Abstract
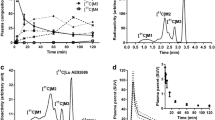
The regional pharmacokinetic behavior in baboon brain of 18F-fluoroethyl-and 18F-fluoropropylspiperone (18FESP, 18FPSP) at specific activities≥1000 Ci/mmol was studied with PET. Four hours after injection of 5–10 mCi 18FESP, uptake in striatum was 0.048%±0.005% of injected dose per cm3, which is almost the same as with 18F-and 11C-methylspiperone. While 18FPSP was taken up in much smaller amounts than 18FESP, striatum to cerebellum activity ratios were quite similar for both ligands (about 9 to 10 at 4 h p.i.). Because of its higher striatal uptake, 18FESP seems to be better suited for PET. Furthermore, relative binding to S2 receptors was much smaller for FESP: competing cold S2 antagonists (ritanserin, ketanserin) did not alter 18FESP binding to striatum, concurrently reducing uptake in frontal cortex by only 15%–20%. With coninjection of increasing amounts of cold FESP, saturation of 18FESP binding to striatum occurred at doses exceeding 10 μg per kg. Quantitative analysis of radiolabelled ligand in arterial plasma (decrease to 8% at 4 h p.i.) demonstrated identical metabolic turnover for both ligands. Direct use of binding fractions from the saturation curve resulted in overestimation of the receptor density in striatum. Using the 18FESP plasma concentration time curve and the dynamic uptake data, k 3 of a three compartment model could be determined by non linear regression. However, dramatic changes of the dependence of k 3 on the specifically bound ligand concentration were observed even at small loading doses of FESP. Estimation of B max yielded a D2 receptor density of only 6 pmol per cm3 in baboon striatum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnett CD, Shiue C-Y, Wolf AP, Fowler JS, Logan J, Watanabe M (1985a) Comparison of three 18F-labeled butyrophenone neuroleptic drugs in the baboon using positron emission tomography. J Neurochem 44:835–844
Arnett CD, Fowler JS, Wolf AP, Shiue C-Y, McPerson DW (1985b) [18F]-N-methylspiperone: the radioligand of choice for PETT studies of the dopamine receptor in human brain. Life Sci 36:1359–1366
Baron JC, Mazière B, Loc'h C, Cambon H, Sgouropoulos P, Bonnet AM, Agid Y (1986) Loss of striatal [76Br]bromospiperone binding sites demonstrated by positron tomography in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 6:131–136
Blessing G, Coenen HH, Franken K, Qaim SM (1986) Production of 18F-F2, H18F and 18F aq− using the 20Ne(d,α)18F process. Appl Radiat Isot 37:1135–1139
Block D, Coenen HH, Laufer P, Stöcklin G (1986) N.c.a. 18F-fluoroalkylation via nucleophilic fluorination of disubstituted alkanes and application to the preparation of N-[18F]-fluoroethylspiperone. J Label Compds Radiopharm 23:1042–1044
Block D, Coenen HH, Stöcklin G (1988) N.c.a. 18F-fluoroalkylation of H-acidic compounds. J Label Compds Radiopharm 25:201–216
Chi DY, Kilbourn MR, Katzenellenbogen JA, Brodack JW, Welch MJ (1986) Synthesis of no-carrier-added N-([18F]fluoralkyl)spiperone derivatives. Appl Radiat Isot 37:1173–1180
Chugani DC, Ackermann RF, Phelps ME (1985) [3H]spiperone and [18F]2-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose studies of nigrostriatal stimulation in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol [Suppl. 1] 5:S161-S162
Coenen HH, Laufer P, Stöcklin G, Wienhard K, Pawlik G, Böcher-Schwarz HG, Heiss W-D (1987) 3-N-(2-[18F]-fluoroethyl)-spiperone: a novel ligand for cerebral dopamine receptor studies with PET. Life Sci 40:81–88
DeJesus OT, Van Moffaert GJC, Dinerstein RJ, Friedman AM (1986) Exogenous 1-dopa alters spiroperidol binding, in vivo, in the mouse striatum. Life Sci 39:341–349
Hamacher K, Coenen HH, Stöcklin G (1986) N.c.a. radiofluorination of spiperone and N-methylspiperone via aminopolyether supported direct nucleophilic substitution. J Label Compds Radiopharm 23:1047
Holman BL, Wick MW, Kaplan ML, Hill TC, Lee RGL, Wu J-L, Liu T-H (1984) The relationship of the eye uptake of N-isopropyl-p-[123I]-iodoamphetamine to melanin production. J Nucl Med 25:315–319
Huang SC, Barrio JR, Phelps ME (1986) Neuroreceptor assay with positron emission tomography: equilibrium versus dynamic approaches. J Cereb Blood Flow metabol 6:515–521
Höllt V, Czlonkowski A, Herz A (1977) The demonstration in vivo of specific binding sites for neuroleptic drugs in mouse brain. Brain Res 130:176–183
Inoue Y, Wagner HN, Wong DF, Links JM, Frost JJ, Dannals RF, Rosenbaum AE, Takeda K, DiChiro G, Kuhar MJ (1985) Atlas of dopamine receptor images (PET) of the human brain. J Comput Ass Tomogr 9:129–140
Kiesewetter DO, Eckelmann WC, Cohen RM, Firm RD, Larson SM (1986) Synthesis and D2 receptor affinities of derivatives of spiperone containing aliphatic halogens. Appl Radiat Isot 37:1181–1188
Kuhar MJ, Murrin LC, Malauf AT, Klemm N (1978) Dopamine receptor binding in vivo: the feasibility of autoradiographic studies. Life Sci 22:203–210
Laduron PM, Janssen PFM, Leysen JE (1982) In vivo binding of [3H] ketanserin on serotonin S2-receptors in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 81:43–48
Leysen JE, Gommeren W, Van Gompel P, Wynants J, Janssen PFM, Laduron PM (1985) Receptor-binding properties in vitro and in vivo of ritanserin. Mol Pharm 27:600–611
List SJ, Seeman P (1981) Resolution of dopamine and serotonin receptor components of [3H]spiperone binding to rat brain regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:2620–2624
Madras BK, Canfield D, Fahey M, Spealman R (1988) D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in striatum of non-human primates (macaca facicularif). J Neurochem 50 (in press)
Mazière B, Loc'h C, Hantraye P, Guillon R, Duquesnoy N, Soussaline F, Naquet R, Comar D, Mazière M (1984) 76Br-Bromospiroperidol: a new tool for quantitative in-vivo imaging of neuroleptic receptors. Life Sci 35:1349–1356
Moerlein SM, Laufer P, Stöcklin G (1985) Effect of lipophilicity on the in vivo localization of radiolabelled spiperone analogues. Nucl Med Biol 12:353–356
Moerlein SM, Laufer P, Stöcklin G, Pawlik G, Wienhard K, Heiss W-D (1986) Evaluation of 75Br-labelled butyrophenone neuroleptics for imaging cerebral dopaminergic receptor areas using positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med 12:211–216
Nys GG, Rekker RF (1974) The concept of hydrophobic fragmental constants (f-values) II. Extension of its applicability to the calculation of lipophilicities of aromatic and heteroaromatic structures. Eur J Med Chem Chim Ther 9:361–375
Olsen RW, Reisine TD, Yamamura HI (1980) Neurotransmitter receptors-biochemistry and alterations in neuropsychiatric disorders. Life Sci 27:801–808
Otto CA, Sherman PS, Fisher SJ, Valoppi VL, Marshall JC, Lloyd RV, Rogers WL, Wieland DM (1986) Pituitary localization of 3H-spirperidol by an uptake/storage mechanism? Nucl Med Biol 13:533–537
Pastan JH, Willingham MC (1981) Receptor-mediated endocytosis of hormones in cultured cells. Ann Rev Physiol 43:239–250
Peroutka SJ, Snyder SM (1981) Two distinct serotonin receptors: regional variations in receptor binding in mammalian brain. Brain Res 208:339–347
Satyamurthy N, Bida G, Barrio JR, Luxen A, Mazziotta JC, Huang SC, Phelps ME (1986) No-carrier-added 3(2′-[18F]fluoroethyl)spiperone, a new dopamine receptor-binding tracer for positron emission tomography. Nucl Med Biol 13:617–624
Seemann P (1987) The absolute density of neurotransmitters in brain: example for dopamine receptors. J Pharmacol Methods 17:347–360
Schotte A, Maloteaux JM, Laduron PM (1983) Characterization and regional distribution of serotonin S2-receptors in human brain. Brain Res 276:231–235
Shiue C-Y, Fowler JS, Wolf AP, Watanabe M, Arnett CD (1985) Synthesis and specific activity determinations of no-carrier-added (nca) fluorine-18-labeled butyrophenone neuroleptics-ben-peridol, haloperidol, spiroperidol, and pipamperone. J Nucl Med 26:181–186
Shiue C-Y, Bai L-Q, Teng R-R, Wolf AP (1987) Synthesis of nocarrier-added (nca) [18F]fluoroalkylhalides and their application in the synthesis of [18F]fluoroalkyl derivatives of neurotransmitter receptor active compounds. J Label Comp Radiopharm 24:55–64
Thal LJ, Makman MH, Ahn HS, Mishra PK, Horowitz SG, Dvorkin B, Katzman R (1978) 3H-spiroperidol binding and dopamine-stimulated adenylate cyclase: evidence for multiple classes of receptors in primate brain regions. Life Sci 23:629–634
Wagner HN, Burns HD, Dannals RF, Wong DF, Langström B, Duelfer T, Frost JJ, Ravert HT, Links JM, Rosenbloom SB, Lukas SE, Kramer AV, Kuhar MJ (1983) Imaging dopamine receptors in the brain by positron tomography. Science 221:1264–1266
Welch MJ, Kilbourn MR, Mathias CJ, Mintun MA, Raichle ME (1983) Comparison in animal models of 18F-spiroperidol and 18F-haloperidol: potential agents for imaging the dopamine receptor. Life Sci 33:1687–1693
Welch MJ, Chi DY, Mathias CJ, Kilbourn MR, Brodack JW, Katzenellenbogen JA (1986) Biodistribution of N-alkyl and N-fluoroalkyl derivatives of spiroperidol; radiopharmaceuticals for PET studies of dopamine receptors. Nucl Med Biol 13:523–526
Wong DF, Wagner HN, Dannals RF, Links JM, Frost JJ, Ravert HT, Wilson AA, Rosenbaum AE, Gjedde A, Douglass KH, Petronis JD, Folstein MF, Toung JKT, Burns HD, Kuhar MJ (1984) Effects of age on dopamine and serotonin receptors measured by positron tomography in the living human brain. Science 226:1393–1396
Wong DF, Wagner HN, Tune LE, Dannals RF, Pearlson GD, Links JM, Tamminga CA, Broussolle EL, Ravert HT, Wilson AA, Toung JKT, Malat J, Williams JA, O'Tuama LA, Snyder SH, Kuhar MJ, Gjedde A (1986) Positron emission tomography reveals elevated D2 dopamine receptors in drugnaive schizophrenics. Science 234:1558–1563
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coenen, H.H., Wienhard, K., Stöcklin, G. et al. PET measurement of D2 and S2 receptor binding of 3-N-([2′-18F]fluoroethyl)spiperone in baboon brain. Eur J Nucl Med 14, 80–87 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253446
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253446