Abstract
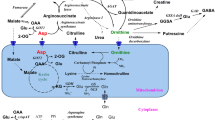
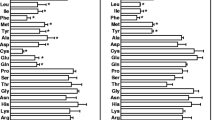
Acetyl-l-carnitine (ALCAR) was found to have beneficial effects in senile patients. In recent years many of its effects on the nervous system have been examined, but its mechanism(s) of action remains to be elucidated. We previously reported that it causes release of dopamine in the striatum. In the present paper we report that ALCAR, when administered at intracerebral sites via microdialysis, stimulates the release of amino acids in a concentration-dependent and regionally heterogeneous manner. The effect was strong in the striatum and cerebellum, less so in the frontal cortex, and weak in the thalamus. Seven amino acids were measured: the increase in the level of aspartate, glutamate, and taurine was substantial, and the increase in the level of glycine, serine, threonine, alanine, and glutamine in the microdialysate was minor. The stimulatory effect of ALCAR on the release of amino acids in the striatum was inhibited by the muscarinic antagonist atropine, but was not inhibited by the nicotinic antagonist mecamylamine. The effect of ALCAR on the levels of most of the amino acids tested was independent of the presence of Ca2+ in the perfused. These results indicate that ALCAR, when administered intracerebrally at fairly high concentrations, can affect the level and the release not only of such neurotransmitters as acetylcholine and dopamine, but also of amino acids. The mechanism of action of ALCAR on the release of cerebral amino acids may involve the participation of muscarinic receptors or may be mediated through the release of dopamine, but the lack of Ca2+ dependence indicates a release from the cytoplasmic amino acid pool, possibly through the effect of ALCAR on cell membrane permeability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonavita, E. 1986. Study of the efficacy and tolerability ofl-acetylcarnitine therapy in the senile brain. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. Toxicol. 24:511–516.
Calvani, M., Iannuccelli, M., Orfalian, Z., Marchionni, A., Benedetti, N., Colonna, V., Caruso, G., and Marchionni, N. 1990. Acetyl-L-carnitine. An anti-aging agent for the treatment of dementia. Aging Brain and Dementia 54:603–622.
Ghirardi, O., Milano, S., Ramacci, M. T., and Angelucci, L. 1989. Long-term acetyl-L-carnitine preserves spatial learning in the senescent rat. Prog. Neuro-Physchopharmacol. & Biol. Psychiat. 13:237–245.
Imperato, A., Ramacci, M. T., and Angelucci, L., 1988. Acetyl-l-carnitine enhances acetylcholine release in the striatum and hippocampus of awake freely moving rats. Neurosci. Lett. 107:251–255.
Sershen, H., Harsing, L. G. Jr., Banay-Schwartz, M., Hashim, A., Ramacci, M. T., and Lajtha, A. 1991. Effect of acetyl-L-carnitine on the dopaminergic system in aging brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 30:555–449.
Huth, P. J., Schmidt, M. J., Hall, P. V., Fariello, R. G., and Shug, A. L. 1980. The uptake of carnitine by slices of rat cerebral cortex. J. Neurochem. 36:715.
Burlina, A. P., Sershen, H., Debler, E. A., and Lajtha, A. 1989. Uptake of acetyl-L-carnitine in the brain. Neurochem. Res. 14:489.
Badiali de Giorgi, L., Bonvicini, F., Bianchi, D., Bossoni, G., and Taschi, R. 1987. Ultrastructural aspects of aging rat hippocampus and effects of L-acetyl-carnitine treatment. Drug Exp. Clin. Res. 13:185.
Ghirardi, O., Milano, S., Ramacci, M. T., and Angelucci, L. 1988. Effect of acetyl-L-carnitine chronic treatment on discrimination models in aged rats. Physiol. Behav. 44:769.
Blum, K., Seifter, E., and Seifter, J. 1971. The pharmacology of D- and L-carnitine and D- and L-acetylcarnitine: comparison with choline and acetylcholine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 178:331.
White, H. L., and Scates, P. W. 1990. Acetyl-L-carnitine as a precursor of acetylcholine. Neurochem. Res. 15:597.
Doleral, V., and Tuček, S. 1980. Utilization of citrate, acetylcarnitine, acetate, pyruvate, and glucose for the synthesis of acetylcholine in rat brain slices. J. Neurochem. 36:12–23.
Bresolin, N., Freddo, L., Vergani, L., and Angelini, C. 1982. Carnitine, carnitine acetyltransferases, and rat brain function. Exp. Neurol. 78:285.
Fariello, R. G., Ferraro, T. N., Golden, G. T., and De Mattei, M. 1988. Systemic acetyl-l-carnitine elevates nigral levels of glutathione and GABA. Life Sci. 43:289.
Patacchioli, F. R., Amenta, F., Ramacci, M. T., Taglialatela, G., Maccari, S., and Angelucci, L. 1989. Acetyl-l-carnitine reduces the age-dependent loss of glucocorticoid receptors in the rat hippocampus: an autoradiographic study. J. Neurosci. Res. 23:462.
Harsing, L. G. Jr., Sershen, H., Toth, E., Hashim, A., Ramacci, M. T., and Lajtha, A. 1992. Acetyl-L-carnitine releases dopamine in rat corpus striatum: an in vivo microdialysis study. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 218:117–121.
Lehman, J. and Langer, S. Z. 1982. Muscarinic receptors on dopamine terminals in the cat caudate nucleus: neuromodulation of [3H]dopamine release in vitro by endogenous acetylcholine. Brain Res. 248:61.
Toth, E., Sershen, H., Hashim, A., Vizi, E. S., and Lajtha, A. 1992. Effect of nicotine on extracellular levels of neurotransmitters assessed by microdialysis in various brain regions: role of glutamic acid. Neurochem. Res. 17:265–271.
Vizi, E. S., Kobayasi, O., Torocsik, A., Kinjo, M., Manabe, N., Goldiner, P.L., Potter, P.E., and Foldes, F.F. 1989. Heterogeneity of presynaptic muscarinic receptors involved in modulation of transmitter release. Neuroscience 31:259–267.
Tossman, U., Delin, A., Eriksson, L. S. and Ungerstedt, U. 1987. Brain cortical amino acids measured by intracerebral dialysis in portacaval shunted rats. Neurochem. Res. 12:67.
Paxinos, G. and Watson, C. 1986. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic Press, NY.
Neidle, A., Banay-Schwartz, M., Sacks, S., and Dunlop, D. 1990. Amino acids analysis using 1-naphthylisocyanate as a precolumn high-performance liquid chromatography derivatization reagent. Anal. Biochem. 180:291.
Onofrj, M., Bodis-Wollner, I., Pola, P., Calvani, M. 1983. Central cholinergic effects of levo-acetylcarnitine. Drug Exp. Clin. Res. 1X(1) 161–169.
Arienti, G., Ramacci, M. T., Maccari, F., Casu, A., and Corazzi, L. 1992. Acetyl-l-carnitine influences the fluidity of brain microsomes and of liposomes made of rat brain microsomal lipid extracts. Neurochem. Res. 17:671–675.
Banay-Schwartz, M., Lajtha, A., and Palkovits, M. 1989. Changes with aging in the levels of amino acids in rat CNS structural elements I. Glutamate and related amino acids. Neurochem. Res. 14:555–562.
Banay-Schwartz, M., Lajtha, A., and Palkovits, M. 1989. Changes with aging in the levels of amino acids in rat CNS structural elements. II. Taurine and small neutral amino acids. Neurochem. Res. 14:563–570.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toth, E., Harsing, L.G., Sershen, H. et al. Effect of acetyl-l-carnitine on extracellular amino acid levels in vivo in rat brain regions. Neurochem Res 18, 573–578 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00966933
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00966933