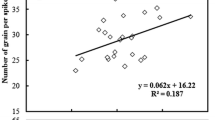
Abstract
Deficiency of micronutrients such as zinc (Zn) and iron (Fe) is a worldwide nutritional constraint in crop production particularly in growth, yield, and grain nutrient of crops, especially cereals such as wheat and rice in calcareous soils. On the other hand, Zn is an important nutrient for the growth and development of animals and humans and shortage in food causes severe damages economically due to malnutrition considerations. Micronutrient malnutrition in humans in developing countries is derived from deficiencies of these elements in staple food. Many approaches have been chosen to increase the Zn and Fe content in crops and ameliorate their malnutrition, including breeding, genetic engineering, and agronomic approaches. In this study, effects of agronomic biofortification components including different dose, proper stage of application, and effective method of micronutrient application are investigated on quantitative and qualitative yield of crops. The investigations of agronomy showed that micronutrient has an important role in the improvement of quantitative and qualitative crop yield. Hence, application of micronutrients such as Zn increased the grain yield due to its effect on the number of fertile spikelet per spike, number of grains per spike, and other agronomic traits. Also, this nutrient increased Zn and other micronutrient concentration in grain, grain protein, amino acid contents, and ascorbic acid content in grain but decreased phytic acid (PA) content and PA/Zn molar ratio in grain crops in most cases which increased bioavailability of micronutrients for human. In most cases, micronutrient application through foliar treatment performed better than other application methods. Studies indicated that application of micronutrients especially Zn and Fe led to increase in grain yield as well as positive aspects of seed quality and decrease in seeds’ negative qualities. Therefore, this approach (agronomic biofortification) can be used as appropriate short-term strategy, capable of improving quantitative and qualitative food security.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ascorbic acid:
-
AsA
- Boron:
-
B
- Cadmium:
-
Cd
- Calcium carbonate:
-
CaCO3
- Calcium:
-
Ca
- Copper:
-
Cu
- Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid:
-
DTPA
- 2-deoxymugineic acid:
-
DMA
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid:
-
EDTA
- Ethylenediamine N,N′ di(2-hydroxy-4-methylphenylacetic) acid:
-
EDDHMA
- Ethylenediamine-N,N′-bis 2-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid:
-
EDDHA
- Glutamine synthetase:
-
GS
- Hectoliter weight:
-
HLW
- Humic acid:
-
HA
- Iodine:
-
I
- Iron sulfate:
-
FeSO4
- Iron:
-
Fe
- Magnesium:
-
Mg
- Manganese:
-
Mn
- Molybdenum:
-
Mo
- Nicotianamine:
-
NA
- Nitrate reductase:
-
NR
- Nitrogen:
-
N
- Phosphorus:
-
P
- Phytic acid:
-
PA
- Potassium:
-
K
- Ribonucleic acid:
-
RNA
- Salicylic acid:
-
SA
- Selenium:
-
Se
- Sodium:
-
Na
- Sulfur:
-
S
- Total daily absorbed Zn:
-
TAZ
- World Health Organization:
-
WHO
- Zinc sulfate heptahydrate:
-
ZnSO4.7H2O
- Zinc sulfate:
-
ZnSO4
- Zinc oxide:
-
ZnO
- Zn-amino acids:
-
Zn-AA
- Zn-loaded chitosan nanocarriers:
-
Zn-CNP
- Zinc:
-
Zn
References
Abbas, G., Khan, M. Q., Khan, M. J., Hussain, F., & Hussai, I. (2009). Effect of iron on the growth and yield contributing parameters of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences, 19, 135–139.
Abdoli, M., & Esfandiari, E. (2014). Effect of zinc foliar application on the quantitative and qualitative yield and seedlings growth characteristics of bread wheat (cv. Kohdasht). Iranian Journal of Dryland Agriculture, 2(1), 77–90.
Abdoli, M., & Esfandiari, E. (2017). Effect of seed zinc content on vigor and seedling growth parameters of wheat grown in different levels of salinity. International Journal of Advanced Life Sciences, 10(2), 263–271. https://doi.org/10.26627/IJALS/2017/10.02.0016.
Abdoli, M., Esfandiari, E., Mousavi, S. B., Sadeghzadeh, B., & Saeidi, M. (2016a). The effect of seed zinc internal content and foliar application of zinc sulfate on yield and storage compositions of wheat grain. Crop Physiology Journal, 28, 91–106.
Abdoli, M., Esfandiari, E., Sadeghzadeh, B., & Mousavi, S. B. (2016b). Zinc application methods affect agronomy traits and grain micronutrients in bread and durum wheat under zinc-deficient calcareous soil. Yuzuncu Yil University Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 26(2), 202–214.
Abdoli, M., Esfandiari, E., & Taheri, R. (2018). Assessment iron application to improve agro-morphological traits and biofortification of grain wheat grown in different nitrogen conditions. Journal of Crop Nutrition Science, 4(1), 60–77.
Aboutalebian, M. A., Fakhimi Paydar, N., & Nazari, S. (2017). Effect of application methods of phosphate and zinc sulfate fertilizers on water use efficiency and qualitative characteristics of corn under water deficit stress. Iranian Journal of Field Crop Science. Special Issue, 11–19. https://doi.org/10.22059/ijfcs.2017.63649.
Aciksoz, S.B., Yazici, A., & Cakmak, I. (2010, August 1–6). Effect of nitrogen and iron fertilizers on grain concentration of iron in wheat. 19th World Congress of Soil Science. Brisbane, Australia.
Akram, M. A., Depar, N., & Memon, M. Y. (2017). Synergistic use of nitrogen and zinc to bio-fortify zinc in wheat grains. Eurasian Journal of Soil Science, 6(4), 319–326. https://doi.org/10.18393/ejss.306698.
Ali, E. A. (2012). Effect of iron nutrient care sprayed on foliage at different physiological growth stages on yield and quality of some durum wheat (Triticum durum L.) varieties in sandy soil. Asian Journal of Crop Science, 4(4), 139–149. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajcs.2012.139.149.
Ali, S., Shah, A., Arif, M., Miraj, G., Ali, I., Sajjad, M., Farhatollah, M., Khan, Y., & Moula Khan, M. (2009). Enhancement of wheat grain yield components through foliar application of zinc and boron. Sarhad Journal of Agriculture, 25(1), 15–19.
Arazmjoo, E., Behdani, M. A., Mahmoodi, S., & Sadeghzadeh, B. (2019). Biofortification of new and old bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars through foliar application of zinc and iron different forms. Journal of Agroecology, 11(2), 453–466.
Arif, M., Dashora, L. N., Choudhary, J., Kadam, S. S., & Mohsin, M. (2019). Effect of varieties and nutrient management on quality and zinc biofortification of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 89(9), 1472–1476.
Astolfi, S., Cesco, S., Zuchi, S., Neumann, G., & Roemheld, V. (2006). Sulphur starvation reduces phytosiderophores release by Fe-deficient barley plants. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, 52(1), 43–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2006.00010.x.
Astolfi, S., Pii, Y., Terzano, R., Mimmo, T., Celletti, S., Allegretta, I., Lafiandra, D., & Cesco, S. (2018). Does Fe accumulation in durum wheat seeds benefit from improved whole-plant sulfur nutrition? Journal of Cereal Science, 83, 74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2018.07.010.
Astolfi, S., Zuchi, S., Cesco, S., Varanini, Z., & Pinton, R. (2004). Influence of iron nutrition on sulphur uptake and metabolism in maize (Zea mays L.) roots. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, 50(7), 1079–1083. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2004.10408577.
Astolfi, S., Zuchi, S., Hubberten, H. M., Pinton, R., & Hoefgen, R. (2010). Supply of sulphur to S-deficient young barley seedlings restores their capability to cope with iron shortage. Journal of Experimental Botany, 61(3), 799–806. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp346.
Aziz-Zade Firozy, F., Bahman Yar, A., Momeny, V., & Ghasem Por, A. (2004). Effect of potassium fertilizers on the agronomic characteristics and quantities of zinc, iron and phosphorus in two wheat cultivars on calcareous soil with low. Proceedings of the 10th Iranian Crop Sciences Congress, Karaj, Iran.
Barunawati N, Giehl RFH, Bauer B, vonWiren N (2013) The influence of inorganic nitrogen fertilizer forms on micronutrient retranslocation and accumulation in grains of winter wheat. Frontiers in Plant Science 4:320. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00320.
Barut, H. (2019). Effects of foliar urea, potassium and zinc sulphate treatments before and after flowering on grain yield, technological quality and nutrient concentrations of wheat. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 17(2), 4325–4342. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1702_43254342.
Barut, H., Şimşek, T., Irmak, S., Sevilmiş, U., & Aykanat, S. (2017). The effect of different zinc application methods on yield and grain zinc concentration of bread wheat varieties. Turkish Journal of Agriculture—Food Science and Technology, 5(8), 898–907. https://doi.org/10.24925/turjaf.v5i8.898-907.1224.
Benedicto, A., Hernández-Apaolaza, L., Rivas, I., & Lucena, J. J. (2011). Determination of 67Zn distribution in navy bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) after foliar application of 67Zn-lignosulfonates using isotope pattern deconvolution. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 59(16), 8829–8838. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2002574.
Bharti, K., Pandey, N., Shankhdhar, D., Srivastava, P. C., & Shankhdhar, S. C. (2013). Improving nutritional quality of wheat through soil and foliar zinc application. Plant Soil, and Environment, 59(8), 348–352.
Bohn, L., Meyer, A. S., & Rasmussen, S. K. (2008). Phytate: Impact on environment and human nutrition. A challenge for molecular breeding. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B, 9, 165–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(03)00415-1.
Boorboori, M. R., & Tehrani, M. M. (2011). A study of the effects of iron and manganese application on quantity and quality characteristics of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Crop Physiology Journal, 3(9), 63–77.
Cakmak, I. (2002). Plant nutrition research: Priorities to meet human needs for food in sustainable ways. Plant and Soil, 247, 3–24. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021194511492.
Cakmak, I. (2008a). Zinc deficiency in wheat in Turkey). In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Micronutrient deficiencies in global crop production (pp. 181–200). Dordrecht: Springer.
Cakmak, I. (2008b). Enrichment of cereal grains with zinc: Agronomic or genetic biofortification? Plant and Soil, 302, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9466-3.
Cakmak, I., Kalayci, M., Kaya, Y., Torun, A. A., Aydin, N., Wang, Y., Arisoy, Z., Erdem, H., Yazici, A., Gokmen, O., Ozturk, L., & Horst, W. J. (2010a). Biofortification and localization of zinc in wheat grain. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58, 9092–9102. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf101197h.
Cakmak, I., & Kutman, U. B. (2018). Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: A review. European Journal of Soil Science, 69(1), 172–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12437.
Cakmak, I., Pfeiffer, W. H., & Mcclafferty, B. (2010b). Biofortification of durum wheat with zinc and iron. Cereal Chemistry, 87(1), 10–20. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM-87-1-0010.
Candan, N., Cakmak, I., & Ozturk, L. (2018). Zinc-biofortified seeds improved seedling growth under zinc deficiency and drought stress in durum wheat. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 181(3), 388–395. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201800014.
Celletti, S., Paolacci, A. R., Mimmo, T., Pii, Y., Cesco, S., Cia, M., & Astolfi, S. (2016a). The effect of excess sulfate supply on iron accumulation in three graminaceous plants at the early vegetative phase. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 128, 31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.04.004.
Celletti, S., Pii, Y., Mimmo, T., Cesco, S., & Astolfi, S. (2016b). The characterization of the adaptive responses of durum wheat to different Fe availability highlights an optimum Fe requirement threshold. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 109, 300–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.10.010.
Chattha, M. U., Hassan, M. U., Khan, I., Chattha, M. B., Mahmood, A., Nawaz, M., Subhani, M. N., Kharal, M., & Khan, S. (2017). Biofortification of wheat cultivars to combat zinc deficiency. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8(281), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00281.
Chen, L., Yin, H., Xu, J., & Liu, X. (2011). Enhanced antioxidative responses of a salt-resistant wheat cultivar facilitate its adaptation to salt stress. African Journal of Biotechnology, 10, 16887–16896. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.1755.
Chen, X. P., Zhang, Y. Q., Tong, Y. P., Xue, Y. F., Liu, D. Y., Zhang, W., Deng, Y., Meng, Q. F., Yue, S. C., Yan, P., Cui, Z. L., Shi, X. J., Guo, S. W., Sun, Y. X., Ye, Y. L., Wang, Z. H., Jia, L. L., Ma, W. Q., He, M. R., Zhang, X. Y., Kou, C. L., Li, Y. T., Tan, D. S., Cakmak, I., Zhang, F. S., & Zou, C. Q. (2017). Harvesting more grain zinc of wheat for human health. Scientific Reports, 7, 7016. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07484-2.
Clemens, S., Deinlein, U., Ahmadi, H., Ho¨reth, S., & Uraguchi, S. (2013). Nicotianamine is a major player in plant Zn homeostasis. Biometals, 26, 623–632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-013-9643-1.
Crawford, N. M. (1995). Nitrate: Nutrient and signal for plant growth. Plant Cell, 7(7), 859–868. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.7.7.859.
Dadkhah, N., Ebadi, A., Parmoon, G. H., Ghlipoori, E., & Jahanbakhsh, S. (2015). The effects of zinc fertilizer on some physiological characteristics of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under water stress. Iranian Journal of Pulses Research, 6(2), 59–72.
Danaee, E., & Abdossi, V. (2019). Evaluation of the effect of foliar application of iron, potassium and zinc nanochelate on the enzymatic activity and nutritional value of some leafy vegetables. Journal of Food Technology and Nutrition, 16(2), 45–54.
Debroy, P., Narwal, R. P., Malik, R. S., & Narender, N. (2013). Enrichment of green gram (Vigna radiata) genotypes with iron through ferti-fortification. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 83(10), 1095–1098.
Deshpande, P., Dapkekar, A., Oak, M., Paknikar, K., & Rajwade, J. (2018). Nanocarrier-mediated foliar zinc fertilization influences expression of metal homeostasis related genes in flag leaves and enhances gluten content in durum wheat. PLoS One, 13(1), 1–21. e0191035. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191035.
Dwivedi, R., & Srivastva, P. C. (2014). Effect of zinc sulphate application and the cyclic incorporation of cereal straw on yields, the tissue concentration and uptake of Zn by crops and availability of Zn in soil under rice-wheat rotation. International Journal of Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture, 3, 53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40093-014-0053-3.
Eagling, T., Wawer, A. A., Shewry, P. R., Zhao, F., & Fairweather-tait, S. J. (2014). Iron bioavailability in two commercial cultivars of wheat: Comparison between wholegrain and white flour and the effects of nicotianamine and 20′-deoxymugineic acid on iron uptake into Caco-2 cells. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62, 10320–10325. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5026295.
Esfandiari, E., & Abdoli, M. (2016). Wheat biofortification through zinc foliar application and its effects on wheat quantitative and qualitative yields under zinc deficient stress. Yuzuncu Yil University Journal of Agricultural Science, 26(4), 529–537.
Esfandiari, E., & Abdoli, M. (2017). Improvement of agronomic and qualitative characters of durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum) genotypes by application of zinc sulfate under zinc deficiency stress. Journal of Crop Ecophysiology, 11(3), 619–636.
Esfandiari, E., Abdoli, M., Mousavi, S. B., & Sadeghzadeh, B. (2016). Impact of foliar zinc application on agronomic traits and grain quality parameters of wheat grown in zinc deficient soil. Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 21(3), 263–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-016-0225-4.
Esfandiari, E., Taheri, R., & Abdoli, M. (2018). The effects of different forms of iron foliar application on yield and concentration of micronutrient elements of wheat grain under nitrogen application conditions. Applied Research of Plant Ecophysiology, 5(1), 16–36.
Farooq, M., Ullah, A., Rehman, A., Nawaz, A., Nadeem, A., Wakeel, A., Nadeem, F., & Siddique, K. H. M. (2018). Application of zinc improves the productivity and biofortification of fine grain aromatic rice grown in dry seeded and puddled transplanted production systems. Field Crops Research, 216, 53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2017.11.004.
Farooq, M., Wahid, A., & Siddique, K. H. M. (2012). Micronutrient application through seed treatments—A review. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 12(1), 125–142. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162012000100011.
Fernandez, V., Orera, I., Abadía, J., & Abadía, A. (2009). Foliar iron fertilisation of fruit trees: Present knowledge and future perspectives—A review. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology, 84, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2009.11512470.
Gao, X., Hoffland, E., Stomph, T., Grant, C. A., Zou, C., & Zhang, F. (2012). Improving zinc bioavailability in transition from flooded to aerobic rice. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 32, 465–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-011-0053-x.
Gao, X., Zou, C., Fan, X., Zhang, F., & Hoffland, E. (2006). From flooded to aerobic conditions in rice cultivation: Consequences for zinc uptake. Plant and Soil, 280, 41–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-7652-0.
Ghafari, H., & Razmjoo, J. (2015). Response of durum wheat to foliar application of varied sources and rates of iron fertilizers. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 17, 321–331.
Ghasemi-Fasaei, R., & Ronaghi, A. (2008). Interaction of iron with copper, zinc, and manganese in wheat as affected by iron and manganese in a calcareous soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 31(5), 839–848. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904160802043148.
Ghoneim, A. M. (2016). Effect of different methods of Zn application on rice growth, yield and nutrient dynamics in plant and soil. Journal of Agriculture and Ecology Research International, 6, 1–9.
Gibson, R. S. (2006). Zinc: The missing link in combating micronutrient malnutrition in developing countries. The Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 65(1), 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1079/pns2005474.
Gomez-Coronado, F., Almeida, A. S., Santamaria, O., Cakmak, I., & Poblaciones, M. J. (2019). Potential of advanced breeding lines of bread-making wheat to accumulate grain minerals (Ca, Fe, Mg and Zn) and low phytates under Mediterranean conditions. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 205(3), 341–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12325.
Gomez-Coronado, F., Poblaciones, M. J., Almeida, A. S., & Cakmak, I. (2017). Combined zinc and nitrogen fertilization in different bread wheat genotypes grown under Mediterranean conditions. Cereal Research Communications, 45(1), 154–165. https://doi.org/10.1556/0806.44.2016.046.
Graham, R. D., Senadhira, D., Beebe, S., Iglesias, C., & Monasterio, I. (1999). Breeding for micronutrient density in edible portions of staple food crops: Conventional approaches. Field Crops Research, 60(1-2), 57–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(98)00133-6.
