Abstract
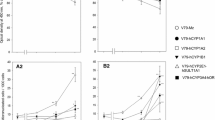
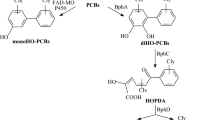
Potential bacterial biodegradation products of polychlorobiphenyls (PCBs) were evaluated as environmental mutagens.p-Chlorophenylglyoxylic acid,p-chloromandelic acid and three monochlorinated benzoic acids were not mutagenic in either the sister chromatid exchange (SCE) orSalmonella typhimurium histidine reversion mutagenesis assays. Bacterial degradation may, therefore, tend to decrease the mutagenic potential of lesser chlorinated PCBs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adlerova, E., P. Vejdelkova, and M. Protiva: Synthetische spasmolytica XIX. Basiche ester substituerter hexahydrobenzilsauren and deren quartare salze. Coll. Czech. Chem. Comm.29, 70 (1964).
Ahmed, M., and D. D. Focht: Oxidation of polychlorinated biphenyls byArchromobacter. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.10, 70 (1973).
Ames, B. N., J. McCann, and E. Yamasaki: Methods for detecting carcinogens and mutagens with the Salmonella/ mammalian-microsome mutagenicity test. Mutation Res.31, 347 (1975).
Ballschmiter, R., Ch. Unglert, and H. J. New: Abbau von chlorientern aromaten: Mikrobiologischer Abbau der polychlorierten biphenyle (PCB) III: chlorierte benzoesauren als metabolite der PCB. Chemosphere7, 51 (1977).
Carey, A. E., and G. R. Harvey: Metabolism of polychlorinated biphenyls by marine bacteria. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.20, 527 (1978).
Carson, B. B., R. A. Dodge, S. A. Harris, and J. S. Yeaw: Organic synthesis collective Vol 1. H. A. Blatt, ed. New York: John Wiley (1944).
Catelani, D., A. Colombi, C. Sorlini, and V. Trecanni: 2-Hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoate: The metacleavage product from 2,3-dihydroxy-biphenyl byPseudomonas putida. J. Biochem.134, 1063 (1973).
Cordle, F., and A. E. Kolbye: Polyhalogenated biphenyls: Biotoxicity and epidemiology. Vet. Human. Toxicol.20, 245 (1978).
Craig-Holmes, A. P., and M. W. Shaw: Effects of six carcinogens on SCE frequency and cell kinetics in culture human lymphocytes. Mutation Res.46, 375 (1977).
Dagley, S.: Catabolism of Aromatic compounds by microorganisms. Adv. Microbiol. Physiol.6, 1 (1971).
DiGiovani, J., A. Viage, D. L. Berry, T. J. Slager, and M. R. Juchau: Tumor-initiating ability of 2,3,7,8 tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and Aroclor 1254 in the two-stage system of mouse skin carcinogenesis. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.18, 552 (1977).
DuFrain, F. J., L. G. Littlefield, and J. L. Wilmer: Cyclophosphamide induced SCE's in rabbit lymphocytes. Environmental Mutagenesis1, 283 (1979).
Furukawa, K., F. Matsumura, and K. Tonomura:Alcaligenes andAcinetobacter strains capable of degrading polychlorinated biphenyls. Agri. Biol. Chem.42, 543 (1978).
Gibson, D. T., R. L. Roberts, M. C. Wells, and V. M. Kobal: Oxidation of biphenyl by aBiijerinckia species. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm.50, 211 (1973).
Kalmaz, E. V., and G. D. Kalmaz: Transport, distribution, and toxic effects of polychlorinated biphenyls in ecosystems. Review Ecol. Model.6, 223 (1979).
Perry, P., and H. J. Evans: Cytological detection of mutagencarcinogen exposure by sister chromatid exchange. Nature258, 121 (1975).
Sayler, G. S., M. Shon, and R. R. Colwell: Growth of an estuarinePseudomonas sp. on polychlorinated biphenyls. Microbiol Ecol.3, 241 (1977).
Shiaris, M. P., and G. S. Sayler: Interactions of PCBs and microbial populations in freshwater environments. In Press, Sci. and Technol. (1982).
Tucker, E. S., V. W. Saeger, and O. Hicks: Activated sludge primary biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyls. Bull. Environ. Contain. Toxicol.14, 705 (1975).
Uchiyama, M., and T. Chiba: Co-carcinogenic effect of DDT and PCB feedings on methylcholanthrene-induced chemical carcinogenesis. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.12, 687 (1974).
Vogel, H. J., and D. M. Bonner: Acetylornithase ofE. coli partial purification and some properties. J. Biol. Chem.218, 97 (1956).
Wyndham, D., J. Devenish, and S. Safe: Thein vitro metabolism, macromolecular binding and bacterial mutagenicity of 4-chlorobiphenyl, a model PCB substrate. Res. Comm. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol.15, 563 (1976).
Yagi, O., and R. Sudo: Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by microorganisms. J. Water Poll. Cont. Fed.52, 1035 (1980).
Yoshihara, S., K. Kawono, H. Yoshimura, H. Kuroki, and Y. Masuda: Toxicological assessment of highly chlorinated biphenyl congeners retained in the Yusho patients. Chemosphere8, 531 (1979).
Zinkl, J. G.: Skin and liver lesions in rats fed a polychlorinated biphenyl mixture. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.5, 217 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sayler, G.S., Reid, M.C., Perkins, B.K. et al. Evaluation of the mutagenic potential of bacterial polychlorinated biphenyl biodegradation products. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 11, 577–581 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01056365
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01056365