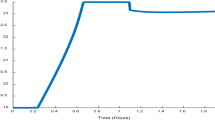
Abstract
Qualitative Reasoning is a set of Artificial Intelligence theories, methods, and techniques that provide an answer to modeling problems in domains in which one can have a clear notion of how a system is functioning without being able to express it as classical mathematical equations, and where is posed the problem of using jointly quantitative and qualitative data, as well as processing a big amount of complex knowledge. SIMAO (‘a System to Interpret Measurements And Observations’) is an attempt to deal with such problems. Although primarily devised for heterogeneous data interpretation in hydroecology, it was thought possible to use SIMAO in a wider context, like biotechnological processes. Starting from specific problems posed by a batch fermentation, the D-xylose conversion into ethanol by the yeast Pichia stipitis, this paper describes how was built and used a SIMAO model aimed at predicting the fermentation issue from initial conditions, i.e. set-points values and substrate concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- QS:
-
quantity space
- {pp, p, m, f, ff}:
-
quantity space elements
- TR-m:
-
measurement translation rule
- TR-o:
-
observation translation rule
- TR-q:
-
qualitative transfer rule
- incr, decr, inv:
-
primitive unary operators
- [+], [-], [⋆], [/]:
-
primitive binary operators
References
Weld, D. S.; de Kleer, J. (Ed.): Readings in qualitative reasoning about physical systems. San Mateo (USA) Morgan Kaufmann 1990
De Kleer, J.; Williams, B. C. (Ed.): Special volume — Qualitative reasoning about physical systems II. Artificial Intelligence. 51 (1991)
Steyer, J. P.: Sur une approche qualitative des systèmes physiques: aide en temps réel à la conduite des procédés fermentaires. Ph.D. dissertation, Paul Sabatier University. Toulouse (F) 1991
Bousson, K.; Guerrin, F.; Travé-Massuyès, L.: Qualitative prediction and interpretation for bioprocess supervision. In: Proc. Tooldiag'93 Int. Conf. on Fault Diagnosis, vol. 3, pp. 1044–1053. Toulouse (F) 1993
Guerrin, F.: Qualitative reasoning about an ecological process: interpretation in Hydro-ecology. Ecological Modelling. 59 (1991) 165–201
Guerrin, F.: Model-based interpretation of measurements, analyses and observations of an ecological process. AI Applications. 6 (1992) 89–101
Gong, C.S.; Chen, L. F.; Flickinger, M. C.; Tsao, G. T.: Conversion of hemicellulose carbohydrate. Advances in Biochemical Engineering. 20 (1981) 93–118
Skoog, K.; Hahn Hagerdal, B. H.: Xylose fermentation. Enzyme and Microbial Technology. 10 (1988) 65–80
Delgenès, J.-P.; Moletta, R.; Navarro, J. M.: The effect of aeration on D-xylose fermentation by Pachysolen tannophilus, Pichia stipitis, Kluyveromyces marxianus and Candida shehatae. Biotechnol. Lett. 8 (1986) 897–900
Prior, B. A.; Kilian, S. G.; Du Preez, J. C.: Fermentation of D-xylose by the yeasts Candida shehatae and Pichia stipitis: prospects and problems. Process Biochem. 24 (1989) 21–32
Bruinenberg, P. M.; De Bot, P. M.; Van Dijken, J. P.; Scheffers, W. A.: The role of redox balance in the anaerobic fermentation of xylose by yeasts. European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 18 (1983) 287–292
Sims, A. P.; Barnett, J. A.: The requirement of oxygen for the utilization of maltose, cellobiose and D-galactose by certain anaerobically fermenting yeasts (Kluyver effect). J. Gen. Microbiol. 106 (1978) 277–288
Delgenès, J.-P.; Moletta, R.; Navarro, J. M.: Fermentation of D-xylose, D-glucose and L-arabinose mixture by Pichia stipitis Y7124: sugar tolerance. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29 (1988) 155–161
Van Dijken, J. P.; Scheffers, W. A.: Redox balances in the metabolism of sugars by yeasts. FEMS. Microbiol. Reviews. 32 (1986) 199–224
Delgenès, J.-P.; Moletta, R.; Navarro, J. M.: The ethanol tolerance of Pichia stipitis Y7124 grown on a D-xylose, D-glucose and L-arabinose mixture. J. Ferment. Technol. 66 (1988) 417–422
Du Preez, J. C.; Bosch, M.; Prior, B. A.: Xylose fermentation by Candida shehatae and Pichia stipitis; effects of pH, temperature and substrate concentration. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 8 (1986) 360–364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerrin, F., Delgenès, J.P. & Moletta, R. Modeling the alcoholic fermentation of xylose by Pichia stipitis using a qualitative reasoning approach. Bioprocess Engineering 10, 115–122 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369466
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369466