Guo, J. X., Feng, X. M., Hu, X. Y., Tian, G. L., Ling, N., Wang, J. H., Shen, Q. R., & Guo, S. W. (2015). Effects of soil zinc availability, nitrogen fertilizer rate and zinc fertilizer application method on zinc biofortification of rice. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 154(4), 584–597. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859615000441.
Gupta, R. K., Gangoliya, S. S., & Singh, N. K. (2015). Reduction of phytic acid enhancement of bioavailable micronutrients in food grains. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(2), 676–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-0978-y.
Habib, M. (2012). Effect of supplementary nutrition with Fe, Zn chelates and urea on wheat quality and quantity. African Journal of Biotechnology, 11(11), 2661–2665. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.1762.
Haider, M. U., Farooq, M., Nawaz, A., & Hussain, M. (2018a). Foliage applied zinc ensures better growth, yield and grain biofortification of mung bean. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 20(12), 2817–2822. https://doi.org/10.17957/IJAB/15.0840.
Haider, M. U., Hussain, M., Farooq, M., & Nawaz, A. (2018b). Soil application of zinc improves the growth, yield and grain zinc biofortification of mung bean. Soil and Environment, 37(2), 123–128. https://doi.org/10.25252/SE/18/71610.
Hao, H. L., Wei, Y. Z., Yang, X. E., Feng, Y., & Wu, C. Y. (2007). Effects of different nitrogen fertilizer levels on Fe, Mn, Cu and Zn concentrations in shoot and grain quality in rice (Oryza sativa). Rice Science, 14(4), 289–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6308(08)60007-4.
Harris, D., Rashid, A., Miraj, G., Arif, M., & Yunas, M. (2008). ‘On-farm’ seed priming with zinc in chickpea and wheat in Pakistan. Plant and Soil, 306, 3–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9465-4.
Havlin, J. L., Beaton, J. D., Tisdale, S. L., & Nelson, W. L. (2010). Soil fertility and fertilizers—An introduction to nutrient management. New Delhi: PHI Learning Private Limited.
Heidarzade, A., Esmaeili, M. A., Bahmanyar, M. A., & Abbasi, R. (2016). Response of soybean (Glycine max) to molybdenum and iron spray under well-watered and water deficit conditions. Journal of Experimental Biology and Agricultural Sciences, 4(1), 37–46. https://doi.org/10.18006/2015.4(1).37.46.
Hossain, M. A., Jahiruddin, M., Islam, M. R., & Mian, M. H. (2008). The requirement of zinc for improvement of crop yield and mineral nutrition in maize-mungbean-rice system. Plant and Soil, 306, 13–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9529-5.
Hu, Y., Norton, G. J., Duan, G., Huang, Y., & Liu, Y. (2014). Effect of selenium fertilization on the accumulation of cadmium and lead in rice plants. Plant and Soil, 384(1-2), 131–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2189-3.
Hurrell, R., & Egli, I. (2010). Iron bioavailability and dietary reference values. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 91, 1461S–1467S. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2010.28674F.
Hussain, S., Maqsood, M. A., Rengel, Z., & Aziz, T. (2012). Biofortification and estimated human bioavailability of zinc in wheat grains as influenced by methods of zinc application. Plant and Soil, 361, 279–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1217-4.
Hussain, S., Maqsood, M. A., Rengel, Z., Aziz, T., & Abid, M. (2013). Estimated zinc bioavailability in milling fractions of biofortified wheat grains and in flours of different extraction rates. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 15(5), 921–926.
Hussain, S., Shah, M. A. A., Khan, A. M., Ahmad, F., & Hussain, M. (2020). Potassium enhanced grain zinc accumulation in wheat grown on a calcareous saline-sodic soil. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 52(1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.30848/PJB2020-1(40).
Impa, S. M., & Johnson-Beebout, S. E. (2012). Mitigating Zn deficiency and achieving high grain Zn in rice through integration of soil chemistry and plant physiology research. Plant and Soil, 361, 3–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1315-3.
Imran, M., Kanwal, S., Hussain, S., Aziz, T., & Aamer-Maqsood, M. (2015). Efficacy of zinc application methods for concentration and estimated bioavailability of zinc in grains of rice grown on a calcareous soil. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Science, 52(1), 169–175.
Ivanov, K., Tonev, T., Nguyen, N., Peltekov, A., & Mitkov, A. (2019). Impact of foliar fertilization with nanosized zinc hydroxy nitrate on maize yield and quality. Emirates Journal of Food and Agriculture, 31(8), 597–604. https://doi.org/10.9755/ejfa.2019.v31.i8.2003.
Jan, M., Anwar-ul-Haq, M., Tanveer-ul-Haq, A. A., & Wariach, E. A. (2016). Evaluation of soil and foliar applied Zn sources on rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes in saline environments. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 18(3), 643–648. https://doi.org/10.17957/IJAB/15.0146.
Jiang, W., Struik, P. C., Lingna, J., van-Keulen, H., Ming, Z., & Stomph, T. J. (2007). Uptake and distribution of root-applied or foliar-applied 65Zn after flowering in aerobic rice. The Annals of Applied Biology, 150(3), 383–391. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2007.00138.x.
Johnson, S. E., Lauren, J. G., Welch, R. M., & Duxbury, J. M. (2005). A comparison of the effects of micronutrient seed priming and soil fertilization on the mineral nutrition of chickpea (Cicer arietinum), lentil (Lens culinaris), rice (Oryza sativa) and wheat (Triticum aestivum) in Nepal. Experimental Agriculture, 41, 427–448. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0014479705002851.
Joyce, C., Deneau, A., Peterson, K., Ockenden, I., Raboy, V., & Lott, J. N. A. (2005). The concentrations and distribution of phytic acid phosphorous and other mineral nutrients in wild-type and low phytic acid Js-12-LPA wheat (Triticum aestivum) grain parts. Canadian Journal of Botany, 83, 1599–1607. https://doi.org/10.1139/b05-128.
Kabir, A. H., Paltridge, N., & Stangoulis, J. (2016). Chlorosis correction and agronomic biofortification in field peas through foliar application of iron fertilizers under Fe deficiency. Journal of Plant Interactions, 11(1), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2015.1125534.
Kumar, A., Denre, M., & Prasad, R. (2018). Agronomic biofortification of zinc in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Current Science, 115(5), 944–948. https://doi.org/10.18520/cs/v115/i5/944-948.
Kumar, S., Yadav, M., & Singh, G. K. (2010). Effect of iron and zinc on fruit yield and quality of strawberry (Fragaria ananassa). Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 80(2), 171–173.
