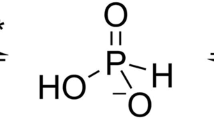
Abstract
The combination of MicroScale Thermophoresis (MST) and near-native site-specific His-tag labeling enables simple, robust, and reliable determination of the binding affinity between proteins and ligands. To demonstrate its applicability for periplasmic proteins, we provide a detailed protocol for determination of the binding affinity of phosphite to three ABC transporter periplasmic-binding proteins from environmental microorganisms. ABC transporters are central to many important biomedical phenomena, including resistance of cancers and pathogenic microbes to drugs. The protocol described here can be used to quantify protein-ligand and protein-protein interactions for other soluble, membrane-associated and integral membrane proteins.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky SL, Matsudaria P, Baltiomore D, Darnell J (2000) Section 3.4, Membrane proteins. In: Freeman WH (ed) Molecular cell, New York
Almén MS et al (2009) Mapping the human membrane proteome: a majority of the human membrane proteins can be classified according to function and evolutionary origin. BMC Biol 7:50–50
Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL (2006) How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:993–996
Jones P, George A (2004) The ABC transporter structure and mechanism: perspectives on recent research. Cell Mol Life Sci 61(6):682–699
Dean M, Hamon Y, Chimini G (2001) The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. J Lipid Res 42(7):1007–1017
Koning SM et al (2001) Cellobiose uptake in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus is mediated by an inducible, high-affinity ABC transporter. J Bacteriol 183(17):4979–4984
Gorbulev S, Abele R, Tampé R (2001) Allosteric crosstalk between peptide-binding, transport, and ATP hydrolysis of the ABC transporter TAP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(7):3732–3737
Abdullah HQ et al (2017) ATP binding and hydrolysis disrupts the high-affinity interaction between the heme ABC transporter HmuUV and its cognate substrate binding protein. J Biol Chem 292(35):14617–14624
Su C-C, Nikaido H, Yu EW (2007) Ligand-transporter interaction in the AcrB multidrug efflux pump determined by fluorescence polarization assay. FEBS Lett 581(25):4972–4976
Jerabek-Willemsen M et al (2014) MicroScale Thermophoresis: interaction analysis and beyond. J Mol Struct 1077:101–113
Berna-Erro A et al (2017) Structural determinants of 5′, 6′-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid binding to and activation of TRPV4 channel. Sci Rep 7(1):10522
Roche JV et al (2017) Phosphorylation of human aquaporin 2 (AQP2) allosterically controls its interaction with the lysosomal trafficking protein LIP5. J Biol Chem 292(35):14636–14648
Parker JL, Newstead S (2014) Molecular basis of nitrate uptake by the plant nitrate transporter NRT1.1. Nature 507(7490):68–72
Girke C et al (2015) High yield expression and purification of equilibrative nucleoside transporter 7 (ENT7) from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochim Biophys Acta 1850(9):1921–1929
Koch S et al (2016) Lipids activate SecA for high affinity binding to the SecYEG complex. J Biol Chem 291(43):22534–22543
Eggensperger S et al (2014) An annular lipid belt is essential for allosteric coupling and viral inhibition of the antigen translocation complex TAP (transporter associated with antigen processing). J Biol Chem 289(48):33098–33108
Denèfle T et al (2016) Thrombospondin-1 mimetic agonist peptides induce selective death in tumor cells: design, synthesis, and structure–activity relationship studies. J Med Chem 59(18):8412–8421
Wan C et al (2015) Insights into the molecular recognition of the granuphilin C2A domain with PI (4, 5) P2. Chem Phys Lipids 186:61–67
Baaske P et al (2010) Optical thermophoresis for quantifying the buffer dependence of aptamer binding. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(12):2238–2241
Lou J et al (1999) Fluorescence-based thermometry: principles and applications. Rev Anal Chem 18(4):235–284
Ross D, Gaitan M, Locascio LE (2001) Temperature measurement in microfluidic systems using a temperature-dependent fluorescent dye. Anal Chem 73(17):4117–4123
Dhont JK et al (2007) Thermodiffusion of charged colloids: single-particle diffusion. Langmuir 23(4):1674–1683
Duhr S, Braun D (2006) Why molecules move along a temperature gradient. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(52):19678–19682
Bartoschik T et al (2018) Near-native, site-specific and purification-free protein labeling for quantitative protein interaction analysis by MicroScale Thermophoresis. Sci Rep 8(1):4977
Polyviou D et al (2015) Phosphite utilization by the globally important marine diazotroph Trichodesmium. Environ Microbiol Rep 7(6):824–830
Feingersch R et al (2012) Potential for phosphite and phosphonate utilization by Prochlorococcus. ISME J 6(4):827
Metcalf WW, Wolfe RS (1998) Molecular genetic analysis of phosphite and hypophosphite oxidation by Pseudomonas stutzeri WM88. J Bacteriol 180(21):5547–5558
Bisson C et al (2017) The molecular basis of phosphite and hypophosphite recognition by ABC-transporters. Nat Commun 8(1):1746
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Bartoschik, T., Gupta, A., Kern, B., Hitchcock, A., Adams, N.B.P., Tschammer, N. (2020). Quantifying the Interaction of Phosphite with ABC Transporters: MicroScale Thermophoresis and a Novel His-Tag Labeling Approach. In: Postis, V.L.G., Goldman, A. (eds) Biophysics of Membrane Proteins. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2168. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0724-4_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0724-4_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-0723-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-0724-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols