Abstract
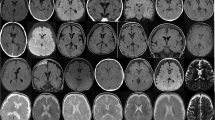
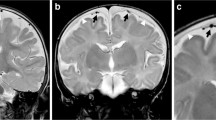
External hydrocephalus (EH) was identified in 58 infants under 3 years of age during the period 1 June 1986 to 28 February 1990. Radiological images and clinical features were compared with 11 cases of cerebral atrophy (CA). Significant differences were found in delivery, head circumference, and the incidence of motor and developmental abnormalities. The population with EH was found to be quite heterogeneous, with a male preponderance. Intracranial pressure was normal in 15 cases in which lumbar puncture was done. The flow of cerebral spinal fluid was considered to be within the normal range in 6 cases. The results of a few cases examined with metrizamide cisternography are presented. The prognosis in our cases was not as benign as previously published, and use of the name EH is questioned. The less committal term “hypodense extracerebral images” is proposed when computed tomography (CT) is the only study done. The hypothesis that encephalocranial disproportion is the basic underlying entity for the CT images is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez LA, Maytal J Shinar S (1986) Idiopathic external hydrocephalus: natural history and relationship to benign familial macrocephaly. Pediatrics 77: 901–907
Andersson H, Elfverson J, Svendsen P (1984) External hydrocephalus in infants. Child's Brain 11: 398–402
Aoki N, Masuzawa H (1984) Infantile acute subdural hematoma. Clinical analysis of 26 cases. J Neurosurg 61: 273–280
Bode H, Strassburg HM (1987) Craniocerebral disproportion. A contribution to the significance of extracerebral fluid collections in infancy. Klin Pädiatr 199: 399–402
Briner S, Bodensteiner J (1980) Benign subdural collections of infancy. Pediatrics 67: 802–804
Carnell S, Chiu LC, Christie JH (1978) Diagnosis of extracerebral fluid collections by computed tomography. Am J Roentgenol 131: 107–110
Dandy WE (1918) Extirpation of the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles in communicating hydrocephalus. Ann Surg 68: 569–579
Dandy WE, Blackfan KD (1914) Internal hydrocephalus: an experimental clinical and pathological study. Am J Dis Child 8: 406–482
Enzman DR, Lane B (1978) Enlargement of the subarachnoid spaces and lateral ventricles in patients undergoing chemotherapy. J Pediatr 92: 535–539
Frankenburg WK, Dodds JB (1967) The Denver Development Screening Test. J Pediatr 71: 181–191
Gooskens RHJM, Willemse J, Gielen CCAM (1985) Cerebrospinal fluids dynamics and cerebrospinal fluid infusion in children. II. Clinical application of lumbar cerebrospinal fluid infusion in children with macrocephaly and normal growth rate of the head circumference. Neuropediatrics 16: 121–125
Gooskens RHJM, Gielen CCAM, Willemse J (1988) The value of estimating pressure-volume index in childhood macrocephaly. Child's Nerv Syst 4: 233–236
Gordon N (1980) Apparent cerebral atrophy in patients on treatment with steroids. Dev Med Child Neurol 22: 502–506
Kapila A, Trice J, Spies WG, Siegel BA, Gado MH (1982) Enlarged cerebrospinal fluid spaces in infants with subdural hematomas. Radiology 142: 669–672
Kendall B, Hollan I (1981) Benign communicating hydrocephalus in children. Neuroradiology 21: 93–96
Kleinman PK, Zito JL, Davidson RI, Raptopoulos V (1983) The subarachnoid space in children: normal variations in size. Radiology 147: 455–457
Marks HG, Borns P, Steg NL, Stine SB, Stroud HH, Vates SS (1978) Catch-up growth demonstration by CAT scan. J Pediatr 93: 254–256
Maytal J, Alvarez LA, Elkin CM, Shinnar S (1987) External hydrocephalus: radiologic spectrum and differentiation from cerebral atrophy. AJNR 8: 271–278
Ment LR, Duncan CC, Geeghr R (1981) Benign enlargement of the subarachnoid space in the infant. J Neurosurg 54: 504–508
Modic MT, Kafmann B, Bonstelle CT, Tomsick T, Weinstein MA (1981) Megalocephaly and hypodense extracerebral fluid collections. Radiology 141: 93–100
Mori K, Handa H, Itoh M, Okuno T (1980) Benign subdural effusion in infants. J Comp Assist Tomogr 4: 466–471
Mulke R (1972) Nervale Gesichtspunkte zur Pathogenese und Therapie der Kraniosynostose. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 26: 191–250, 293–326
Myriantopoulos NC (1977) Epidemiology of central nervous system malformations. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Hand-book of clinical neurology, vol 30. Elsevier Amsterdam New York Oxford, pp 139–172
Nickel RE, Gallenstein JS (1987) Developmental prognosis for infants with benign enlargement of the subarachnoid spaces. Dev Med Child Neurol 29: 181–186
Petit RE, Kilroy AW, Allen JH (1980) Macrocephaly with head growth parallel to normal growth pattern: neurological, developmental and computerized tomography findings in full term infants. Arch Neurol 37: 518–521
Baimondi AJ (1987) Pediatric neurosurgery. Theoretic principles, art of surgical techniques. Springer New York Berlin Heidelberg, pp 453–491
Robertson WC, Gomez MR (1978) External hydrocephalus: early finding in communicating hydrocephalus. Arch Neurol 35: 541–544
Robertson WC, Chun RWN, Orrison W, Sackett JF (1979) Benign subdural collection of infancy. J Pediatr 94: 382–385
Sahar A (1978) Pseudohydrocephalus-megalocephaly, increased intracranial pressure and widened subarachnoid space. Neuropädiatrie 9: 131–139
Velardi F, Hoffman HJ, Ash JM, Hendrick B, Humphreys RP (1986) The value of CSF flow studies in infants with communicating hydrocephalus. Child's Nerv Syst 2: 139–143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nogueira, G.J., Zaglul, H.F. Hypodense extracerebral images on computed tomography in children. Child's Nerv Syst 7, 336–341 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00304833
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00304833