Kutman, U. B., Yildiz, B., & Cakmak, I. (2011a). Effect of nitrogen on uptake, remobilization and partitioning of zinc and iron throughout the development of durum wheat. Plant and Soil, 342, 149–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0679-5.
Kutman, U. B., Yildiz, B., & Cakmak, I. (2011b). Improved nitrogen status enhances zinc and iron concentrations both in the whole grain and the endosperm fraction of wheat. Journal of Cereal Science, 53, 118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2010.10.006.
Kutman, U. B., Yildiz, B., Ozturk, L., & Cakmak, I. (2010). Biofortification of durum wheat with zinc through soil and foliar applications of nitrogen. Cereal Chemistry, 87, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM-87-1-0001.
Leite, C. M. C., da Silva, A., César, F. R. C. F., Guimarães, G. G. F., Almeida, E., & Muraoka, T. (2020). Low efficiency of Zn uptake and translocation in plants provide poor micronutrient enrichment in rice and soybean grains. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 43(1), 79–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2019.1659341.
Li, M., Wang, S., Tian, X., Li, S., Chen, Y., Jia, Z., Liu, K., & Zhao, A. (2016). Zinc and iron concentrations in grain milling fractions through combined foliar applications of Zn and macronutrients. Field Crops Research, 187, 135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2015.12.018.
Li, M., Yang, X. W., Tian, X. H., Wang, S. X., & Chen, Y. L. (2014). Effect of nitrogen fertilizer and foliar zinc application at different growth stages on zinc translocation and utilization efficiency in winter wheat. Cereal Research Communications, 42(1), 81–90. https://doi.org/10.1556/CRC.2013.0042.
Liu, H., Zhao, P., Qin, S., & Nie, Z. (2018). Chemical fractions and availability of zinc in winter wheat soil in response to nitrogen and zinc combinations. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 1489. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01489.
Mabesa, R. L., Impa, S. M., Grewal, D., & Johnson-Beebout, S. E. (2013). Contrasting grain-Zn response of biofortification rice (Oryza sativa L.) breeding lines to foliar Zn application. Field Crops Research, 149, 223–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.05.012.
Marschner, H. (2012). Mineral nutrition of higher plants (Vol. 672, 3rd ed.). London: Academic Press.
Mazarloo, R., Valadabadi, S. A. R., & Zakerin, H. R. (2017). Effect of foliar application of Fe and Zn on yield of rapeseed under different irrigation regimes in Boin-Zahra region. Research in Agriculture, 9(2), 17–27.
McBeath, T. M., & McLaughlin, M. J. (2014). Efficacy of zinc oxides as fertilisers. Plant and Soil, 374, 843–855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1919-2.
Meena, K. K., Meena, R. S., & Kumawat, S. M. (2013). Effect of sulphur and iron fertilization on yield attributes, yield and nutrient uptake of mung bean (Vigna radiata). Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 83(4), 472–476.
Melash, A. A., Mengistu, D. K., Aberra, D. A., & Tsegay, A. (2018). The influence of seeding rate and micronutrients foliar application on grain yield and quality traits and micronutrients of durum wheat. Journal of Cereal Science, 85, 221–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2018.08.005.
Miransari, H., Mehrafarin, A., & Naghdi Badi, H. (2015). Morpho-physiological and phytochemical responses of dill (Anethum graveolens L.) to foliar application of iron sulfate and zinc sulfate. Journal of Medicinal Plants, 14(2), 15–30.
Mishra, L. K., & Abidi, A. B. (2010). Phosphorus-zinc interaction: Effects on yield components, biochemical composition and bread making qualities of wheat. World Applied Sciences Journal, 10, 568–573.
Moghadam, E., Mahmoodi Sourestani, M., Farrokhian Firozi, A., Ramazani, Z., & Eskandari, F. (2015). The effect of foliar application of iron chelate type on morphological traits and essential oil content of holy basil (Ocimum sanctum). Journal of Agricultural and Crop Management, 17(3), 595–606.
Monsef Afshar, R., Hadi, H., & Pirzad, A. (2012). Effect of nano-iron foliar application on qualitative and quantitative characteristics of cowpea, under end season drought stress. The International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences, 3(8), 1709–1717.
Morgounov, A., Gomez-Becerra, H. F., Abugalieva, A., Dzhunusova, M., Yessimbekova, M., Muminjanov, H., Zelenskiy, Y., Ozturk, L., & Cakmak, I. (2007). Iron and zinc grain density in common wheat grown in Central Asia. Euphytica, 155, 193–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9321-2.
Mortvedt, J. J. (1991). Micronutrient fertilizer technology. In J. J. Mortvedt, F. R. Cox, L. M. Shuman, & R. M. Welch (Eds.), Micronutrients in agriculture (SSSA Book Series) (Vol. 4, pp. 89–112). Madison, WI: Soil Science Society of America. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser4.2ed.c14.
Movahhedi Dehnavi, M., Misagh, M., Yadavi, A. R., & Merajipoor, M. (2017). Physiological responses of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) to foliar application of boron and zinc under drought stress. Journal of Plant Process and Function, 6(20), 27–35.
Movahhedi Dehnavi, M., & Modarres Sanavy, S.A.M. (2008) Effects of withholding irrigation and foliar application of zinc and manganese on fatty acid composition and seed oil content in winter safflower. In 7th International Safflower Conference, 3–6 November 2008, Wagga, Australia.
Naeem, A., Aslam, M., & Lodhi, A. (2018). Improved potassium nutrition retrieves phosphorus-induced decrease in zinc uptake and grain zinc concentration of wheat. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 98(11), 4351–4356. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8961.
Narwal, R. P., Malik, R. S., & Yadak, H. K. (2017). In B. R. Singh, M. J. McLaughlin, & E. C. Brevik (Eds.),. The nexus of soils, plants and human health Micronutrients in soils and plants and their impact on animal and human health (pp. 64–71). Stuttgart: Catena-Schweizerbart.
Nateghi, S. H., Pirzad, A. R., & Darvishzadeh, R. (2015). The impact of micronutrient fertilizers, iron and zinc on yield and yield component of anise. Journal of Horticultural Science, 29(1), 37–46.
Nayyar, V. K., Sadana, U. S., & Takkar, T. N. (1985). Methods and rates of application of Mn and its critical levels for wheat following rice on coarse textured soils. Fertility Research, 8(2), 173–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01048900.
