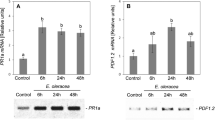
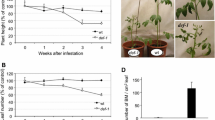
Abstract
Jasmonates are essential engineers of plant defense responses against many pests, including herbivorous insects. Herbivory induces the production of jasmonic acid (JA) and its bioactive conjugate jasmonoyl-l-isoleucine (JA-Ile), which then triggers a large transcriptional reprogramming to promote plant acclimation. The contribution of the JA pathway, including its components and regulators, to defense responses against insect herbivory can be evaluated by conducting bioassays with a wide range of host plants and insect pests. Here, we describe a detailed and reproducible protocol for testing feeding behavior of the generalist herbivore Spodoptera littoralis on the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana and hence infer the contribution of JA-mediated plant defense responses to a chewing insect.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu-Salzman K, Luthe DS, Felton GW (2008) Arthropod-inducible proteins: broad spectrum defenses against multiple herbivores. Plant Physiol 146(3):852–858. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.112177
Fonseca S, Chini A, Hamberg M, Adie B, Porzel A, Kramell R, Miersch O, Wasternack C, Solano R (2009) (+)-7-iso-Jasmonoyl-l-isoleucine is the endogenous bioactive jasmonate. Nat Chem Biol 5(5):344–350. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.161
Koo AJ, Howe GA (2009) The wound hormone jasmonate. Phytochemistry 70(13–14):1571–1580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.07.018
Farmer EE, Johnson RR, Ryan CA (1992) Regulation of expression of proteinase inhibitor genes by methyl jasmonate and jasmonic acid. Plant Physiol 98(3):995–1002
Farmer EE, Ryan CA (1990) Interplant communication: airborne methyl jasmonate induces synthesis of proteinase inhibitors in plant leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87(19):7713–7716
Agrawal AA (2011) Current trends in the evolutionary ecology of plant defence. Functional Ecology 25(2):420–432. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2010.01796.x
Gatehouse JA (2002) Plant resistance towards insect herbivores: a dynamic interaction. New Phytologist 156(2):145–169. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2002.00519.x
Schuman MC, Baldwin IT (2016) The layers of plant responses to insect herbivores. Annu Rev Entomol 61:373–394. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-010715-023851
Verhage A, Vlaardingerbroek I, Raaymakers C, Van Dam NM, Dicke M, Van Wees SC, Pieterse CM (2011) Rewiring of the jasmonate signaling pathway in Arabidopsis during insect herbivory. Front Plant Sci 2:47. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2011.00047
Howe GA, Jander G (2008) Plant immunity to insect herbivores. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:41–66. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092825
McConn M, Creelman RA, Bell E, Mullet JE, Browse J (1997) Jasmonate is essential for insect defense in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(10):5473–5477
Moran PJ, Thompson GA (2001) Molecular responses to aphid feeding in Arabidopsis in relation to plant defense pathways. Plant Physiol 125(2):1074–1085
Stotz HU, Koch T, Biedermann A, Weniger K, Boland W, Mitchell-Olds T (2002) Evidence for regulation of resistance in Arabidopsis to Egyptian cotton worm by salicylic and jasmonic acid signaling pathways. Planta 214(4):648–652
Dombrecht B, Xue GP, Sprague SJ, Kirkegaard JA, Ross JJ, Reid JB, Fitt GP, Sewelam N, Schenk PM, Manners JM, Kazan K (2007) MYC2 differentially modulates diverse jasmonate-dependent functions in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19(7):2225–2245. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.048017
Kessler A, Halitschke R, Baldwin IT (2004) Silencing the jasmonate cascade: induced plant defenses and insect populations. Science 305(5684):665–668. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1096931
Abe H, Onnishi J, Narusaka M, Seo S, Narusaka Y, Tsuda S, Kobayashi M (2008) Arabidopsis-thrips system for analysis of plant response to insect feeding. Plant Signal Behav 3(7):446–447
Zhurov V, Navarro M, Bruinsma KA, Arbona V, Santamaria ME, Cazaux M, Wybouw N, Osborne EJ, Ens C, Rioja C, Vermeirssen V, Rubio-Somoza I, Krishna P, Diaz I, Schmid M, Gomez-Cadenas A, Van de Peer Y, Grbic M, Clark RM, Van Leeuwen T, Grbic V (2014) Reciprocal responses in the interaction between Arabidopsis and the cell-content-feeding chelicerate herbivore spider mite. Plant Physiol 164(1):384–399. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.231555
