Abstract
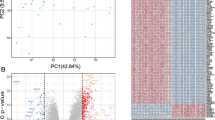
Mitofusin-2 (MFN2) was initially identified as a hyperplasia suppressor in hyper-proliferative vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) of hypertensive rat arteries, which has also been implicated in various cancers. There exists a controversy in whether it is an oncogene or exerting anti-proliferative effect on tumor cells. Our previous cell cycle analysis and MTT assay showed that cell proliferation was inhibited in MFN2 deficient A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells, without investigating the changes in regulatory network or addressing the underlying mechanisms. Here, we performed expression profiling in MFN2 knockdown A549 cells and found that cancer-related pathways were among the most susceptible pathways to MFN2 deficiency. Through comparison with expression profiling of a cohort consisting of 61 pairs of tumor-normal matched samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), we teased out the specific pathways to address the impact that MFN2 ablation had on A549 cells, as well as identified a few genes whose expression level associated with clinicopathologic parameters. In addition, transcriptional factor target enrichment analysis identified E2F as a potential transcription factor that was deregulated in response to MFN2 deficiency. Although bioinformatics analysis usually entail further verification, our study provided considerable information for future scientific inquiries in related areas as well as a paradigm for characterizing perturbation in regulatory network.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sakashita S, Sakashita M, Sound Tsao M. Genes and pathology of non-small cell lung carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 2014;41(1):28–39.
Ferlay J, Shin H-R, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893–917.
Kim ES, Herbst RS, Wistuba II, Lee JJ, Blumenschein GRJ, Tsao A, et al. The BATTLE trial: personalizing therapy for lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2011;1(1):44–53.
Hanahan D, R. a W. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–74.
Sholl LM. Biomarkers in lung adenocarcinoma: a decade of progress. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015;139(4):469–80.
Chen K-H, Guo X, Ma D, Guo Y, Li Q, Yang D, et al. Dysregulation of HSG triggers vascular proliferative disorders. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(9):872–83.
Hall a R, Burke N, Dongworth RK, Hausenloy DJ. Mitochondrial fusion and fission proteins: novel therapeutic targets for combating cardiovascular disease. Br J Pharmacol. 2014;171(8):1890–906.
de Brito OM, Scorrano L. Mitofusin 2 tethers endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria. Nature. 2008;456(7222):605–10.
Wang R, He J, Li J-J, Ni W, Wu Z-Y, Chen W-J, et al. Clinical and genetic spectra in a series of Chinese patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;451(Pt B):263–70.
Lv H, Wang L, Zhang W, Wang Z, Zuo Y, Liu J, et al. A cohort study of Han Chinese MFN2-related Charcot-Marie-Tooth 2A. J Neurol Sci. 2015;358(1-2):153–7.
Stuppia G, Rizzo F, Riboldi G, Del Bo R, Nizzardo M, Simone C, et al. MFN2-related neuropathies: clinical features, molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic perspectives. J Neurol Sci. 2015;356(1–2):7–18.
Chen H, Detmer SA, Ewald AJ, Griffin EE, Fraser SE, Chan DC. Mitofusins Mfn1 and Mfn2 coordinately regulate mitochondrial fusion and are essential for embryonic development. J Cell Biol. 2003;160(2):189–200.
Zhang G-E, Jin H-L, Lin X-K, Chen C, Liu X-S, Zhang Q, et al. Anti-tumor effects of mfn2 in gastric cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(7):13005–21.
Chen KH, Dasgupta A, Ding J, Indig FE, Ghosh P, Longo DL. Role of mitofusin 2 (Mfn2) in controlling cellular proliferation. FASEB J. 2014;28(1):382–94.
Wang W, Lu J, Zhu F, Wei J, Jia C, Zhang Y, et al. Pro-apoptotic and anti-proliferative effects of mitofusin-2 via Bax signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Med Oncol. 2012;29(1):70–6.
Ding Y, Gao H, Zhao L, Wang X, Zheng M. Mitofusin 2-deficiency suppresses cell proliferation through disturbance of autophagy. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0121328.
Lou Y, Li R, Liu J, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Jin B, et al. Mitofusin-2 over-expresses and leads to dysregulation of cell cycle and cell invasion in lung adenocarcinoma. Med Oncol. 2015;32(4):132.
Wang L, Zhou G-B, Liu P, Song J-H, Liang Y, Yan X-J, et al. Dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Realgar-Indigo naturalis as an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(12):4826–31.
Zhang B, Kirov S, Snoddy J. WebGestalt: an integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(Web Server issue):W741–8.
Walter W, Sanchez-Cabo F, Ricote M. GOplot: an R package for visually combining expression data with functional analysis. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(17):2912–4.
Kamburov A, Pentchev K, Galicka H, Wierling C, Lehrach H, Herwig R. ConsensusPathDB: toward a more complete picture of cell biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39 suppl 1:D712–7.
Kamburov A, Wierling C, Lehrach H, Herwig R. ConsensusPathDB—a database for integrating human functional interaction networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(Database issue):D623–8.
Nishimura D. BioCarta. Biotech Softw Internet Rep Comput Softw J Sci. 2001;2(3):117–20.
Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28(1):27–30.
Joshi-Tope G, Gillespie M, Vastrik I, D’Eustachio P, Schmidt E, de Bono B, et al. Reactome: a knowledgebase of biological pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33 suppl 1:D428–32.
Frolkis A, Knox C, Lim E, Jewison T, Law V, Hau DD, et al. SMPDB: the small molecule pathway database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38 suppl 1:D480–7.
Kandasamy K, Mohan SS, Raju R, Keerthikumar S, Kumar GSS, Venugopal AK, et al. NetPath: a public resource of curated signal transduction pathways. Genome Biol. 2010;11(1):R3.
Pico AR, Kelder T, Van Iersel MP, Hanspers K, Conklin BR, Evelo C. WikiPathways: pathway editing for the people. PLoS Biol. 2008;6(7):e184.
Sporn MB, Liby KT. NRF2 and cancer: the good, the bad and the importance of context. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(8):564–71.
Ohta T, Iijima K, Miyamoto M, Nakahara I, Tanaka H, Ohtsuji M, et al. Loss of Keap1 function activates Nrf2 and provides advantages for lung cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 2008;68(5):1303–9.
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK. edgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(1):139–40.
Pradeep A, Sharma C, Sathyanarayana P, Albanese C, Fleming JV, Wang TC, et al. Gastrin-mediated activation of cyclin D1 transcription involves beta-catenin and CREB pathways in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 2004;23:3689–99. December 2003.
Zhang C, Guo H, Li B, Sui C, Zhang Y, Xia X, et al. Effects of Slit3 silencing on the invasive ability of lung carcinoma A549 cells. Oncol Rep. 2015;34(2):952–60.
Sharma J, Gray KP, Harshman LC, Evan C, Nakabayashi M, Fichorova R, et al. Elevated IL-8, TNF-α, and MCP-1 in men with metastatic prostate cancer starting androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) are associated with shorter time to castration-resistance and overall survival. Prostate. 2014;74(8):820–8.
Wang H, Meyer CA, Fei T, Wang G, Zhang F, Liu XS. A systematic approach identifies FOXA1 as a key factor in the loss of epithelial traits during the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:680.
Sharma J, Gray KP, Evan C, Nakabayashi M, Fichorova R, Rider J, et al. Elevated insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) in men with metastatic prostate cancer starting androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is associated with shorter time to castration resistance and overall survival. Prostate. 2014;74(3):225–34.
Ell B, Kang Y. Transcriptional control of cancer metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2013;23(12):603–11.
Lee H-J, Yun C-H, Lim SH, Kim B-C, Baik KG, Kim J-M, et al. SRF is a nuclear repressor of Smad3-mediated TGF-beta signaling. Oncogene. 2007;26(2):173–85.
Khatri P, Sirota M, Butte AJ. Ten years of pathway analysis: current approaches and outstanding challenges. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(2):e1002375.
Ozcan U. XMitofusins: mighty regulators of metabolism. Cell. 2013;155(1):17–8.
Rhodes DR, Chinnaiyan AM. Integrative analysis of the cancer transcriptome. Nat Genet. 2005;37:S31–7.
