th Ann. Int. Mtg., Soc. Explor. Geophys. in Anaheim, U.S.A.
Chen, J., Dosso, H. W., and Nienaber, W.: 1989, ‘Laboratory Electromagnetic Model Results for the EMSLAB Region’,J. Geophys. Res. 94, 14167–14172.
Constable, S. C.: 1990, ‘Electrical Studies of the Australian Lithosphere’, in Drummond, B. J. (ed.),The Australian Lithosphere, Geol. Soc. Aust. Spec. Pub. (in press).
Constable, S. C., Cox. C. S., and Chave, A. D.: 1986, ‘Offshore Electromagnetic Surveying Techniques’, Soc Explor. Geophys. 56th Ann. Internat Mtg. Extended Abstracts, pp. 81–82.
Constable, S. C. and Duba, A.: 1990, ‘The Electrical Conductivity of Olivine, a Dunite and the Mantle’,J. Geophys. Res. (in press).
Cox, C. S.: 1980, ‘Electromagnetic Induction in the Oceans and Inferences on the Constitution of the Earth’,Geophys. Surv. 4, 137–156.
Cox, C. S., Filloux, J. H., and Larsen, J.: 1971, ‘Electromagnetic Studies of Ocean Currents and Electrical Conductivity Below the Ocean Floor’, in Maxwell (ed.),The Sea, Vol. 4 Part 1, Wiley, pp. 637–693.
Cox, C. S., Filloux, J. H., Gough, D. I., Larsen, J. C., Poehls, K. A., von Herzen, R. P., and Winter, R.: 1980, ‘Atlantic Lithospheric Sounding’, in U. Schmucker, (ed.),Electromagnetic Induction in the Earth and Moon, Centr. Acad Publ. Japan. Tokyo and Kluwer Acad. Publ. Dordrecht, pp. 13–32.
Cox, C. S., Constable, S. C., Chave, A. D., and Webb, S. C.: 1986, ‘Controlled Source Electromagnetic Sounding of the Oceanic Lithosphere’,Nature 320, 52–54.
DeLaurier, J. M., Auld, D. R., and Law, L. K.: 1983, ‘The Geomagnetic Response across the Continental Margin off Vancouver Island: Comparison of Results from Numerical Modelling and Field Data’,J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 35, 517–528.
Detrick, R. S., Buhl, P., Vera, E., Mutter, J., Orcutt, J., Madsen, J., and Brocher, T.: 1987, ‘Multi-Channel Seismic Imaging of a Crustal Magma Chamber Along the East Pacific Rise’,Nature 326, 35–41.
Dosso, H. W., Nienaber, W., and Parkinson, W. D.: 1985, ‘An Analogue Model Study of Electromagnetic Induction in the Tasmanian Region’,Phys. Earth. Planet. Inter. 39, 118–133.
Dosso, H. W., Chan, G. H. and Nienaber, W.: 1986, ‘An Analogue Model Study of EM Induction for an Island near Bay and Cape Coastlines’,Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 42, 178–183.
Dosso, H. W. and Nienaber, W.: 1986, ‘A Laboratory Electromagnetic Model Study of the Juan de Fuca Plate Region’,Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 43, 34–46.
Duba, A., Heard, H. C., and Schock, R. N.: 1974, ‘Electrical Conductivity of Olivine at High Pressure and Under Controlled Oxygen Fugacity’,J. Geophys. Res. 79, 1667–1673.
Edwards, R. N.: 1974, ‘The Magnetometric Resistivity (MMR) Method and its Application to the Mapping of a Fault’,Can. J. Earth Sci. 11, 1136–1156.
Edwards, R. N.: 1988a, ‘A Downhole Magnetometric Resistivity Technique for Electrical Sounding Beneath a Conductive Surface Layer’,Geophysics 53, 528–536.
Edwards, R. N.: 1988b, ‘Two-Dimensional Modeling of a Towed in-Line Electric Dipole-Dipole Sea Floor Electromagnetic System: The Optimum Time Delay or Frequency for Target Resolution’,Geophysics 53, 528–536.
Edwards, R. N., Law, L. K., DeLaurier, J. N.: 1981, ‘On Measuring the Electrical Conductivity of the Oceanic Crust by a Modified Magnetometric Resistivity Method’,J. Geophys. Res. 86, 11609–11615.
Edwards, R. N., Nobes, D. C. and Gómez-Treviño, E.: 1984, ‘Offshore Electrical Exploration of Sedimentary Basins: The Effects of Anisotropy in Horizontally Isotropic, Layered Media’,Geophysics 49, 566–576.
Edwards, R. N., Law, L. K., Wolfgram, P. A., Nobes, D. C., Bone, M. N., Trigg, D. F., and DeLaurier, J. M.: 1985, ‘First Results of the MOSES Experiment: Sea Sediment Conductivity and Thickness Determination, Bute Inlet, British Columbia, by Magnetometric Offshore Electrical Sounding’,Geophysics 50, 153–160.
Edwards, R. N. and Chave, A. D.: 1986, ‘A Transient Electric Dipole-Dipole Method for Mapping the Conductivity of the Sea Floor’,Geophysics 51, 984–987.
Edwards, R. N and Cheesman, S. J.: 1987, ‘Two-Dimensional Modelling of a Towed Transient Magnetic Dipole-Dipole Sea Floor EM System’,J. Geophys. 61, 110–121.
Edwards, R. N., Wolfgram, P. A., and Judge, M. N.: 1988, ‘The ICE-MOSES Experiment: Mapping Permafrost Zones Electrically Beneath the Beaufort Sea’,Mar. Geophys. Res. 9, 265–290.
EMSLAB Group.: 1988, ‘The EMSLAB Electromagnetic Sounding Experiment’,EOS 69, 89, 98–99.
Everett, M. E. and Edwards, R. N.: 1989, ‘Electromagnetic Expression of Axial Magma Chambers’,Geophys. Res. Lett. 16, 1003–1006.
Ferguson, I. J., Filloux, J. H., Lilley, F. E. M., Bindoff, N. L., and Mulhearn, P. J.: 1985, ‘A Seafloor Magnetotelluric Sounding in the Tasman Sea’,Geophys. Res. Lett. 12, 545–548.
Filloux, J. H.: 1979, ‘Magnetotelluric and Related Electromagnetic Investigations in Geophysics’,Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 17, 282–294.
Filloux, J. H.: 1987, ‘Instrumentation and Experimental Methods for Oceanic Studies’, in J. A. Jacobs, (ed.),Geomagnetism, Academic Press, pp. 143–248.
Filloux, J. H. and Tarits, P.: 1986, ‘Pacific Rise: Electrical Conductivity Anomaly at Ridge Crust and Implications on Structure (abstract)’,EOS 67, 919.
Filloux, J. H., Law, L. K., Yukutake, T., Segawa, J., Hamao, Y., Utada, H., White, A., Chave, A., Tarits, P., and Green, A. W.: 1989, ‘OFFSHORE EMSLAB: Objectives, Experimental Phase and Early Results’,Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 53, 422–431.
Fischer, G. and Weaver, J. T.: 1986, ‘Theoretical Investigations of the Ocean-Coast Effect at a Passive Continental Margin’,Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 42, 246–254.
Flosadottir, A. H. and Cox, C. S.: 1989, ‘Modeling of the Electromagnetic Controlled Source Response of Two Dimensional Mid-Ocean Ridge Structures (abstract)’,EOS 70, 1074.
Fonarev, G. A.: 1982, ‘Electromagnetic Research in the Ocean’,Geophys. Surv. 4, 501–508.
Francis, T. J. G.: 1985, ‘Resistivity Measurements of an Ocean Floor Sulphide Mineral Deposit from the Submersible Cyana’,Marine Geophys. Res. 7, 419–438.
Hamano, Y., Segawa, J., Law, L. K., White, A., Heinson, G., Utada, H., and Yukutake, Y.: 1989, ‘An Electromagnetic Sounding Across the Juan de Fuca Ridge (EMRIDGE)’, Contributed paper presented at 6th assembly of IAGA in Exeter, U.K.
Harding, A. J., Orcutt, J. A., Kappus, M. E., Vera, E. E., Mutter, J. C., Buhl, P., Detrick, R. S., and Brocher, T. M.: 1989, ‘Structure of Young Oceanic Crust at 13° N on the East Pacific Rise from Expanding Spread Profiles’,J. Geophys. Res. 94, 12163–12196.
Herbert, D., Dosso, H. W., and Nienaber, W.: 1983, ‘Analogue Model Study of Electromagnetic Induction in the Newfoundland Region’,Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 32, 65–84.
Herbert, D., Wright, J. A., Dosso, H. W., and Nienaber, W.: 1983, ‘Comparison of Analogue Model and Field Station Results for the Newfoundland Region’,J. Geomagn. Geoelectr.,35, 673–682.
Hu, W. B., Dosso, H. W., and Nienaber, W.: 1984, ‘Analogue-Model Magnetic Field Responses of an Ocean Channel, an Island and a Seamount in the Hainan Island Region’,J. Geophys. 55, 222–227.
Kellett, R. L., White, A., Ferguson, I. J., and Lilley, F. E. M.: 1988a, Geomagnetic Fluctuation Anomalies Across the Southeast Australian Coast’,Explor. Geophys. 19, 294–297.
Kellett, R. L., I. J. Ferguson, and Lilley, F. E. M.: 1988b, ‘Magnetic Field Fluctuations at the Eyrewell Observatory, Christchurch, New Zealand’,New Zealand J. Geol. Geophys. 31, 87–93.
Kendall, P. C. and Quinney, D. A.: 1983, ‘Induction in the Oceans’,Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 74, 239–255.
Koizumi, K., Segawa, J., Toh, H., Oubina Carretero, J. L., and Tanaka, Y.: 1989, ‘Simultaneous Magnetic Measurements and their Comparison at the Sea Floor Using a Fluxgate Vector Magnetometer and a Proton Scalar Magnetometer’,J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 41, 491–506.
Korotayev, S. M., Trofimov, I. L., Zhdanov, M. S., Shabelyanskiy, S. V., Lapitskiy, A. I., Abroamov, Yu. M., and Gaydash, S. P.: 1985, ‘Electromagnetic Investigations in the Southwest Portion of the Black Sea’,Geomag. Aeronomy 25, 228–232.
Korotayev, S. M., Kutkin, V. V., and Lapitsky, A. I.: 1986, ‘Investigation of the Filtration Anomaly of Natural Electric Field in the Western Part of the Black Sea’,Ann. Geophys. 4, 639–644.
Kurtz, R. D., DeLaurier, J. M., and Gupta, J. C.: 1986, ‘A Magnetotelluric Sounding Across Vancouver Island Sees the Subducting Juan de Fuca Plate’,Nature 321, 596–599.
Larsen, J. C. and Sanford, T. B.: 1985, ‘Florida Current Volume Transports from Voltage Measurements’,Science 227, 302–304.
Law, L. K.: 1983, ‘Marine Electromagnetic Research’,Geophys. Surv. 6, 123–135.
Lilley, F. E. M., Filloux, J. H., Bindoff, N. L., Ferguson, I. J., and Mulhearn, P. J.: 1986, ‘Barotropic Flow of a Warm-Core Ring from Seafloor Electric Measurements’,J. Geophys. Res. 91, 979–984.
Lilley, F. E. M., Filloux, J. H., Ferguson, I. J., Bindoff, N. L. and Mulhearn, P. J.: 1989, ‘The Tasman Project of Seafloor Magnetotelluric Exploration: Experiment and Observations’,Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 53, 405–421.
Luther, D. S., Chave, A. D. and Filloux, J. H.: 1987, ‘BEMPEX: A Study of Barotropic Ocean Currents and Lithospheric Conductivity’,EOS 68, 618–619, 628–629.
Mackie, R. L., Bennett, B. R., and Madden, T. R.: 1988, ‘Long-Period Magnetotelluric Measurements Near the Central California Coast: A Land-Locked View of the Conductivity Structure Under the Pacific Ocean’,Geophys J. 95, 181–194.
Mulhearn, P. J., Filloux, J. H., Lilley, F. E. M., Bindoff, N. L., and Ferguson, I. J.: 1986, ‘Abyssal Currents During the Formation and Passage of a Warm-Core Ring in the East Australian Current’,Deep-Sea Res. 33, 1563–1576.
Neumann, G. A. and Hermance, J. F.: 1985, ‘The Geomagnetic Coast Effect in the Pacific Northwest of North America’,Geophys. Res. Lett. 12, 502–505.
Niblett, E. R., Kurtz, R. D., and Michaud, C.: 1987, ‘Magnetotelluric Measurements over the Alpha Ridge’,Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 45, 101–118.
Oldenburg, D. W.: 1981, ‘Conductivity Structure of Oceanic Upper Mantle Beneath the Pacific Plate’,Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 65, 359–394.
Oldenburg, D. W., Whittall, K. P., and Parker, R. L.: 1984, ‘Inversion of Ocean Bottom Magnetotelluric Data Revisisted’,J. Geophys. Res. 89, 1829–1833.
Quist, A. S. and Marshall, W. L.: 1968, ‘Electrical Conductances of Aqueous Sodium Chloride Solutions from 0 to 800° and at Pressures to 4000 Bars’,J. Phys. Chem. 71, 684–703.
Sanford, T.: 1982, ‘Temperature Transport and Motional Induction in the Florida Current’,J. Mar. Res. 40 (suppl), 621–639.
Sato, H., Sacks, I. S., and Murase, T.: 1989, ‘The Use of Laboratory Velocity Data for Estimating Temperature and Partial Melt Fraction in the Low-Velocity Zone: Comparison with Heat Flow and Electrical Conductivity Studies’,J. Geophys. Res. 94, 5689–5704.
Schock, R. N., Duba, A., and Shankland, T. J.: 1989, ‘Electrical Conduction in Olivine’,J. Geophys. Res. 94, 5829–5839.
Segawa, J., Yukutake, T., Hamano, Y., Kasuga, T., and Utada, H.: 1982, ‘Sea Floor Measurements of the Geomagnetic Field Using Newly Developed Ocean Bottom Magnetometers’,J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 34, 571–585.
Segawa, J., Hamano, Y., Yukutake, T., Utada, H., and Tou, H.: 1986, ‘A Sea Floor Magnetometer Model OBM-S4’,J. Geodetic Soc. Japan,32, 248–273.
Shankland, T. J. and Waff, H. S.: 1977, ‘Partial Melting and Electrical Conductivity Anomalies in the Upper Mantle’,J. Geophys. Res. 82, 5409–5417.
Singer, B. S., Kuvshinov, A. V., and Fainberg, E. B.: 1985,Electrical Induction in the Spherical Earth, Covering the Inhomogeneous Oceans and in Contact with a Stratified Section, Inst. Terrestrial Magnetism, Ionosphere and Radio Wave Propagation, preprint No. 46.
Sleep, N. H.: 1978, ‘Thermal Structure and Kinematics of Mid-Oceanic Ridge Axis, Some Complications to Basaltic Volcanism’,Geophys. Res. Lett. 5, 426–428.
Spain, P, and Sanford, T. B.: 1987, ‘Accurately Monitoring the Florida Current with Motionally Induced Voltages’,J. Mar. Res. 45, 843–870.
Tyburczy, J. A. and Waff, H. S.: 1983, ‘Electrical Conductivity of Molten Basalt and Andesite to 25 kilobars Pressure: Geophysical Significance and Implications for Charge Transport and Melt Structure’,J. Geophys. Res. 88, 2413–2430.
Waff, H. S. and Weill, D. F.: 1985, ‘Electrical Conductivity of Magmatic Liquids: Effects of Temperature, Oxygen Fugacity and Composition’,Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 28, 254–260.
Wannamaker, P. E. and 14 others: 1989a, ‘Magnetotelluric Observations across the Juan de Fuca Subduction System in the EMSLAB Project’,J. Geophys. Res. 94, 14111–14125.
Wannamaker, P. E., Booker, J. R., Jones, A. G., Chave, A. D., Filloux, J. H., Waff, H. S., and Law, L. K.: 1989b, ‘Resistivity Cross Section Through the Juan de Fuca Subduction System and its Tectonic Implications’,J. Geophys. Res. 94, 14127–14144.
Webb, S. C. and Cox, C. S.: 1982, ‘Electromagnetic Fields Induced at the Seafloor by Rayleigh-Stoneley Waves’,J. Geophys. Res. 87, 4093–4102.
Webb, S. C. and Cox, C. S.: 1984, ‘Presure and Electric Fluctuations on the Deep Sea Floor: Background Noise for Seismic Detection’,Geophys. Res. Lett. 11, 967–970.
Webb, S. C., Constable, S. C., Cox, C. S., and Deaton, T.: 1985, ‘A Seafloor Electric Field Instrument’,J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 37, 1115–1130.
Webb, S. C. and Cox, C. S.: 1986, ‘Observations and Modeling of Seafloor Microseisms’,J. Geophys. Res. 91, 7343–7358.
Webb, S. C. and Constable, S. C.: 1986, ‘Microseism Propagation Between Two Sites on the Deep Seafloor’,Bull. Seis. Soc. Am. 76, 1433–1445.
Winch, D. E.: 1989, ‘Induction in a Model Ocean’,Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 53, 328–336.
Wolfgram, P. A., Edwards, R. N., Law, L. K., and Bone, M. N.: 1986, ‘Polymetallic Sulphide Exploration on the Deep Sea Floor: The Feasibility of the MINI-MOSES Experiment’,Geophysics 51, 1808–1818.
Wynn, J. C.: 1988, ‘Titanium Geophysics: The Application of Induced Polarization to Sea-Floor Mineral Exploration’,Geophysics 53, 386–401.
Young, P. D. and Cox, C. S.: 1981, ‘Electromagnetic Active Source Sounding near the East Pacific Rise’,Geophys. Res. Lett. 8, 1043–1046.
Yukutake, T., Filloux, J. H., Segawa, J., Hamano, Y., and Utada, H.: 1983, ‘Preliminary Report on a Magnetotelluric Array Study in the Northwest Pacific’,J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 35, 575–587.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Constable, S.C. Marine electromagnetic induction studies. Surv Geophys 11, 303–327 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01901663
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01901663