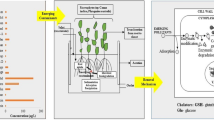
Abstract
Sewage generation in India accounts for 61,754 million liters per day (MLD) in urban areas, where 22,963 MLD is treated and 38791MLD remains untreated. Due to the ever-increasing population explosion and urbanization, sewage effluent generation has been increasing. Sewage effluent is a kind of wastewater comprising of 99.9% water content along with TDS (total dissolved solids), TSS (total suspended solids), heavy metals, nitrogen, phosphorus, and also waterborne pathogens. Because of its enriched nutrient, supply can be utilized for irrigation, thereby reducing the water demands for sustainable agriculture. Though many conventional technologies are available for treating sewage, CWT (constructed wetland technology) with low maintenance and simple construction looks very promising. In this technique, macrophytes and the filtration medium play a dynamic role in eradicating the pollutants in sewage. Macrophytes utilized in CWT enhance the pollutant removal mechanism by creating oxygenated environments around the rhizosphere of plants. This chapter explains the role of macrophytes, their remediation potential, types, and mechanisms involved in constructed wetland technology to treat the sewage effluent for its effective utilization for sustainable agriculture.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari, S., Gupta, S. K., & Banerjee, S. K. (1997). Long-term effect of raw sewage application on the chemical composition of groundwater. Journal of the Indian Society of Soil Science, 45, 392–394.
Anderson, T. A., Guthrie, E. A., & Walton, B. T. (1993). Bioremediation in the rhizosphere. Environmental Science and Technology, 27(13), 2630–2636. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00049a001.
Arora, B. R., Azad, A. S., Singh, B., & Sekhon, G. S. (1985). Pollution potential of municipal wastewaters of Ludhiana, Punjab. Indian Journal of Ecology, 12, 1–7.
Bais, H. P., Weir, T. L., Perry, L. G., Gilroy, S., & Vivanco, J. M. (2006). The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 57, 233–266. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105159.
Bhattacharya, T., Banerjee, D. K., & Gopal, B. (2006). Heavy metal uptake by Scirpus littoralis schrad. From fly ash dosed and metal spiked soils. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 121(1–3), 363–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9133-1.
Bonanno, G., Borg, J. A., & Di Martino, V. (2017). Levels of heavy metals in wetland and marine vascular plants and their biomonitoring potential: A comparative assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 576, 796–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.171.
Bravo, S., Amorós, J. A., Pérez-de-los-Reyes, C., García, F. J., Moreno, M. M., Sánchez-Ormeño, M., & Higueras, P. (2017). Influence of the soil pH in the uptake and bioaccumulation of heavy metals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Pb and Mn) and other elements (Ca, K, Al, Sr and Ba) in vine leaves, Castilla-la Mancha (Spain). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 174, 79–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.12.012.
Brisson, J., & Chazarenc, F. (2009). Maximizing pollutant removal in constructed wetlands: Should we pay more attention to macrophyte species selection? Science of the Total Environment, 407(13), 3923–3930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.05.047.
Brix, H., & Arias, C. A. (2005). The use of vertical flow constructed wetlands for the onsite treatment of sewage wastewater: New Danish guidelines. Ecological Engineering, 25(5), 491–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2005.07.009.
Chen, J., Wei, X. D., Liu, Y. S., Ying, G. G., Liu, S. S., He, L. Y., Su, H. C., Hu, L. X., Chen, F. R., & Yang, Y. Q. (2016). Removal of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes from domestic sewage by constructed wetlands: Optimization of wetland substrates and hydraulic loading. Science of the Total Environment, 565(15), 240–248.
Coppella, S. J., DelaCruz, N. D., Payne, G. F., Pogell, B. M., Speedie, M. K., Karns, J. S., … Connor, M. A. (1990). Genetic engineering approach to toxic waste management case study for organophosphate waste treatment. Biotechnology Progress, 6(1), 76–81. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp00001a012.
Dan, A., Oka, M., Fujii, Y., Soda, S., Ishigaki, T., & Machimura, T. (2017). Removal of heavy metals from synthetic landfill leachate in lab-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands. ke, M. Science of the Total Environment, 584, 742–775.
Durán, N., & Esposito, E. (2000). Potential applications of oxidative enzymes and phenoloxidase-like compounds in wastewater and soil treatment: A review. Applied Catalysis, B: Environmental, 28(2), 83–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(00)00168-5. Enzym, B., 28, 83–99.
Gianfreda, L., & Bollag, J.-M. (2002). Isolated enzymes for the transformation and detoxification of organic pollutants. In R. G. Burns & R. Dick (Eds.), Enzymes in the environment: Activity, ecology and applications (pp. 491–538). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Gianfreda, L., Iamarino, G., Scelza, R., & Rao, M. A. (2006). Oxidative catalysts for the transformation of phenolic pollutants: A brief review. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation, 24(3), 177–187. https://doi.org/10.1080/10242420500491938.
Gianfreda, L., & Rao, M. A. (2004). Potentials of extracellular enzymes in remediation of polluted soils: A review. Enzyme and Microbial Technology 35(4), 339–354.
Gupta, S. K., & Mitra, A. (2002). Advances in land resource management for 21st. Century (pp. 446–469). New Delhi: Soil Conservation Society of India.
Gupta, A. P., Antil, R. S., & Singh, A. (1986). CSIO. Proceedings of the National Seminar on environmental pollution control and monitoring (pp. 419–425). Chandigarh, India: October 22–26.
Kong, L., Wang, Y.-B., Zhao, L.-N., & Chen, Z.-H. (2009). Enzyme and root activities in surface-flow constructed wetlands. Chemosphere, 76(5), 601–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.04.056.
Kumar, J. E., Suganya, K., Sebastian, S. P., & Kannan, T. G. (2019). Changes in physico-chemical characteristics of the sewage effluent under constructed wetland technology treatment. The Madras Agricultural Journal, 106(13), 58–62.
Ladislas, S., Gérente, C., Chazarenc, F., Brisson, J., & Andrès, Y. (2015). Floating treatment wetlands for heavy metal removal in highway stormwater ponds. Ecological Engineering, 80, 85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.09.115.
Lee, C. G., Fletcher, T. D., & Sun, G. (2009). Nitrogen removal in constructed wetland systems. Engineering in Life Sciences, 9(1), 11–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.200800049.
Leung, H. M., Duzgoren-Aydin, N. S., Au, C. K., Krupanidhi, S., Fung, K. Y., & Cheung, K. C. (2017). Monitoring and assessment of heavy metal contamination in a constructed wetland in Shaoguan (Guangdong Province, China): Bioaccumulation of Pb, Zn, Cu and Cd in aquatic and terrestrial components. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 24(10), 9079–9088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6756-4.
Mojiri, A. (2012). Phytoremediation of heavy metals from municipal wastewater by Typha domingensis. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 6, 643–647.
Morari, F., Dal Ferro, N., & Cocco, E. (2015). Municipal wastewater treatment with Phragmites australis L. and Typha latifolia L. for irrigation reuse. Boron and heavy metals. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 226(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2336-3.
Mulbry, W. W., & Eaton, R. W. (1991). Purification and characterization of the N-methylcarbamate hydrolase from Pseudomonas strain CRL-OK. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 57(12), 3679–3682. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.57.12.3679-3682.1991.
Narwal, R. P., Gupta, A. P., Singh, A., & Karwasra, S. P. S. (1993). Composition of some city waste waters and their effect on soil characteristics. Annals of Biology, 9, 239–245.
Nguyen, X. C., Chang, S. W., Nguyen, T. L., Ngo, H. H., Kumar, G., Banu, J. R., Vu, M. C., Le, H. S., & Nguyen, D. D. (2018). A hybrid constructed wetland for organic-material and nutrient removal from sewage: Process performance and multi-kinetic models. Journal of Environmental Management, 222, 378–384.
Nowak, R., & Imperowicz, A. (2016). Liquid waste from septic tanks as a source of microbiological pollution of groundwater. Inżynieria Ekologiczna, 10(47), 60–67. https://doi.org/10.12912/23920629/62848.
Palamuleni, L. G. (2002). Effect of sanitation facilities, domestic solid waste disposal and hygiene practices on water quality in Malawi’s urban poor areas: A case study of South Lunzu Township in the city of Blantyre. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 27(11–22), 845–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-7065(02)00079-7.
Pedescoll, A., Sidrach-Cardona, R., Hijosa-Valsero, M., & Bécares, E. (2015). Design parameters affecting metals removal in horizontal constructed wetlands for domestic wastewater treatment. Ecological Engineering, 80, 92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.10.035.
Rai, P. K. (2019). Heavy metals/metalloids remediation from wastewater using free floating macrophytes of a natural wetland. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100393, PubMed: 100393.
Rodríguez Couto, S., & Toca Herrera, J. L. (2006). Industrial and biotechnological applications of laccases: A review. Biotechnology Advances, 24(5), 500–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2006.04.003.
Ryan, P. R., Delhaize, E., & Jones, D. L. (2001). Function and mechanism of organic anion exudation from plant roots. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 52, 527–560. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.527.
Saeed, T., & Sun, G. (2012). A review on nitrogen and organics removal mechanisms in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Dependency on environmental parameters, operating conditions and supporting media. Journal of Environmental Management, 112, 429–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.08.011.
Shelef, O., Gross, A., & Rachmilevitch, S. (2013). Role of plants in a constructed wetland: Current and new perspectives. Water, 5(2), 405–419. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5020405.
Singh, J., & Kansal, B. D. (1985). Amount of heavy metal in the waste water of different towns of Punjab and its evaluation for irrigation. Journal of Research. Punjab Agricultural University,, 22, 17–24.
Suganya, K. (2017). Pollutant removal efficiency of hybrid constructed wetland system for recycling the sewage by utilizing aquatic plants. The Madras Agricultural Journal, 104(4–6), 121–123.
Suganya, K., & Sebastian, S. P. (2017). Phytoremediation prospective of Indian shot (Canna indica) in treating the sewage effluent through hybrid reed bed (HRB) technology. International Journal of Chemical Studies, 5(4), 102–105.
Sukumaran, D. (2013). Phytoremediation of heavy metals from industrial effluent using constructed wetland technology. Applied Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 1(5), 92–97. https://doi.org/10.12691/aees-1-5-4.
Sutherland, T., Russell, R., & Selleck, M. (2002). Using enzymes to clean pesticide residues. Pesticide Outlook, 13(4), 149–151. https://doi.org/10.1039/b206783h.
Tiwana, N. S., Panesar, R. S., & Kansal, B. D. (1987). Nanital, India. Proceedings of the national seminar on impact of environmental protection for future development of India (pp. 119–126).
Torres, E., Bustos-Jaimes, I., & Le Borgne, S. (2003). Potential use of oxidative enzymes for the detoxification of organic pollutants. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 46(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(03)00228-5.
Vymazal, J. (2007). Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Science of the Total Environment, 380(1–3), 48–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.09.014.
Walker, T. S., Bais, H. P., Grotewold, E., & Vivanco, J. M. (2003). Root exudation and rhizosphere biology. Plant Physiology, 132(1), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.102.019661.
Wu, H., Wang, X., & He, X. (2017). Effects of selected root exudate components on nitrogen removal and development of denitrifying bacteria in constructed wetlands. Water, 9(6), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9060430.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Suganya, K. et al. (2022). Exploring the Phytoremediation Potential of Macrophytes for Treating Sewage Effluent Through Constructed Wetland Technology (CWT) for Sustainable Agriculture. In: Bandh, S.A. (eds) Sustainable Agriculture. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-83066-3_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-83066-3_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-83065-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-83066-3
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)