Abstract
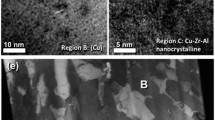
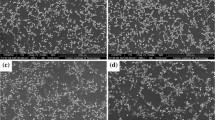
Incorporated SiC nanoparticles are demonstrated to influence the solidification of magnesium-zinc alloys resulting in strong, ductile, and castable materials. By ultrasonically dispersing a small amount (less than 2 vol pct) of SiC nanoparticles, both the strength and ductility exhibit marked enhancement in the final casting. This unusual ductility enhancement is the result of the nanoparticles altering the selection of intermetallic phases. Using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), the MgZn2 phase was discovered among SiC nanoparticle clusters in hypoeutectic compositions. Differential thermal analysis showed that the MgZn2 formation resulted in elimination of other intermetallics in the Mg-4Zn nanocomposite and reduced their formation in Mg-6Zn and Mg-8Zn nanocomposites.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
PHILIP is a trademark of FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR.
References
X.C. Tong and H.S. Fang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 893–902.
Y.T. Zhao, S.L. Zhang, G. Chen, X.N. Cheng, and C.Q. Wang: Compos. Sci. Technol., 2008, vol. 68, pp. 1463–70.
S.F. Hassan and M. Gupta: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2004, vol. 20, pp. 1383–88.
S.F. Hassan and M. Gupta: J. Compos. Mater., 2007, vol. 41, pp. 2533–43.
R.M. Heavenrich: EPA420-R-06-011, Office of Transportation and Air Quality, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, 2006, pp. 1–80.
A.F. Zimmerman, G. Palumbo, K.T. Aust, and U. Erb: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2002, vol. 328, pp. 137–46.
M.J. Tan and X. Zhang: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1998, vol. 244, pp. 80–85.
H. Ferkel and B.L. Mordike: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2001, vol. 298, pp. 193–99.
D.Y. Ying and D.L. Zhang: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2000, vol. 286, pp. 152–56.
Y.S. Kwon, D.V. Dudina, M.A. Korchagin, and O.I. Lomovsky: J. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 39, pp. 5325–31.
J. Lan, Y. Yang, and X. Li: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2004, vol. 386, pp. 284–90.
Y. Yang, J. Lan, and X. Li: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2004, vol. 380, pp. 378–83.
Y. Yang and X. Li: J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME, 2007, vol. 129, pp. 252–55.
K.S. Suslick and G.J. Price: Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci., 1999, vol. 29, pp. 295–326.
G. Cao, H. Konishi, and X. Li: J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME, 2008, vol. 130, pp. 031105.1–031105.6.
A. Luo: Can. Metall. Q., 1996, vol. 35, pp. 375–83.
M. De Cicco, L.S. Turng, X. Li, and J.H. Perepezko: Solid State Phenomena, 2008, vols. 141–143, pp. 487–92.
G. Cao, J. Kobliska, H. Konishi, and X. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, vol. 39A, pp. 880–86.
Z. Zhang and D.L. Chen: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, vols. 483–484, pp. 148–52.
Z. Zhang and D.L. Chen: Scripta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 1321–26.
C.S. Goh, J. Wei, L.C. Lee, and M. Gupta: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 5115–21.
L.H. Dai, Z. Ling, and Y.L. Bai: Compos. Sci. Technol., 2001, vol. 61, pp. 1057–63.
ASM Handbook, vol. 2, Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials, Properties of Magnesium Alloys, Cast Magnesium Alloys, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1992, http://products.asminternational.org/hbk/index.jsp.
CoorsTek Inc. website, http://www.coorstek.com/materials/ceramics/carbides/puresichr.asp, 2009.
J. Lin, Q. Wang, L. Peng, Y. Zhou, and W. Ding: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, vols. 546–549, pp. 319–22.
M. De Cicco, L. Turng, X. Li, and J.H. Perepezko: Solid State Phenomena, 2006, vols. 116–117, pp. 478–83.
ASM Handbook, vol. 21, Composites, Introduction to Composites, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1992, http://products.asminternational.org/hbk/index.jsp.
Y. Yang and X. Li: J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME, 2007, vol. 129, pp. 497–501.
X. Gao and J.F. Nie: Scripta Mater., 2007, vol. 57, pp. 655–58.
X. Gao and J.F. Nie: Scripta Mater., 2007, vol. 56, pp. 645–48.
J.B. Clark, L. Zabdyr, and Z. Moser: in Phase Diagrams of Binary Magnesium Alloys, A.A. Nayeb-Hashemi and J.B. Clark, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1988, pp. 353–64.
J. Miettinen: CALPHAD, 2008, vol. 32, pp. 389–98.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 16, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Cicco, M., Konishi, H., Cao, G. et al. Strong, Ductile Magnesium-Zinc Nanocomposites. Metall Mater Trans A 40, 3038–3045 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0013-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0013-0