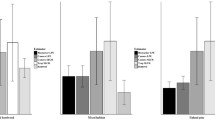
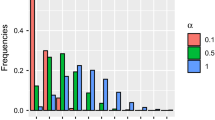
Abstract
The few distance sampling studies that use Bayesian methods typically consider only line transect sampling with a half-normal detection function. We present a Bayesian approach to analyse distance sampling data applicable to line and point transects, exact and interval distance data and any detection function possibly including covariates affecting detection probabilities. We use an integrated likelihood which combines the detection and density models. For the latter, densities are related to covariates in a log-linear mixed effect Poisson model which accommodates correlated counts. We use a Metropolis-Hastings algorithm for updating parameters and a reversible jump algorithm to include model selection for both the detection function and density models. The approach is applied to a large-scale experimental design study of northern bobwhite coveys where the interest was to assess the effect of establishing herbaceous buffers around agricultural fields in several states in the US on bird densities. Results were compared with those from an existing maximum likelihood approach that analyses the detection and density models in two stages. Both methods revealed an increase of covey densities on buffered fields. Our approach gave estimates with higher precision even though it does not condition on a known detection function for the density model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bates, D. (2009a), “Adaptive Gauss–Hermite Quadrature for Generalized Linear or Nonlinear Mixed Models. R Package Version 0.999375-31,” Technical Report. http://lme4.r-forge.r-project.org/.
Bates, D. (2009b), “Computational Methods for Mixed Models. R Package Version 0.999375-31,” Technical Report. http://lme4.r-forge.r-project.org/.
Buckland, S. T., Burnham, K. P., and Augustin, N. H. (1997), “Model Selection: An Integral Part of Inference,” Biometrics, 53 (2), 603–618.
Buckland, S. T., Goudie, I. B. J., and Borchers, D. L. (2000), “Wildlife Population Assessment: Past Developments and Future Directions,” Biometrics, 56, 1–12.
Buckland, S. T., Anderson, D. R., Burnham, K. P., Laake, J. L., Borchers, D. L., and Thomas, L. (2001), Introduction to Distance Sampling, London: Oxford University Press.
Buckland, S. T., Anderson, D. R., Burnham, K. P., Laake, J. L., Borchers, D. L., and Thomas, L. (2004), Advanced Distance Sampling, London: Oxford University Press.
Buckland, S. T., Russell, R. E., Dickson, B. G., Saab, V. A., Gorman, D. G., and Block, W. M. (2009), “Analysing Designed Experiments in Distance Sampling,” Journal of Agricultural, Biological, and Environmental Statistics, 14, 432–442.
Cañadas, A., and Hammond, P. S. (2006), “Model-Based Abundance Estimates for Bottlenose Dolphins off Southern Spain: Implications for Conservation and Management,” Journal of Cetacean Research and Management, 8 (1), 13–27.
Chelgren, N. D., Samora, B., Adams, M. J., and McCreary, B. (2011), “Using Spatiotemporal Models and Distance Sampling to Map the Space Use and Abundance of Newly Metamorphosed Western Toads (Anaxyrus Boreas),” Herpetological Conservation and Biology, 6 (2), 175–190.
Conn, P. B., Laake, J. L., and Johnson, D. S. (2012), “A Hierarchical Modeling Framework for Multiple Observer Transect Surveys,” PLoS ONE, 7 (8), e42294.
Davison, A. C. (2003), Statistical Models, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Durban, J. W., and Elston, D. A. (2005), “Mark-Recapture with Occasion and Individual Effects: Abundance Estimation Through Bayesian Model Selection in a Fixed Dimensional Parameter Space,” Journal of Agricultural, Biological, and Environmental Statistics, 10 (3), 291–305.
Eguchi, T., and Gerrodette, T. (2009), “A Bayesian Approach to Line-Transect Analysis for Estimating Abundance,” Ecological Modelling, 220, 1620–1630.
Evans, K. O., Burger, L. W., Oedekoven, C. S., Smith, M. D., Riffell, S. K., Martin, J. A., and Buckland, S. T. (2013), “Multi-Region Response to Conservation Buffers Targeted for Northern Bobwhite,” The Journal of Wildlife Management, 77, 716–725.
Gelman, A., Roberts, G. O., and Gilks, W. R. (1996), “Efficient Metropolis Jumping Rules,” in Bayesian Statistics, Vol. 5, eds. M. Bernardo, J. O. Berger, A. P. Dawid, and A. F. M. Smith, Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 599–608.
Gerrodette, T., and Eguchi, T. (2011), “Precautionary Design of a Marine Protected Area Based on a Habitat Model,” Endangered Species Research, 15 (2), 159–166.
Gimenez, O., Bonner, S. J., King, R., Parker, R. A., Brooks, S. P., Jamieson, L. E., Grosbois, V., Morgan, B. J. T., and Thomas, L. (2009), “WinBUGS for Population Ecologists: Bayesian Modeling Using Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods,” in Modeling Demographic Processes in Marked Populations. Environmental and Ecological Statistics, Vol. 3, eds. D. L. Thomson, E. G. Cooch, and M. J. Conroy, Berlin: Springer, pp. 883–915.
Green, P. J. (1995), “Reversible Jump Markov Chain Monte Carlo Computation and Bayesian Model Determination,” Biometrika, 82 (4), 711–732.
Hastings, W. K. (1970), “Monte Carlo Sampling Methods Using Markov Chains and Their Applications,” Biometrika, 57 (1), 97–109.
Hedley, S. L., and Buckland, S. T. (2004), “Spatial Models for Line Transect Sampling,” Journal of Agricultural, Biological, and Environmental Statistics, 9, 181–199.
Johnson, D. S., Laake, J. L., and Ver Hoef, J. M. (2010), “A Model-Based Approach for Making Ecological Inference from Distance Sampling Data,” Biometrics, 66, 310–318.
Karunamuni, R. J., and Quinn II., T. J. (1995), “Bayesian Estimation of Animal Abundance for Line Transect Sampling,” Biometrics, 51, 1325–1337.
King, R., Morgan, B. J. T., Gimenez, O., and Brooks, S. P. (2010), Bayesian Analysis for Population Ecology, London/Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC Press.
Marcot, B. G., Holthausen, R. S., Raphael, M. G., Rowland, M. M., and Wisdom, M. J. (2001), “Using Bayesian Belief Networks to Evaluate Fish and Wildlife Population Viability Under Land Management Alternatives from an Environmental Impact Statement,” Forest Ecology and Management, 153, 29–42.
Marques, F. F. C., and Buckland, S. T. (2003), “Incorporating Covariates Into Standard Line Transect Analyses,” Biometrics, 53, 924–935.
McCulloch, C. E., and Searle, S. R. (2001), Generalized, Linear, and Mixed Models, New York: Wiley.
Metropolis, N., Rosenbluth, A. W., Rosenbluth, M. N., Teller, A. H., and Teller, E. (1953), “Equations of State Calculations by Fast Computing Machines,” Journal of Chemical Physics, 21 (6), 1087–1091.
Moore, J. E., and Barlow, J. (2011), “Bayesian State-Space Model of Fin Whale Abundance Trends from a 1991–2008 Time Series of Line-Transect Surveys in the California Current,” Journal of Applied Ecology, 48 (5), 1195–1205.
Oedekoven, C. S., Buckland, S. T., Mackenzie, M. L., Evans, K. O., and Burger, L. W. (2013), “Improving Distance Sampling: Accounting for Covariates and Non-independency Between Sampled Sites,” Journal of Applied Ecology, 50 (3), 786–793.
Royle, J. A., and Dorazio, R. M. (2008), Hierarchical Modeling and Inference in Ecology: The Analysis of Data from Populations, Metapopulations and Communities, San Diego: Academic Press.
Royle, J. A., Dawson, D. K., and Bates, S. (2004), “Modelling Abundance Effects in Distance Sampling,” Ecology, 85 (6), 1591–1597.
Schmidt, J. H., Lindberg, M. S., Johnson, D. S., Conant, B., and King, J. (2009), “Evidence of Alaskan Trumpeter Swan Population Growth Using Bayesian Hierarchical Models,” The Journal of Wildlife Management, 73 (5), 720–727.
Schmidt, J. H., Rattenbury, K. L., Lawler, J. P., and MacCluskie, M. C. (2012), “Using Distance Sampling and Hierarchical Models to Improve Estimates of Dall’s Sheep Abundance,” The Journal of Wildlife Management, 76 (2), 317–327.
Sillett, T. S., Chandler, R. B., Royle, J. A., Kéry, M., and Morrison, S. A. (2012), “Hierarchical Distance-Sampling Models to Estimate Population Size and Habitat-Specific Abundance of an Island Endemic,” Ecological Applications, 22, 1997–2006.
Thomas, L., Buckland, S. T., Rexstad, E. A., Laake, J. L., Strindberg, S., Hedley, S. L., Bishop, J. R. B., Marques, T. A., and Burnham, K. P. (2010), “Distance Software: Design and Analysis of Distance Sampling Surveys for Estimating Population Size,” Journal of Applied Ecology, 47, 5–14.
Zhang, S. (2011), “On Parametric Estimation of Population Abundance for Line Transect Sampling,” Environmental and Ecological Statistics, 18, 79–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oedekoven, C.S., Buckland, S.T., Mackenzie, M.L. et al. Bayesian Methods for Hierarchical Distance Sampling Models. JABES 19, 219–239 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13253-014-0167-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13253-014-0167-0