Knolhoff LM, Heckel DG (2014) Behavioral assays for studies of host plant choice and adaptation in herbivorous insects. Annu Rev Entomol 59:263–278. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-011613-161945
Ali JG, Agrawal AA (2012) Specialist versus generalist insect herbivores and plant defense. Trends Plant Sci 17(5):293–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.02.006
Gols R, Bukovinszky T, van Dam NM, Dicke M, Bullock JM, Harvey JA (2008) Performance of generalist and specialist herbivores and their endoparasitoids differs on cultivated and wild Brassica populations. J Chem Ecol 34(2):132–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-008-9429-z
Kliebenstein D, Pedersen D, Barker B, Mitchell-Olds T (2002) Comparative analysis of quantitative trait loci controlling glucosinolates, myrosinase and insect resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 161(1):325–332
Lankau RA (2007) Specialist and generalist herbivores exert opposing selection on a chemical defense. New Phytol 175(1):176–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02090.x
Health EPP (2015) Scientific Opinion on the pest categorisation of Spodoptera littoralis. EFSA J 13:1. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2015.3987
Yan Y, Stolz S, Chetelat A, Reymond P, Pagni M, Dubugnon L, Farmer EE (2007) A downstream mediator in the growth repression limb of the jasmonate pathway. Plant Cell 19(8):2470–2483. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.050708
Gasperini D, Chetelat A, Acosta IF, Goossens J, Pauwels L, Goossens A, Dreos R, Alfonso E, Farmer EE (2015) Multilayered organization of jasmonate signalling in the regulation of root growth. PLoS Genetics 11(6):e1005300. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005300
Kanchiswamy CN, Takahashi H, Quadro S, Maffei ME, Bossi S, Bertea C, Zebelo SA, Muroi A, Ishihama N, Yoshioka H, Boland W, Takabayashi J, Endo Y, Sawasaki T, Arimura G (2010) Regulation of Arabidopsis defense responses against Spodoptera littoralis by CPK-mediated calcium signaling. BMC Plant Biol 10:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-97
Khan GA, Vogiatzaki E, Glauser G, Poirier Y (2016) Phosphate deficiency induces the jasmonate pathway and enhances resistance to insect herbivory. Plant Physiol 171(1):632–644. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00278
Reymond P, Bodenhausen N, Van Poecke RM, Krishnamurthy V, Dicke M, Farmer EE (2004) A conserved transcript pattern in response to a specialist and a generalist herbivore. Plant Cell 16(11):3132–3147. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.026120
Scholz SS, Vadassery J, Heyer M, Reichelt M, Bender KW, Snedden WA, Boland W, Mithofer A (2014) Mutation of the Arabidopsis calmodulin-like protein CML37 deregulates the jasmonate pathway and enhances susceptibility to herbivory. Mol Plant 7(12):1712–1726. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssu102
Schweizer F, Fernandez-Calvo P, Zander M, Diez-Diaz M, Fonseca S, Glauser G, Lewsey MG, Ecker JR, Solano R, Reymond P (2013) Arabidopsis basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 regulate glucosinolate biosynthesis, insect performance, and feeding behavior. Plant Cell 25(8):3117–3132. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.115139
Park JH, Halitschke R, Kim HB, Baldwin IT, Feldmann KA, Feyereisen R (2002) A knock-out mutation in allene oxide synthase results in male sterility and defective wound signal transduction in Arabidopsis due to a block in jasmonic acid biosynthesis. Plant J 31(1):1–12
Xie DX, Feys BF, James S, Nieto-Rostro M, Turner JG (1998) COI1: an Arabidopsis gene required for jasmonate-regulated defense and fertility. Science 280(5366):1091–1094
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to O. Kindler and R. Reist (Stein, CH) for providing S. littoralis eggs; to E. Warkus (Halle, DE) for manufacturing the custom-made bioassay cages; and to the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (grant GA 2419/2-1 to D.G.) and IPB–Leibniz Association for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Mielke, S., Gasperini, D. (2020). Plant–Insect Bioassay for Testing Arabidopsis Resistance to the Generalist Herbivore Spodoptera littoralis. In: Champion, A., Laplaze, L. (eds) Jasmonate in Plant Biology. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2085. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0142-6_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0142-6_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-0141-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-0142-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols