Summary
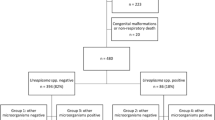
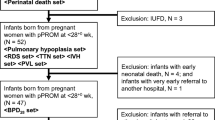
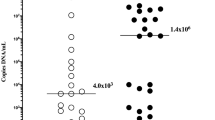
The effects ofUreaplasma urealyticum colonization on pregnancy and neonatal outcome was prospectively studied in women with impending term or preterm delivery. One hundred and seventy women colonized withU. urealyticum as the only pathogenic microorganism and 83 women with negative cultures were enrolled for study. Compared to the controls,U. urealyticum colonization was associated with a significantly increased rate of amnionitis (2% vs 35%; p<0.001), chorioamnionitis (0% vs 10%; p<0.05), premature rupture of membranes (12% vs 35%; p<0.001) and preterm delivery (10% vs 41%; p<0.001). The rate of vertical transmission ranged from 38% in term infants to 95% in very low birth weight infants.U. urealyticum colonization at birth was associated with an increased risk for the development of respiratory distress syndrome (9% vs 51%), intraventricular hemorrhage (1% vs 7%) and bronchopulmonary dysplasia (4% vs 17%) in very low birth weight infants (<1500 g). It is concluded that maternalU. urealyticum colonization is associated with amnionitis, chorioamnionitis and preterm delivery, and that tracheal colonization withU. urealyticum increases the risk for respiratory and neurological complications in very low birth weight infants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cassell, G. H., Waites, K. B., Taylor-Robinson, D. Genital mycoplasmas. In:Morse, S. A., Moreland, A. A., Thompson, S. E. (eds.): Atlas of sexually transmitted diseases. Lippincott, Philadelphia, Gower, New York, London 1990, pp. 7.2–7.15.
Hillier, S. L., Martius, J., Krohn, M., Kiviat, M., Holmes, K. K., Eschenbach, D. A. A case-control study of chorioamniotic infection and histologic chorioamnionitis in prematurity. N. Engl. J. Med. 19 (1988) 972–978.
Lamont, R. F., Taylor-Robinson, D., Wigglesworth, J. S., Furr, P. M., Evans, R. T., Elder, M. G. The role of mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas and chlamydiae in the genital tract of women presenting in spontaneous early preterm labour. J. Med. Microbiol. 24 (1987) 253–257.
Sanchez, P. J., Regan, J. A. Vertical transmission ofUreaplasma urealyticum from mothers to preterm infants. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 9 (1990) 398–401.
Sanchez, P. J., Regan, J. A. Vertical transmission ofUreaplasma urealyticum in full term infants. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 6 (1987) 825–828.
Brus, F., van Waarde, W. M., Schoots, C., Bambang Oetomo, S. Fatal ureaplasmal pneumonia and sepsis in a newborn infant. Eur. J. Pediatr. 150 (1991) 782–783.
Waites, K. B., Crouse, D. T., Phillips, J. B. III, Canupp, K. C., Cassell, G. H. Ureaplasma pneumonia and sepsis associated with persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Pediatrics 83 (1989) 79–85.
Waites, K. B., Rudd, P. T., Crouse, D. T., Canupp, K. C., Nelson, K. G., Ramsey, C. ChronicUreaplasma urealyticum andMycoplasma hominis infections of central nervous system in preterm infants. Lancet i (1988) 17–21.
Cassell, G. H., Waites, K. B., Crouse, D. T., Rudd, P. T., Canupp, K. C., Stagno, S., Cutter, G. R. Association ofUreaplasma urealyticum infection of the lower respiratory tract with chronic lung disease and death in very low birth weight infants. Lancet ii (1988) 240–245.
Wang, E. E. L., Ohlsson, A., Kellner, J. D. Association ofUreaplasma urealyticum colonization with chronic lung disease of prematurity: results of a metaanalysis. J. Paediatr. 127 (1995) 640–644.
Abele-Horn, M., Hentschel, J. Ureaplasma urealyticum bei Neuund Frühgeborenen: Assoziation mit der bronchopulmonalen Pneumonie. Dtsch. med. Wochenschr. 117 (1992) 408–414.
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Hygiene und Mikrobiologie Isolierung und Identifizierung von Mycoplasmen und Chlamydien. Zentralbl. Bakt. Hyg. A 270 (1989) 470–486.
Ballard, J. L., Novak, K. K., Doriver, M. A simplified score for assessment of fetal maturation of newly born infants. J. Pediatr. 95 (1979) 769–774.
Northway, W. H., Rosan, R. C., Porter, D. Y. Pulmonary disease following respiratory therapy of hyaline membrane disease: bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 276 (1967) 357–368.
Kundsin, R. B., Driscoll, S. G., Monson, R. R., Yeh, C., Biano, S. A., Cochran, W. Y. Association ofUreaplasma urealyticum in the placenta with perinatal morbidity and mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 310 (1984) 941–945.
Embree, J. E., Krause, V. W., Embil, J. A., MacDonald, S. Placental infection withMycoplasma hominis undUreaplasma urealyticum: clinical correlation. Obstet. Gynecol. 56 (1980) 475–481.
Foulon, W., Naessens, A., Dewaele, M., Lauwers, S., Amy, J. J. ChronicUreaplasma urealyticum amnionitis associated withabruptio placentae. Obstet. Gynecol. 68 (1986) 280–282.
Cassell, G. H., Waites, K. B., Watson, H. L., Crouse, D. T., Harasawa, R. Ureaplasma urealyticum intrauterine infection: role in prematurity and disease in newborns. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 6 (1993) 69–87.
Naessens, A., Foulon, W., Cammu, H., Goosens, A., Lauwers, S. Epidemiology and pathogenesis ofUreaplasma urealyticum in spontaneous abortion and early preterm labor. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 66 (1987) 513–516.
Ollikainen, J., Hiekkaniemi, H., Korppi, M., Sarkkinen, H., Heinonen, K. Ureaplasma urealyticum infection associated with acute respiratory insufficiency and death in premature infants. J. Pediatr. 122 (1993) 756–760.
Cassell, G. H., Davis, R. O., Waites, K. B., Brown, M. B., Marriott, P. A., Stagno, S., Davis, Y. K. Isolation ofMycoplasma hominis andUreaplasma urealyticum from amniotic fluid at 16–20 weeks of gestation: potential effect on outcome of pregnancy. Sex. Transm. Dis. 10 (Suppl. 4) (1983) 294–302.
Taylor-Robinson, D. Evaluation of the role ofUreaplasma urealyticum in infertility. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 5 (1986) S262-S265.
Eschenbach, A. D., for the Vaginal Infections and Prematurity Study Group A randomized placebo-controlled trial of erythromycin for the treatment ofUreaplasma urealyticum to prevent premature delivery. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 164 (1991) 734–742.
Hauth, J. C., Goldenberg, R. L., Andrews, W. W., Du Bard, M. B., Copper, R. L. Reduced incidence of preterm delivery with metronidazole and erythromycin in women with bacterial vaginosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 333 (1995) 1732–1736.
Wang, E. L., Frayha, H., Watts, J., Hammerberg, O., Chernesky, M. A., Mahony, J., Cassell, G. H. Role ofUreaplasma urealyticum and other pathogens in the development of chronic lung disease in prematurity. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 7 (1988) 547–551.
Romano, N., Romano, F., Carollo, F. T-strains of mycoplasma in bronchopneumonia lungs of an aborted fetus. N. Engl. J. Med. 285 (1971) 950–952.
Taylor-Robinson, D., Furr, P. M., Libermann, M. M. The occurrence of genital mycoplasmas in babies with and without respiratory distress. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 73 (1984) 383–386.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abele-Horn, M., Peters, J., Genzel-Boroviczény, O. et al. VaginalUreaplasma urealyticum colonization: Influence on pregnancy outcome and neonatal morbidity. Infection 25, 286–291 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01720398
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01720398