Summary
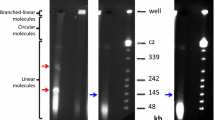
The linear N1 and N2 plasmid-like DNAs were recovered from mitochondria of the IS1112C line of cytoplasmic male-sterile (CMS) Sorghum bicolor (S. bicolor). Molecular clones containing internal sequences of these plasmids were constructed. These clones were used to probe Southern blots of mitochondrial genomes from six CMS and five male-fertile (MF) lines of S. bicolor, as well as Southern blots of IS1112C chloroplast, IS1112C nuclear and kafir nuclear genomes. We found no evidence for integrated copies of N1 or N2 in any of the mitochondrial, chloroplast or nuclear genomes probed in this study. Our clones did detect an N1-homologous transcript of 3.1 kb and N2-homologous transcripts of 3.9 and 1.4 kb in IS1112C mitochondrial RNA prepared from lines with and without nuclear, fertility-restoring genes.
N1 and N2 DNAs were degraded by exonuclease III but were resistant to lambda exonuclease, presumably due to the presence of 5′ terminal proteins. We detected multimeric forms of N1 and N2 in Southern blots of unrestricted, IS1112C mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). These forms apparently also had associated protein molecules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchert JG: The stage of the genome — plasmon interaction in the restoration of fertility to cytoplasmically pollen sterile maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 47:1436–1440, 1961.
Dixon LK, Leaver CJ: Mitochondrial gene expression and cytoplasmic male sterility in sorghum. Plant Mol Biol 1:89–102, 1982.
Hallick RB, Chelm BK, Gray PW, Orozco EMJr: Use of aurintricarboxylic acid as an inhibitor of nucleases during nucleic acid isolation. Nucl Acids Res 4:3055–3063, 1977.
Hanson MR, Conde MF: Functioning and variation of cytoplasmic genomes: lessons from cytoplasmic-nuclear interactions affecting male fertility in plants. Int Rev Cytol 94:214–267, 1984.
Harding NE, Ito J, David GS: Identification of the protein firmly bound to the ends of bacteriophage Φ 29 DNA. Virol 84:279–292, 1978.
Kemble RJ, Thompson RD: S1 and S2, the linear mitochondrial DNAs present in a male sterile line of maize, possess terminally attached proteins. Nucl Acids Res 10:8131–8190, 1982.
Kemble RJ, Gunn RE, Flavell RB: Mitochondrial DNA variation in races of maize indigenous to Mexico. Theor Appl Genet 65:129–144, 1983.
Kemble RJ, Mans RJ: Examination of the mitochondrial genome of revertant progeny from S cms maize with cloned S-1 and S-2 hybridization probes. J Mol Appl Genet 2:161–171, 1983.
Kemble RJ, Mans RJ, Gabay-Laughnan S, Laughnan JR: Sequences homologous to episomal mitochondrial DNAs in the maize nuclear genome. Nature 304:744–747, 1983.
Laughnan JR, Gabay-Laughnan S, Carlson JE: Characteristics of cms-S reversion to male fertility in maize. Stadler Symp 13:93–114, 1981.
Levings CSIII, Pring DR: Diversity of mitochondrial genomes among normal cytoplasms of maize. J Hered 68:350–354, 1977.
Levings CSIII, Kim BD, Pring DR, Conde MF, Mans RJ, Laughnan JR, Gabay-Laughnan SJ: Cytoplasmic reversion of cms-S in maize: association with a transpositional event. Science 209:1021–1023, 1980.
Levings CSIII, Sederoff RR: Nucleotide sequence of the S-2 mitochondrial DNA from the S cytoplasm of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4055–4059, 1983.
Levings CSIII, Sederoff RR, Hu WWL, Timothy DH: Relationships among plasmid-like DNAs of the maize mitochondria. In: Ciferri O, Dure LIII (eds) Structure and Function of Plant Genomes. Plenum Press, New York, pp 363–371, 1983.
Lonsdale DM, Thompson RD, Hodge TP: The integrated forms of the S1 and S2 DNA elements of maize male-sterile mitochondrial DNA are flanked by a large repeated sequence. Nucl Acid Res 9:3657–3669, 1981.
McNay JW, Pring DR, Lonsdale DM: Polymorphism of mitochondrial DNA ‘S’ regions among normal cytoplasms of maize. Plant Mol Biol 2:177–187, 1983.
Palmer JD, Shields CR, Cohen DB, Orton TJ: An unusual mitochondrial DNA plasmid in the genus Brassica. Nature 301:725–728, 1983.
Pring DR, Levings CSIII, Hu WWL, Timothy DH: Unique DNA associated with mitochondria in the ‘S’-type cytoplasm of male-sterile maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 74:2904–2908, 1977.
Pring DR, Conde MF, Schertz KF, Levings CSIII: Plasmid-like DNAs associated with mitochondria of cytoplasmic male-sterile sorghum. Mol Gen Genet 186:180–184, 1982.
Radding CM: Regulation of lambda exonuclease. I. Properties of lambda exonuclease purified from lysogens of lambda T11 and wild type. J Mol Biol 18:235–250, 1966.
Rekosh DMK, Russell WC, Bellet AJD, Robinson AJ: Identification of a protein linked to the ends of adenovirus DNA. Cell 11:283–295, 1977.
Richardson CC, Lehman IR, Kornberg A: A deoxyribonucleic acid phosphatase-exonuclease from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 239-251-258, 1964.
Rigby PWJ, Dieckman M, Rhoades C, Berg P: Labeling deoxy-ribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol 113:237–251, 1977.
Schardl CL, Lonsdale DM, Pring DR, Rose KR: Linearization of maize mitochondrial chromosomes by recombination with linear episomes. Nature 310:292–296, 1984.
Schardl CL, Fauron CM, Lonsdale DM, Pring DR: Mitochondrial DNA rearrangements resulting in fertile revertants of S-type male sterile maize. 1984 (submitted).
Southern EM: Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517, 1975.
Stern DB, Newton KJ: Isolation of intact plant mitochondrial RNA using Aurintricarboxylic acid. Plant Mol Biol Reporter 2:8–15, 1984.
Thomas PS: Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted to nitrocellulose paper. Methods in Enzymol 100:255–266, 1983.
Thompson RD, Kemble RJ, Flavell RB: Variations in mitochondrial DNA organization between normal and male-sterile cytoplasms of maize. Nucl Acids Res 8:1999–2008, 1980.
Timothy DH, Levings CSIII, Hu WWL, Goodman MM: Plasmid-like mitochondrial DNAs in diploperennial teosinte. Maydica 28:139–149, 1983.
Weissinger AK, Timothy DH, Levings CSIII, Goodman MM: Patterns of mitochondrial DNA variation in indigenous maize races of Latin America. Genetics 104:365–379, 1983.
Wilson JW, Chourey PS: A rapid inexpensive method for the isolation of restrictable mitochondrial DNA from various plant sources. Plant Cell Rept 3:237–239, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
United States Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Research Service, Plant Science Research Unit
Mention of a trademark, proprietary product, or vendor does not constitute a guarantee of the product by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and does not imply its approval to the exclusion of other products or vendors that may also be suitable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chase, C.D., Pring, D.R. Properties of the linear N1 and N2 plasmid-like DNAs from mitochondria of cytoplasmic male-sterile Sorghum bicolor . Plant Mol Biol 6, 53–64 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00021306
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00021306