Abstract
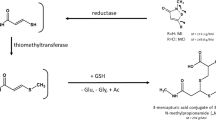
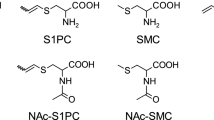
4-Cyanoacetanilide (PCAA, b in Scheme 1) is a metabolite of 4-cyano-N,N-dimethyl-aniline (CDA, Scheme 1). Whilst the metabolism of CDA, a designed analogue of butter yellow (Ashby, Styles, Paton, 1980) was being investigated, a novel involvement of glutathione was detected (Hutson, Lakeman and Logan, 1984). From the structure of the mercapturic acid conjugate (C), which was isolated from the urine of the rats that had been dosed with CDA, it was postulated that the CDA had been de-methylated (A), acetylated (b), and that the methyl group of the acetyl group had been activated to form an electrophilic intermediate, the intermediate then being trapped, at least in part, by glutathione and eventually excreted as the mercapturic acid (C). interestingly, mice seemed to be unable to form this electrophilic intermediate.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Ashby, J. A. Styles, and D. Paton, 1980, Carcinogenesis 1, 1.
S. Edwards, D. Hesk, C. J. Logan, and R. Waters, 1985, in: 2nd U. K. Environmental Mutagen Society Ring-Test, eds. C. Arlot, J. Ashby, and J. Parry. Pub. McMillan, London.
D. H. Hutson, S. K. Lakeman, and C. J. Logan, 1984, Xenobiotica, 14, 925.
G. J. Mulder, and E. Scholtens, 1977, Biochem. J., 165, 553.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1986 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Logan, C.J., Hesk, D., Hutson, D.H. (1986). The Fate of 4-Cyanoacetanilide in Rats and Mice: The Mechanism of Formation of a Novel Electrophilic Metabolite. In: Kocsis, J.J., Jollow, D.J., Witmer, C.M., Nelson, J.O., Snyder, R. (eds) Biological Reactive Intermediates III. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 197. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5134-4_69
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5134-4_69
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-5136-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-5134-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive