Abstract
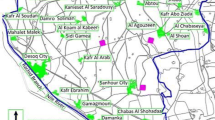
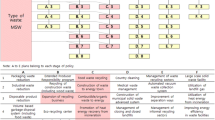
Qatar is one of the most developed countries that became the ideal destination for residence, which led to an increase in the population and this resulted in an increase in the solid waste generation in the country. The paper proposes models and approaches for selecting the waste transfer station locations in Qatar. Optimization models were developed to describe four different configurations that attempt to optimize the current and future system. The four configurations are the result of several combinations of employing permanent or temporary waste transfer stations that accept single or multiple types of wastes. Among the considered configurations the results showed that the best one consists in selecting three out of five existing waste transfer stations, three permanent potential sites and, four temporary waste transfer stations which results in a minimum overall cost compared to the other models output.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balakrishnan, P., Harish, M. and Al-Kuwari, M., 2019. Urban Solid Waste Management using Geographic Information Systems (GIS): A Case Study in Doha, Qatar. International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS, 8(1), pp.2901-2918.
Zafar, S. 2016. Solid Waste Management in Qatar. Available from: https://www.ecomena.org/solid-waste-management-in-qatar/.
Clarke, S., Nawaz, W., Skelhorn, C. and Amato, A., 2017. Towards a more sustainable waste management in Qatar: Retrofitting mindsets and changing behaviours. QScience Connect, 2017(1), 4.
Death, C. (2011). ‘Greening’ the 2010 FIFA World Cup: Environmental Sustainability and the Mega-Event in South Africa. J. of Environmental Policy & Planning, 13(2), 99-117.
Dragan, U., Milorad, V., & Makajić-Nikolić, D. (2018). XIII Balkan Conference on Operational Research (pp. 174–178). Belgrade, Serbia: The Mathematical Institute of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts (SANU) Kneza Mihaila 36, 11001.
EcoMENA. (2018b). Solid waste management in qatar. Retrieved from https://www.ecomena.org/solid-waste-management-in-qatar/.
Farah I. A. 2016. “Sustainable Solutions For Domestic Solid Waste Management in Qatar”, Qatar University.
Grichting. (2013). Scales of Flows: Qatar And the Urban Legacies of Mega Events. International Journal of Architectural Research, 7(2), 173-191.
Habibi, F., Asadi, E., Sadjadi, S., & Barzinpour, F. (2016). A multi-objective robust optimization model for site-selection and capacity allocation of municipal solid waste facilities: A case study in Tehran. Journal Of Cleaner Production, 166, 816-834.
Hoornweg, D., Bhada-Tata, P., 2012. What a waste: a global review of solid waste man,,agement. In: World Bank Washington, D. (Ed.), World Bank Washington, DC.
Kirca, O., Erkip, N., 1988. Selecting transfer station locations for large solid waste systems. Eur. J. Operational Res. 35, 339e349.
McDougall F, White P, Franke M, Hindle P. 2001. Integrated Solid Waste Management: A Life Cycle Inventory. Oxford, UK/Malden, MA: Blackwell Sci. 2nd ed.
Meza Talavera, Abel; Al-Ghamdi, Sami G.; Koç, Muammer. 2019. "Sustainability in Mega-Events: Beyond Qatar 2022" Sustainability 11, no. 22: 6407.
Ramachandra T, Bachamanda S (2007). Environmental audit of municipal solid waste management. International J. of Environmental Technology and Management7:369–391.
Sharholy, M., Ahmad, K., Mahmood, G., & Trivedi, R. C. (2008). Municipal solid waste management in Indian cities–A review. Waste management, 28(2), 459-467.
Sustainability Report - FIFA. resources.fifa.com/image/upload/sustainability-report-of-the-2014-fifa-world-cup-2509269.pdf?cloudid=educsd2hgasief3yeoyt.
Tanmoy Karak , R. M. Bhagat andPradip Bhattacharyya (2012) Municipal Solid Waste Generation, Composition, and Management: The World Scenario, Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 42:15, 1509-1630
Tolba, M.K. and Saab, N.W. (2008). Arab environment future challenges. Technical Publications and Environment & Development magazine.
Triki C. (2017). Solving the Periodic Edge Routing Problem in the Urban Waste Collection. Asia-Pacific Journal of Operational Research 34(3), 1-13
Yadav, V., Bhurjee, A., Karmakar, S., & Dikshit, A. (2017). A facility location model for municipal solid waste management system under uncertain environment. Science of the Total Environment, 603–604, 760–771.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nasr, S., Triki, C. (2022). Sustainable Optimization of the Wastes Transfer Stations Location During FIFA-2022 in Qatar. In: Ha-Minh, C., Tang, A.M., Bui, T.Q., Vu, X.H., Huynh, D.V.K. (eds) CIGOS 2021, Emerging Technologies and Applications for Green Infrastructure. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 203. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7160-9_172
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7160-9_172
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-7159-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-7160-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)