Summary
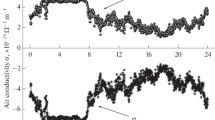
The annual and diurnal variation of the conductivity near the ground at Athens, based on long-term data, are presented. The diurnal double oscillation is a characteristic of the “atmospheric electric climate” of Athens. In addition, the influence of air pollution due to smoke and sulfur dioxide and of wind speed (as an element affecting the dispersion of pollulants) on large ion concentration and on conductivity has been examined. The air pollution, which is often severe in Athens area, results in decreasing conductivity and increasing large ion concentration, while the influence of wind speed is also pronounced. The results justify the use of conductivity as a pollution index. Finally the plausible influence of air temperature and relative humidity and of their rate of change on air electrical conductivity, has been examined. The results are ambiguous and depending on the season, especially for relative humidity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R. V., 1974: Atmospheric electricity in the real world. Fifth Intern. Conf. on Atmos. Electr., Sept. 1974, Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany.
Anderson, R. V., Bailey, J. C., 1991: Errors in the gerdien measurement of atmospheric electric conductivity. With a note by H. Tammet.Meteorol. Atmos. Phys.,46, 101–112.
Brownlee, J. N. 1975: Some measurements of atmospheric ion mobility spectra and conductivity at Auckland.J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 37, 1145–1149.
Chalmers, J. A. 1967:Atmospheric Electricity, 2nd ed., Oxford: Pergamon Press, 195 pp.
Cobb, W. E., 1968: The atmospheric electric climate at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii.J. Atmos. Sci.,25, 470–480.
Cobb, W. E., 1973a: Oceanic aerosol levels deduced from measurements of the electrical conductivity of the atmosphere.J. Atmos. Sci.,30, 101–106.
Cobb, W. E., 1973b: Reply.J. Atmos. Sci.,30, 1460–1462.
Cobb, W. E., Wells, H. J., 1970: The electrical conductivity of oceanic air and its correlation to global atmospheric pollution.J. Atmos. Sci.,27, 814–819.
Dolezalek, H., 1969: On the correlation between atmospheric electricity measurements.J. Appl. Meteor.,8, 462–464.
Dolezalek, H., 1978: The application of atmospheric electricity concepts and methods to other parts of meteorology, WMO No 507, T. N. 162, Geneva, WMO 21.
Gish, O. H., 1951: Universal aspects of atmospheric electricity. In: Malone, T. F. (ed.)Compendium of meteorology, Boston: A.M.S., 101–119.
Israel, H., 1971: Atmospheric Electricity, vol. 1 Israel Program for Scientific Translations, Jerusalem, 129 pp.
Junge C., 1951: Nuclei of atmospheric condensation. In: Malone, T. F. (ed.)Compendium of meteorology, Boston; A.M.S., 182–191.
Law, J., 1963: The ionization of the atmosphere near the ground in fair weather.Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc.,89, 107–121.
Michalopoulou, Ch., 1978: Thunderstorms over Athens area, Ph.D. Thesis, Athens, (in greek).
Misaki, M., Ikegami, M., Kanazawa, J., 1972: Atmospheric electrical conductivity measurement in the Pacific Ocean, exploring the background level of global pollution.J. Meteor. Soc. Japan,50, 497–500.
Misaki, M., Takeuti, T., 1970: The extension of air pollution from land over the ocean revealed in the variation of atmospheric electrical conductivity.J. Meteor. Soc. Japan,48, 263–270.
Morita, Y., 1971: The diurnal and latitudinal variation of electric conductivity in the atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean.J. Meteor. Soc. Japan,49, 56–58.
P.E.P.C. (Program for the Environmental Pollution Control), 1989: The Air Pollution over Athens Area. Technical Report, vol. 1. Base informations. Ministry of Environment, Land Planning and Public Works, Athens, 36 pp.
Retalis, D., 1977: On the relationship between small atmospheric ions concentration and (1) smoke, (2) sulfur dioxide and (3) wind speed.Pure Appl. Geophys.,115, 575–581.
Retalis, D., 1987: Chernobyl reactor accident consequences on small atmospheric ions concentration above Athens.Pure Appl. Geophys.,125, 669–678.
Retalis, D., 1991: Study of the air-earth electrical current density in Athens. Accepted in Pure Appl. Geophys.
Retalis, D., Carapiperis, L., 1972: Contribution to the study of the influence of the air pollution on the potential gradient of the electric field of the atmosphere. Memoirs of the NOA, Ser. II, Meteorology, No 26.
Retalis, D., Pitta, A. 1989: Effects on electrical parameters at Athens, Greece, by radioactive fallout from a nuclear power plant accident.J. Geophys. Res.,94, 13093–13097.
Retalis, D., Zervos, P., 1976: Study of the electrical conductivity of the air above Athens.J. Atmos. Terr. Phys.,38, 299–305.
Retalis, D., Zambakas, J., 1975: The influence of temperature and relative humidity of the air on atmospheric small ions concentrations over Athens. Praktika of the Academy of Athens,50, 96–106 (in greek).
Saxer, L., Sigrist, W., 1966: Die luftelektrische Station in Aarau, Technical Report, Switzerland.
Wait, G. R., Parkinson, W. D., 1951: Ions in the atmosphere. In: Malone, T. F. (ed.) Compendium of Meteorology, Boston, AMS, 120–127.
World Meteorological Organization (W.M.O.), 1966: Climatic change, W.M.O. No 195, T.N. 79, W.M.O., Geneva, pp 64–65.
Wright, H. L., 1934: The association between relative humidity and the ratio of the number of large ions to the total number of nuclei.Terr. Magn. Atmos. Elec.,39, 280–282.
Zambakas, J., Retalis, D., Mavrakis, D., 1985: A simultaneous interpretation by wind speed and direction of ambient air polar conductivities in Athens, Greece.Arch. Met. Geoph. Biocl., Ser. A,33, 381–388.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 3 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Retalis, D., Pitta, A. & Psallidas, P. The conductivity of the air and other electrical parameters in relation to meteorological elements and air pollution in Athens. Meteorl. Atmos. Phys. 46, 197–204 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01027345
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01027345