Abstract
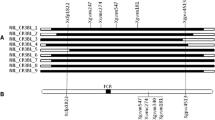
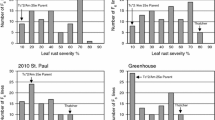
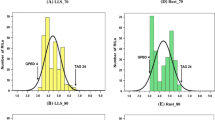
We report the tagging of genes involved in blackleg resistance, present in the French cultivar Crésor of B. napus, with RFLP markers. A total of 218 cDNA probes were tested on the parental cultivars Crésor (resistant) and Westar (susceptible), and 141 polymorphic markers were used in a segregating population composed of 98 doubled-haploid lines (DH). A genetic map from this cross was constructed with 175 RFLP markers and allowed us to scan for specific chromosomal associations between response to blackleg infection and RFLP markers. Canola residues infested with virulent strains of Leptosphaeria maculans were used as inoculum and a suspension of pycnidiospores from cultures of L. maculans, including the highly virulent isolate Leroy, was sprayed to increase disease pressure. QTL mapping suggested that a single chromosomal region was responsible for resistance in each of the four environments tested. This QTL accounted for a high proportion of the variation of blackleg reaction in each of the assays. A second QTL, responsible for a small proportion of the variation of blackleg reaction, was present in one of four year-site assays. A Mendelian approach, using blackleg disease ratings for classifying DH lines as resistant or susceptible, also allowed us to map resistance in the region of the highly significant LOD scores observed in each environment by interval mapping. Results strongly support the presence of a single major gene, named LmFr 1 controlling adult plant resistance to blackleg in spring oil-seed rape cultivar Crésor. Several RFLP markers were found associated with LmFr 1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cargeeg LA, Thurling N (1980) Contribution of host-pathogen interactions to the expression of the blackleg disease of spring rape (Brassica napus L.) caused by Leptospaeria maculans (Desm.) Ces. et de Not. Euphytica 29:465–476
Delourme R, Bouchereau A, Hubert N, Renard M, Landry BS (1994) Identification of RAPD markers linked to a fertility restorer gene for Ogura radish cytoplasmic male sterility of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 88:741–748
Delwiche PA (1980) Genetic aspects of blackleg (Leptosphaeria maculans) resistance in rapeseed (Brassica napus). PhD thesis, University of Wisconsin, Madison, USA
Ferreira M, Teutonico R, Osborn T (1993) Mapping trait loci in oilseed Brassica. Proc 8th Crucifer Geneti Wksh. July 21–24, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada: 10
Goodwin PH, Annis SL, Xue BG (1993) PCR applications to differentiate pathotypes of Leptosphaeria maculans. Blackleg News 1:5
Gugel RK, Petrie GA (1992) History, occurrence, impact and control of blackleg of rapeseed. Can J Plant Pathol 14:36–45
Hall R (1992) Epidemiology of blackleg of oilseed rape. Can J Plant Pathol 14:46–55
Hammond KE, Lewis (1987). Variation in stem infections caused by aggressive and non-agressive isolates of Leptosphaeria maculans on Brassica napus var. oleifera. Plant Pathol 36:53–65
Harada JJ, Baden CS, Comai L (1988) Spatially regulated genes expressed during seed germination and post-germinative development are activated during embryogeny. Mol Gen Genet 212:466–473
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daley M, Lincoln S, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Landry BS, Hubert N, Eton T, Harada JJ, Lincoln SE (1991) A genetic map for Brassica napus based on restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP) detected with expressed DNA sequences. Genome 34:543–552
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander E (1992a) Constructing Genetic Maps with MAPMAKER/EXP 3.0. Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research. Technical Report, 3rd ed., Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander E (1992b) Mapping genes controlling quantitative traits with MAPMAKER/QTL 1.1. Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research. Technical Report, 2nd edn., Cambridge Massachusetts, USA
Mithen RF, Lewis BG, Heaney RK, Fenwick GR (1987) Resistance of leaves of Brassica species to Leptosphaeria maculans. Trans Br Mycol Soc 88:525–531
Monteiro AA, Williams PH (1989) The exploration of genetic resources of Portuguese cabbage and kale for resistance to several Brassica diseases. Euphytica 41:215–225
Morales VM, Séguin-Swartz G, Taylor JL (1993) Chromosome size polymorphism in Leptosphaeria maculans. Phytopathology 83:503–509
Paterson A, Lander E, Lincoln S, Hewitt J, Peterson S, Tanksley S (1988) Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors using a complete RFLP linkage map. Nature 335:721–726
Rimmer SR, van den Berg CGJ (1992) Resistance of oilseed Brassica spp to blackleg caused by Leptosphaeria maculans. Can J Plant Pathol 14:56–66
Roy NN (1978) A study on disease variation in the populations of an interspecific cross of Brassica juncea L.xB. napus L. Euphytica 27:145–149
Salisbury P, Ballinger D (1993) Race variability in Leptosphaeria maculans. Blackleg News 1:3–4
Sawatsky WM (1989) Evaluation of screening techniques for resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans and genetic studies of resistance to the disease in Brassica napus. MSc thesis, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Canada
Sippell DW, McNabb W, Hall R, Patel J (1991) Inheritance of resistance to blackleg (Leptosphaeria maculans) of canola. Proc 8th GCIRC Congress, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada vol 1:232-237
Sjödin C, Glimelius K (1988) Screening for resistance to blackleg Phoma lingam (Tode ex Fr.) Desm. within Brassicaceae. J Phytopathol 123:322–332
Stringam GR, Bansal VK, Thiagarajah MR, Tewari JP (1992) Genetic analysis of blackleg (Leptosphaeria maculans) resistance in Brassica napus L. using the doubled haploid method. XIII Eucarpia Congress, July 6–11, Angers, France
Thurling N, Venn LA (1977). Variation in the response of rapeseed (Brassica napus and B. campestris) cultivars to blackleg (Leptosphaeria maculans) infection. Aust J Exp Agric Anim Husb 17:445–451
Wahl GM, Stern M, Stark GR (1979) Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:3683–3687
Williams PH (1992) Biology of Leptosphaeria maculans. Can J Plant Pathol 14:30–35
Wittern I (1984) Untersuchungen zur Erfassung der Resistenz von Winterraps (Brassica napus L. var. oleifera Metzger) gegenüber Phoma lingam (Tode ex Fr.) Desm. und zu der durch den Erreger verursachten Wurzelhals- und Stengelfäule. PhD thesis, Universität Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dion, Y., Gugel, R.K., Rakow, G.F.W. et al. RFLP mapping of resistance to the blackleg disease [causal agent, Leptosphaeria maculans (Desm.) Ces. et de Not.] in canola (Brassica napus L.). Theoret. Appl. Genetics 91, 1190–1194 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220928
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220928