Summary
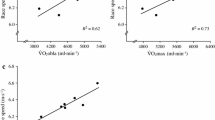
Maximal aerobic power (\(\dot V_{O_2 }\) max) was determined during running, cycling, or rowing in 14 winners of international championship (European, world or Olympic) regattas in rowing, in 13 less qualified international competitive oarsmen, and in 10 lightweights. Ventilation (\(\dot V_E\)), heart rate (HR), and blood lactate after maximal exercise were also measured. The winners had a weight of 93 kg, a \(\dot V_{O_2 }\) max of 5.89 l×min−1, a \(\dot V_E\) of 200 l×min−1, and a HR of 185 beats×min−1, as compared with 84kg, 5.58 l×min−1, 173 l×min−1, and 190 beats×min−1 in the less successful oarsmen, and 72kg, 5.13 l×min−1, and 164 l×min−1 in the lightweights. \(\dot V_{O_2 }\) max and \(\dot V_E\) were correlated to body weight, while HR and blood lactate were not, the latter showing an average value of 12.5 (SE 0.45) mmol×l−1. If expressed neutral to body dimensions all oarsmen had a \(\dot V_{O_2 }\) max of about 293 ml×min−1×kg−2/3. It is suggested that the large \(\dot V_{O_2 }\) max values found in oarsmen mainly reflect their large body dimensions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asmussen E, Secher NH, Andersen E (1981) Heart rate and ventilatory frequency as dimensional-dependent variables. Eur J Appl Physiol 46: 379–386
åstrand P-O (1952) Experimental studies of physical working capacity in relation to sex and age. Munksgaard, Copenhagen
åstrand P-O, Rodahl K (1977) Textbook of work physiology. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 367–388
Bergh U (1977) Figure 12-5. In: åstrand P-O, Rodahl K, Textbook of work physiology. McGraw-Hill, New York
Carey P, Stensland M, Hartley LH (1974) Comparison of oxygen uptake during maximal work on the treadmill and the rowing ergometer. Med Sci Sports 6: 101–103
Cunningham DA, Goode PB, Critz JB (1975) Cardiorespiratory response to exercise on a rowing and bicycle ergometer. Med Sci Sports 7: 37–43
Döbeln, W v (1966) Kroppsstorlek, energiomsÄttning och kondition. In: Luthman G, åberg U, Lundgren N (eds) Handbok i Ergonomi. Almqvist and Wiksell, Stockholm, 245–253
Espersen M (1981) En beskrivelse af danske roere i en olympisk sÆson. Laboratory for the Theory of Gymnastics, August Krogh Institute, University of Copenhagen, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark
Hagerman FC, Lee WD (1971) Measurement of oxygen consumption, heart rate, and work output during rowing. Med Sci Sports 3: 155–160
Hagerman FC, Addington WW, Gaensler EA (1972) A comparison of selected physiological variables among outstanding competitive oarsmen. J Sports Med 12: 12–22
Hagerman FC, McKirnan MD, Pompei JA (1975) Maximal oxygen consumption of conditioned and unconditioned oarsmen. J Sports Med 15: 43–48
Hagerman FC, Connors MC, Gault JA, Hagerman GR, Polanski WJ (1978) Energy expenditure during simulated rowing. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 45: 87–93
Hagerman FC, Hagerman GR, Mickelson TC (1979) Physiological profiles of elite rowers. Physcian and Sports Med 7: 74–83
Henderson Y, Haggard HW (1925) The maximum of human power and its fuel. Am J Physiol 72: 264–282
Hermansen L, Döbeln W v (1971) Body fat and skin fold measurements. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 27: 315–319
Hirata KI (1979) Selection of Olympic champions. Karger, Basel, pp 259–305
Jackson RC, Secher NH (1976) The aerobic demands of rowing in two Olympic rowers. Med Sci Sports 8: 168–170
Larsson L, Forsberg A (1980) Morphological muscle characteristics in rowers. Can J Appl Sports Sci 5: 239–244
McMahon (1971) Rowing: a similarity analysis. Science 173: 349–351
Mellerowicz H, Hansen G (1965) SauerstoffkapazitÄt und andere spiro-ergometrische Maximalwerte der Ruder-Olympiasieger in Vierer mit St. vom Berliner Ruderclub. Sportarzt Sportmed 16: 188–191
Mikkelsen F (1980) Eneren Ørsted. Centrum, Copenhagen, p 40
Nowacki P, Krause R, Adam K (1969) Maximal oxygen uptake by the rowing crew winning the Olympic gold medal 1968. Pfluegers Arch 312: R66-R67
Nowacki PE, Adam K, Krause R, Ritter U (1971) Die Spiro-Ergometrie in neuem Untersuchungssystem für den Spitzensport. Rudersport 26: I-VI
Pauw D de, Vrijens J (1971) Untersuchungen bei Elite-Ruderern in Belgien. Sportarzt Sportmed 22: 176–179
Prampero PE di, Cortili G, Celentano F, Cerretelli P (1971) Physiological aspects of rowing. J Appl Physiol 31: 853–857
Saltin B, åstrand P-O (1967) Maximal oxygen uptake in athletes. J Appl Physiol 23: 353–358
Schneider E (1980) Leistungsanalyse bei Rudermannschaften. Limpert Verlag, Bad Homburg, p 42
Scholander PF (1947) Analyzer for accurate estimation of respiratory gases in one-half cubic centimeter samples. J Biol Chem 167: 235–250
Scholtz R, Schmitz H, Buecher T, Lampen JO (1959) über die Wirkung von Nystatin auf Backerhefe. Biochem Z 311: 71–86
Secher NH, Ruberg-Larsen N, Binkhorst RA, Bonde-Petersen (1974) Maximal oxygen uptake during arm cranking and combined arm plus leg exercise. J Appl Physiol 36: 515–518
Secher NH, Vaage O, Jackson RC (1982a) Rowing performance and maximal aerobic power of oarsmen. Scand J Sports Sci 4: 9–11
Secher NH, Espersen M, Binkhorst RA, Andersen PA, Rube N (1982b) Aerobic power at the onset of maximal exercise. Scand J Sports Sci 4: 12–16
Strydom NB, Wyndham CH, Greyson JS (1967) A scientific approach to selection and training of oarsmen. S Afr Med J 419: 1100–1102
StrØmme SB, Ingjer F, Meen HD (1977) Assessment of maximal aerobic power in specifically trained athletes. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 42: 833–837
Taylor CR, Heglund NC (1982) Energetics and mechanics of terrestial locomotion. Ann Rev Physiol 44: 97–107
Vaage O, Hermansen L (1977) Figure 11-4. In: åstrand P-O, Rodahl K, Textbook of work physiol. McGraw-Hill, New York
Yamakawa J, Ishiko T (1966) Standardization of physical fitness test for oarsmen. In: Kato K (ed) Proc Int Cong Sports Sci 1964. Jpn Un Sports Sci. Tokio, pp 435–436
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Danish Sports Research Council
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Secher, N.H., Vaage, O., Jensen, K. et al. Maximal aerobic power in oarsmen. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 51, 155–162 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00455178
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00455178