Niyigaba, E., Twizerimana, A., Mugenzi, I., Ngnadong, W. A., Ye, Y. P., Wu, B. M., & Hai, J. B. (2019). Winter wheat grain quality, zinc and iron concentration affected by a combined foliar spray of zinc and iron fertilizers. Journal of Agronomy, 9(250), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9050250.
Nogueira Arcanjo, F. P., Santos, P. R., Costa Arcanjo, C. P., Meira Magalhães, S. M., & Madeiro Leite, A. J. (2013). Daily and weekly iron supplementations are effective in increasing hemoglobin and reducing anemia in infants. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 59(3), 175–179. https://doi.org/10.1093/tropej/fms071.
Norhaizan, M. E., & Nor Faizadatul Ain, A. W. (2009). Determination of phytate, iron, zinc, calcium contents and their molar ratios in commonly consumed raw and prepared food in Malaysia. Malaysian Journal of Nutrition, 15(2), 213–222.
Nowack, B., Schwyzer, I., & Schulin, R. (2008). Uptake of Zn and Fe by wheat (Triticum aestivum var. Greina) and transfer to the grain in the presence of chelating agents (Ethylenediaminedisuccinic acid and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56, 4643–4649. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf800041b.
Pandey, N., Gupta, B., & Pathak, G. C. (2013). Foliar application of Zn at flowering stage improves plant’s performance, yield and yield attributes of black gram. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 51(7), 548–555.
Panjtandoust, M., Soroosh zadeh, A., & Ghanati, F. (2010). Effect of iron soil and spray applied on some qualify characteristics of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) plants in a calcareous soil. Iranian Journal of Plant Biology, 2(5), 37–50.
Pascoalino, J. A. L., Thompson, J. A., Wright, G., Franco, F. A., Scheeren, P. L., Pauletti, V., Moraes, M. F., & White, P. J. (2018). Grain zinc concentrations differ among Brazilian wheat genotypes and respond to zinc and nitrogen supply. PLoS One, 13(7), e0199464. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199464.
Phattarakal, N., Rerkasem, B., Li, L. J., Wu, L. H., Zou, C. Q., Ram, H., Sohu, V. S., Kang, B. S., Surek, H., Kalayci, M., Yazici, A., Zhang, F. S., & Cakmak, I. (2012). Biofortification of rice grain with zinc through zinc fertilization in different countries. Plant and Soil, 361(1-2), 131–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1211-x.
Phuphong, P., Cakmak, I., Dell, B., & Prom-u-thai, C. (2018). Effects of foliar application of zinc on grain yield and zinc concentration of rice in farmers’ fields. CMU Journal of Natural Sciences, 17(3), 181–190. https://doi.org/10.12982/cmujns.2018.0013.
Prasad, R., Shivay, Y. S., & Kumar, D. (2014). Chapter two—Agronomic biofortification of cereal grains with iron and zinc. Advances in Agronomy, 125, 55–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800137-0.00002-9.
Prasad, R., Shivay, Y. S., & Kumar, D. (2016). Interactions of zinc with other nutrients in soils and plants—A review. Indian Journal of Fertilizers, 12(5), 16–26.
Rafique, E., Yousra, M., Mahmood-Ul-Hassan, M., Sarwar, S., Tabassam, T., & Choudhary, T. K. (2015). Zinc application affects tissue zinc concentration and seed yield of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Pedosphere, 25(2), 275–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(15)60012-1.
Rahmani, F., Sayfzadeh, S., Jabbari, H., Valadabadi, S. A., & Hadidi Masouleh, E. (2019). Alleviation of drought stress effects on safflower yield by foliar application of zinc. International Journal of Plant Production, 13, 297–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-019-00055-7.
Rana, W. K., & Kashif, S. R. (2014). Effect of different zinc sources and methods of application on rice yield and nutrients concentration in rice grain and straw. Journal of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences, 1(9), 1–5.
Rashid, A., Ram, H., Zou, C. Q., Rerkasem, B., Duarte, A. P., Simunji, S., Yazici, A., Guo, S., Rizwan, M., Bal, R. S., Wang, Z., Malik, S. S., Phattarakul, N., Soares de Freitas, R., Lungu, O., Barros, V. L. N. P., & Cakmak, I. (2019). Effect of zinc-biofortified seeds on grain yield of wheat, rice, and common bean grown in six countries. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 182(5), 791–804. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201800577.
Rehman, A., & Farooq, M. (2016). Zinc seed coating improves the growth, grain yield and grain biofortification of bread wheat. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 38, 238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2250-3.
Rehman H (2012) N-Zn dynamics under different rice production systems. PhD dissertation, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad.
Rengel, Z. (2015). Availability of Mn, Zn and Fe in the rhizosphere. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nnutrition, 15(2), 397–409. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162015005000036.
Rostami, B., Asilan, K. S., Yousefzadeh, S., & Mansorifar, S. (2017). Effect of foliar application of iron and zinc sulfate on quantitative traits and essential oil yield of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.). Iranian Journal of Field Crops Science, 48(2), 517–525. https://doi.org/10.22059/ijfcs.2017.209948.654140.
Shahzad, Z., Rouached, H., & Rakha, A. (2014). Combating mineral malnutrition through iron and zinc biofortification of cereals. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 13, 329–346. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.120634337.12063.
Sajedi, N. A., & Rjay, F. (2011). Application of mycorrhizal inoculation on the uptake of zinc and micronutrients in maize. Journal of Soil Research, 25, 83–92.
Sharifianpour, G., Zaharah, A. R., Ishak, C. F., Hanafi, M. M., Khayyambashi, B., Alifar, N., & Sharifkhani, A. (2015). Effects of application of different sources of Zn and composts on Zn concentration and uptake by upland rice. Journal of Agronomy, 14, 23–29. https://doi.org/10.3923/ja.2015.23.29.
Sharma, S., Malhotra, H., Borah, P., Meena, M. K., Bindraban, P., Chandra, S., Pande, V., & Pandey, R. (2019). Foliar application of organic and inorganic iron formulation induces differential detoxification response to improve growth and biofortification in soybean. Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 24, 119–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0412-6.
Shehzad, M. A., Maqsood, M., Abbas, T., & Ahmad, N. (2016). Foliar boron spray for improved yield, oil quality and water use efficiency in water stressed sunflower. Sains Malaysiana Journal, 45(10), 1497–1507.