Murohashi M, Hinohara K, Kuroda M, Isagawa T, Tsuji S, Kobayashi S, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis provides insight into novel signalling pathways in breast cancer stem cells. Br J Cancer. 2010;102(1):206–12.
Nguyen T, Nioi P, Pickett CB. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(20):13291–5.
Furusawa Y, Uruno A, Yagishita Y, Higashi C, Yamamoto M. Nrf2 induces fibroblast growth factor 21 in diabetic mice. Genes to Cells. 2014;19(12):864–78.
Nasrallah CM, Horvath TL. Mitochondrial dynamics in the central regulation of metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10(11):650–8.
Kawalec M, Boratyńska-Jasińska A, Beręsewicz M, Dymkowska D, Zabłocki K, Zabłocka B. Mitofusin 2 deficiency affects energy metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis in MEF cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0134162.
Zhao J, Zhang J, Yu M, Xie Y, Huang Y, Wolff DW, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics regulates migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2013;32(40):4814–24.
Takai D, Yagi Y, Wakazono K, Ohishi N, Morita Y, Sugimura T, et al. Silencing of HTR1B and reduced expression of EDN1 in human lung cancers, revealed by methylation-sensitive representational difference analysis. Oncogene. 2001;20(51):7505–13.
Lu J-W, Liao C-Y, Yang W-Y, Lin Y-M, Jin S-LC, Wang H-D, et al. Overexpression of endothelin 1 triggers hepatocarcinogenesis in Zebrafish and promotes cell proliferation and migration through the AKT Pathway. PLoS One. 2014;1:e85318.
Younes M, Wu Z, Dupouy S, Lupo AM, Mourra N, Takahashi T, et al. Neurotensin (NTS) and its receptor (NTSR1) causes EGFR, HER2 and HER3 over-expression and their autocrine/paracrine activation in lung tumors, confirming responsiveness to erlotinib. Oncotarget. 2014;5(18):8252.
Dallol A, Da Silva NF, Viacava P, Minna JD, Bieche I, Maher ER, et al. SLIT2, a human homologue of the Drosophila Slit2 gene, has tumor suppressor activity and is frequently inactivated in lung and breast cancers. Cancer Res. 2002;62(20):5874–80.
Dallol A, Krex D, Hesson L, Eng C, Maher ER, Latif F. Frequent epigenetic inactivation of the SLIT2 gene in gliomas. Oncogene. 2003;22(29):4611–6.
Dickinson RE, Dallol A, Bieche I, Krex D, Morton D, Maher ER, et al. Epigenetic inactivation of SLIT3 and SLIT1 genes in human cancers. Br J Cancer. 2004;91(12):2071–8.
Tseng R-C, Lee S-H, Hsu H-S, Chen B-H, Tsai W-C, Tzao C, et al. SLIT2 attenuation during lung cancer progression deregulates beta-catenin and E-cadherin and associates with poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 2010;70(2):543–51.
Thakur A, Bollig A, Wu J, Liao DJ. Gene expression profiles in primary pancreatic tumors and metastatic lesions of Ela-c-myc transgenic mice. Mol Cancer. 2008;7:11.
Zhang X, Yee D. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) inhibits breast cancer cell motility. Cancer Res. 2002;62(15):4369–75.
Chen H-Z, Tsai S-Y, Leone G. Emerging roles of E2Fs in cancer: an exit from cell cycle control. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(11):785–97.
Bertino JR, Banerjee D, Minko T, Garbuzenko OB, Xie X, Kerrigan JE, et al. E2F as a target of hormone refractory prostate cancer. Google Patents. 2014.
Zhao X, He L, Li T, Lu Y, Miao Y, Liang S, et al. SRF expedites metastasis and modulates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition by regulating miR-199a-5p expression in human gastric cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(12):1900–13.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science foundation of China (81201839, 81572249, 81402378, and 81472642), the Research Project of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (20124Y108 and 201440032), the Excellent Young Teachers Program of Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, and Shanghai international cooperation project of science and technology (14430723300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Yuqing Lou and Yanwei Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(XLSX 555 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, R. et al. Transcriptional profiling revealed the anti-proliferative effect of MFN2 deficiency and identified risk factors in lung adenocarcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 8643–8655 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4702-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4702-6