Summary
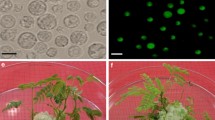
A protocol for obtaining regenerated fertile plants from mesophyll protoplasts of Arabidopsis thaliana is reported. Protoplasts were isolated from leaves of 21-to 28-day-old Arabidopsis plants grown in a controlled environment. Sustained divisions were achieved when protoplasts were embedded in beads formed by 1.4% sodium alginate in the presence of 50mM CaCl2 in 0.4 mannitol, which was then exchanged againts modified B5 medium. About 0.4%–0.6% of the protoplasts developed into colonies of which 80%–90% formed shoots and subsequently regenerated to fertile plants. Seeds harvested from more than 200 independently regenerated plants were sown and germination frequencies of more than 95% were obtained. Furthermore, the F1 plants did not show any evidence of somaclonal variation on visual inspection. This protocol was originally developed for Arabidopsis thaliana “Columbia”; however it was shown to be applicable also for the genotypes “Wassilewskija”, “Landsberg erecta” and “Estland” though with differing efficiencies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FDA:
-
fluorescein diacetate
- CM:
-
culture medium
- SRM:
-
shoot regeneration medium
- SEM:
-
shoot elongation medium
- RM:
-
rooting medium
- PE:
-
plating effciency
- NAA:
-
α-naphthaleneacetic acid
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- IAA:
-
indole-3-acetic acid
- IBA:
-
indole-3-butyric acid
- BAP:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- Kin:
-
kinetin
- 2-iP:
-
2-isopentenyladenine
- GA3 :
-
gibberetic acid
References
Feldmann KA, Marks MD (1987) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of germinating seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana: A nontissue culture approach. Mol Gen Genet 208:1–9
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension culture of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Gleba Y, Kohlenbach H-W, Hoffmann F (1978) Root morphogenesis in somatic hybrid cell lines Arabidopsis thalina+Brassica campestris. Naturwissenschaften 68:655–656
Gresshoff PM (1972) Haploid Arabidopsis thaliana callus and plant from anther culture. Aust J Biol Sci 25:259–264
Kauss H (1987) Some aspects of calcium-dependent regulation in plant metabolism. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 38:147–172
Köhle H, Jeblick W, Poten F, Blaschek W, Kauss H (1985) Chitosan-elicited callose synthesis in soybean cells as a Ca++-dependent process. Plant Physiol 77:544–555
Koorneef M, van Eden J, Hanhart cJ, Stam P, Braaksma FJ, Feenstra WJ (1983) The linkage map of Arabidopsis. J Hered 74:265–272
Kranz AR, Kirchheim B (1987) Genetic resources in Arabidopsis. Arabidopsis Inf Serv 24 (special issue)
Laibach F (1943) Zur Ätiologie der Blütenbildung. Naturwissenschaften 31:246–267
Larkin PJ (1976) Purification and viability determination of plant protoplasts. Planta 128:213–216
Li L-C, Kohlenbach HW (1982) Somatic embryogenesis in quite a direct way in cultures of mesophyll protoplasts of Brassica napus L. Plant Cell Rep 1:209–221
Lloyd AM, Barnason AR, Rogers SG, Byrne MC, Frawley RT, Horsch RB (1986) Transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Science 234:464–468
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Negrutiu I, Beeftink F, Jacobs M (1975) Arabidopsis thaliana as a model system in somatic cell genetics. I. Cell and tissue culture. Plant Sci Lett 5:293–304
Sheikholeslam SN, Weeks DP (1987) Acetosyringone promotes high efficiency transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana explants by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Mol Biol 8:291–298
Shillito RD, Paszkowski J, Potrykus I (1983) Agarose plating and a bead culture technique enable and stimulate development of protoplast derived colonies in a number of plant species. Plant Cell Rep 2:244–247
Xuan LT, Menczel L (1980) Improved protoplast culture and plant regeneration from protoplast-derived callus in Arabidopsis thaliana. Z Pflanzenphysiol 96:77–80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. Saedler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damm, B., Willmitzer, L. Regeneration of fertile plants from protoplasts of different Arabidopsis thaliana genotypes. Molec. Gen. Genet. 213, 15–20 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333392
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333392