Shi, R., Zhang, Y., Chen, X., Sun, Q., Zhang, F., Römheld, V., & Zou, C. (2010). Influence of long-term nitrogen fertilization on micronutrient density in grain of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Journal of Cereal Science, 51(1), 165–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2009.11.008.
Shibahara, A., Fukumizu, M., & Yamashoji, S. (1977). Changes in the composition of lipids, fatty acids and tocopherols in peanut seeds during maturation. Journal of the Agricultural Chemical Society of Japan, 51(10), 575–581.
Shivay, Y. S., Kumar, D., & Prasad, R. (2008a). Effect of zinc-enriched urea on productivity, zinc uptake and efficiency of an aromatic rice-wheat cropping system. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 81(3), 229–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9159-6.
Shivay, Y. S., Kumar, D., Prasad, R., & Ahlawat, L. P. S. (2008b). Relative yield and zinc uptake by rice from zinc sulphate and zinc oxide coatings onto urea. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 80(2), 181–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9131-5.
Shivay, Y. S., Prasad, R., & Pal, M. (2013). Zinc fortification of oat grains through zinc fertilisation. Agricultural Research, 2(4), 375–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-013-0078-2.
Shivay, Y. S., Prasad, R., & Rahal, A. (2008c). Relative efficiency of zinc oxide and zinc sulphate enriched urea for spring wheat. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 82, 259–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-008-9186-y.
Singh, B. R., Timsina, Y. N., Lind, O. C., Cagno, S., & Janssens, K. (2018). Zinc and iron concentration as affected by nitrogen fertilization and their localization in wheat grain. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9(307), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00307.
Singh, H. K., Singh, B. P., & Chauhan, K. S. (1981). Effect of foliar feeding of various chemicals on physico-chemical quality of guava fruits. Journal of Research—Haryana Agricultural University, 11(3), 411–414.
Singh, M. V., Kumar, N., Singh, R. K., & Mishra, B. N. (2010). Effect of phosphorus, sulphur and zinc on growth, yield and uptake of nutrients in late sown wheat in eastern Uttar Pradesh. Annals of Plant and Soil Research, 12(2), 119–121.
Singh, R., Prasad, S. K., & Singh, M. K. (2014). Effect of nitrogen and zinc fertilizer on Zn biofortification in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum). Indian Journal of Agronomy, 59(3), 474–476.
Smoleń, S., Kowalska, I., Kováčik, P., Sady, W., Grzanka, M., & Kutman, U. B. (2019). Changes in the chemical composition of six lettuce cultivars (Lactuca sativa L.) in response to biofortification with iodine and selenium combined with salicylic acid application. Journal of Agronomy, 9(660), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9100660.
Šramková, Z., Gregová, E., & Šturdík, E. (2009). Chemical composition and nutritional quality of wheat grain. Acta Chimica Slovenica, 2(1), 115–138.
Stomph, T.J., Hoebe, N., Spaans, E., Van der Putten, P.E.L. (2011). The relative contribution of post-flowering uptake of Zn to rice grain Zn density. 3rd International Zn Symposium, 10–14 Oct 2011, Hyderabad, India.
Sultana, S., Naser, H. M., Shil, N. C., Akhter, S., & Begum, R. A. (2016). Effect of foliar application of zinc on yield of wheat grown by avoiding irrigation at different growth stages. Bangladesh Journal of Agricultural Research, 41(2), 323–334.
Süzer, S. (2015). Effects of plant nutrition on canola (Brassica napus L.) growth. Trakya University Journal of Natural Sciences, 16(2), 87–90.
Takahashi, M., Terada, Y., Nakai, I., Nakanishi, H., Yoshimura, E., Mori, S., & Nishizawa, N. K. (2003). Role of nicotianamine in the intracellular delivery of metals and plant reproductive development. The Plant Cell, 15(6), 1263–1280.
Tariq, M., Hameed, S., Malik, K. A., & Hafeez, F. Y. (2007). Plant root associated bacteria for zinc immobilization in rice. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 39(1), 245–253.
Towo, E., Mgoba, C., Ndossi, G. D., & Kimboka, S. (2006). Effect of phytate and iron-binding phenolics on the content and availability of iron and zinc in micronutrients fortified cereal flours. African Journal of Food Agriculture Nutrition and Development, 6, 1–14.
Uauy, C., Distelfeld, A., Fahima, T., Blechl, A., & Dubcovsky, J. (2006). A NAC gene regulating senescence improves grain protein, zinc, and iron content in wheat. Science, 314, 1298–1301. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1133649.
Ullah, A., Farooq, M., Hussain, M., Ahmad, R., & Wakeel, A. (2019a). Zinc seed coating improves emergence and seedling growth in desi and kabuli chickpea types but shows toxicity at higher concentration. International Journal of Agriculture and Biological Sciences, 21(3), 553–559. https://doi.org/10.17957/IJAB/15.0928.
Ullah, A., Farooq, M., Hussain, M., Ahmad, R., & Wakeel, A. (2019b). Zinc seed priming improves stand establishment, tissue zinc concentration and early seedling growth of chickpea. The Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences, 29(4), 1046–1053.
Ullah, A., Farooq, M., Rehman, A., Arshad, M. S., Shoukat, H., Nadeem, A., Nawaz, A., Wakeel, A., & Nadeem, F. (2018). Manganese nutrition improves the productivity and grain biofortification of bread wheat in alkaline calcareous soil. Experimental Agriculture, 54(5), 744–754. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0014479717000369.
Ünal, S. (2002). Buğdayda kalitenin önemi ve belirlenmesinde kullanılan yöntemler. Hububat Ürünleri Teknolojisi Kongre ve Sergisi. pp. 25–37, 3–4 Ekim, Gaziantep.
Velu, G., Ortiz-Monasterio, I., Cakmak, I., Hao, Y., & Singh, R. P. (2014). Biofortification strategies to increase grain zinc and iron concentrations in wheat. Journal of Cereal Science, 59(3), 365–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2013.09.001.
Velu, G., Ortiz-Monasterio, I., Singh, R. P., & Payne, T. (2011). Variation for grain micronutrients concentration in wheat core-collection accessions of diverse origin. Asian Journal of Crop Science, 3, 43–48. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajcs.2011.43.48.
Wang, S., Zhang, X., Liu, K., Fei, P., Chen, J., Li, X., Ning, P., Chen, Y., Shi, J., & Tian, X. (2019). Improving zinc concentration and bioavailability of wheat grain through combined foliar applications of zinc and pesticides. Agronomy Journal, 111(3), 1478–1487. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2018.09.0597.
Wei, Y., Shohag, M. J. I., & Yang, X. (2012). Biofortification and bioavailability of rice grain zinc as affected by different forms of foliar zinc fertilization. PLoS One, 7(9), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045428.
Welch, R. M., & Graham, R. D. (2002). Breeding crops for enhanced micronutrient content. Plant and Soil, 245, 205–214. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020668100330.
White, P. J., & Broadley, M. R. (2005). Biofortifying crops with essential mineral elements. Trends in Plant Science, 10(12), 586–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2005.10.001.
White, P. J., & Broadley, M. R. (2011). Physiological limits to zinc biofortification of edible crops. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2, 80. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2011.00080.
WHO. (2011). Micronutrient deficiencies: Vitamin A deficiency. Geneva: World Health Organization. Retrieved from http://www.who.int/nutrition/topics/vad/en.
Wissuwa, M., Ismail, A. M., & Graham, R. D. (2008). Rice grain zinc concentrations as affected by genotype, native soil-zinc availability, and zinc fertilization. Plant and Soil, 306, 37–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9368-4.
Xia, H., Xue, Y., Liu, D., Kong, W., Xue, Y., Tang, Y., Li, J., Li, D., & Mei, P. (2018). Rational application of fertilizer nitrogen to soil in combination with foliar Zn spraying improved Zn nutritional quality of wheat grains. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9(677), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00677.
Yang, X. W., Tian, X. H., Gale, W. J., Cao, X. Y., Lu, X. C., & Zhao, A. Q. (2011). Effect of soil and foliar zinc application on zinc content and bioavailability in wheat grain on potentially zinc-deficient soil. Cereal Research Communications, 39, 535–543. https://doi.org/10.1556/CRC.39.2011.4.8.
Yeilaghi, H., Arzani, A., Ghaderian, M., Fotovat, R., Feizi, M., & Pourdad, S. S. (2012). Effect of salinity on seed oil content and fatty acid composition of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) genotypes. Food Chemistry, 130, 618–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2011.07.085.
Yilmaz, A., Ekiz, H., Torun, B., Gultekin, I., Karanlik, S., Bagci, S. A., & Cakmak, I. (1997). Effect of different zinc application methods on grain yield and zinc concentration in wheat grown on zinc-deficient calcareous soils in central Anatolia. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 20(4-5), 461–471. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904169709365267.
Zeidan, M. S., Mohamed, M. F., & Hamouda, H. A. (2010). Effect of foliar fertilization of Fe, Mn and Zn on wheat yield and quality in low sandy soils fertility. World Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 6(6), 696–699.
Zhang, C. M., Zhao, W. Y., Gao, A. X., Su, T. T., Wang, Y. K., Zhang, Y. Q., Zhou, X. B., & He, X. H. (2017). How could agronomic biofortification of rice be an alternative strategy with higher cost-effectiveness for human iron and zinc deficiency in China? Food and Nutrition Bulletin, 39(2), 246–259. https://doi.org/10.1177/0379572117745661.
Zhang, Y. Q., Deng, Y., Chen, R. Y., Cui, Z. L., Chen, X. P., Yost, R., Zhang, F. S., & Zou, C. Q. (2012a). The reduction in zinc concentration of wheat grain upon increased phosphorus-fertilization and its mitigation by foliar zinc application. Plant and Soil, 361, 143–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1238-z.
Zhang, Y. Q., Pang, L. L., Yan, P., Liu, D. Y., Zhang, W., Yost, R., Zhang, F. S., & Zou, C. Q. (2013). Zinc fertilizer placement affects zinc content in maize plant. Plant and Soil, 372, 81–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1904-9.
Zhang, Y. Q., Sun, Y. X., Ye, Y. L., Rezaul, K. M., Xue, Y., Yan, P., Meng, Q. F., Cui, Z. L., Cakmak, I., Zhang, F. S., & Zou, C. Q. (2012b). Zinc biofortification of wheat through fertilizer applications in different locations of China. Field Crops Research, 125, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2011.08.003.
Zhao, P., Yang, F., Sui, F., Wang, Q., & Liu, H. (2016). Effect of nitrogen fertilizers on zinc absorption and translocation in winter wheat. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 39, 1311–1318. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2015.1106560.
Zhao, P., Yang, F., Sui, F. Q., & Wang, Q. Y. (2013). The effects of zinc and nitrogen on wheat nitrogen using, yield and grain protein content. Journal of China Agricultural University, 18, 28–33.
Zolfaghari Gheshlaghi, M., Pasari, B., Shams, K., Rokhzadi, A., & Mohammadi, K. (2019). The effect of micronutrient foliar application on yield, seed quality and some biochemical traits of soybean cultivars under drought stress. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 42(20), 2715–2730. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2019.1655034.
Zou, C. Q., Zhang, Y. Q., Rashid, A., Ram, H., Savasli, E., Arisoy, R. Z., Ortiz-Monasterio, I., Simunji, S., Wang, Z. H., Sohu, V., Hassan, M., Kaya, Y., Onder, O., Lungu, O., Yaqub Mujahid, M., Joshi, A. K., Zelenskiy, Y., Zhang, F. S., & Cakmak, I. (2012). Biofortification of wheat with zinc through zinc fertilization in seven countries. Plant and Soil, 361(1-2), 119–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1369-2.
Zuchi, S., Cesco, S., & Astolfi, S. (2012). High S supply improves Fe accumulation in durum wheat plants grown under Fe limitation. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 77, 25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2011.11.001.
Zuchi, S., Watanabe, M., Hubberten, H. M., Bromke, M., Osorio, S., Fernie, A. R., Celletti, S., Paolacci, A. R., Catarcione, G., & Ciaffi, M. (2015). The interplay between sulfur and iron nutrition in tomato. Plant Physiology, 169, 2624–2639. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Abdoli, M. (2020). Effects of Micronutrient Fertilization on the Overall Quality of Crops. In: Aftab, T., Hakeem, K.R. (eds) Plant Micronutrients. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49856-6_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49856-6_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-49855-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-49856-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)