Abstract
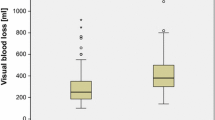
The effect of closed-suction drainage with red-cell reinfusion on patients receiving low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) prophylaxis after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) has not been previously studied. Therefore, our goals were to determine the effect of reinfusion drains and LMWH on allogeneic transfusions and wound complications after TKA by comparing patients treated with and without drains. Overall, transfusion rates were lower in the drain group (40% vs 15%, P=.04). Patients with reinfusion drains had a significantly higher rate of allogeneic transfusion (15.8%) than those predonating autologous blood and no drain (5.4%, P=.0003). The drain group had lower rates of wound complications (P=not significant). We were unable to demonstrate the efficacy of red-cell reinfusion as a substitute for autologous donation in TKA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
MR Bong V Patel E Chang PS Issack R Hebert PE Cesare (2004) ArticleTitleRisks associated with blood transfusion after total knee arthroplasty J Arthroplasty 19 281–287 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.arth.2003.10.013 Occurrence Handle15067638
CW Colwell SuffixJr TE Spiro AA Trowbridge JW Stephens GA Gardiner SuffixJr MA Ritter (1995) ArticleTitleEfficacy and safety of enoxaparin versus unfractionated heparin for prevention of deep venous thrombosis after elective knee arthroplasty. Enoxaparin Clinical Trial Group Clin Orthop 321 19–27 Occurrence Handle7497668
CN Esler C Blakeway NJ Fiddian (2003) ArticleTitleThe use of a closed-suction drain in total knee arthroplasty. A prospective, randomised study J Bone Joint Surg Br 85 215–217 Occurrence Handle10.1302/0301-620X.85B2.13357 Occurrence Handle12678355
RH Fitzgerald SuffixJr TE Spiro AA Trowbridge GA Gardiner SuffixJr TL Whitsett MB O’Connell JA Ohar TR Young (2001) ArticleTitlePrevention of venous thromboembolic disease following primary total knee arthroplasty. A randomized, multicenter, open-label, parallel-group comparison of enoxaparin and warfarin J Bone Joint Surg Am 83 900–906 Occurrence Handle11407799
WH Geerts JA Heit GP Clagett GF Pineo CW Colwell FA Anderson SuffixJr HB Wheeler (2001) ArticleTitlePrevention of venous thromboembolism Chest 119 132S–175S Occurrence Handle10.1378/chest.119.1_suppl.132S Occurrence Handle11157647
CD Han DE Shin (1997) ArticleTitlePostoperative blood salvage and reinfusion after total joint arthroplasty J Arthroplasty 12 511–516 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0883-5403(97)90173-X Occurrence Handle9268790
Healy WL, Pfeifer BA, Kurtz SR, Johnson C, Johnson W, Johnston R, Sanders D, Karpman R, Hallack GN, Valeri CR (1994) Evaluation of autologous shed blood for autotransfusion after orthopaedic surgery. Clin Orthop 53–59
BT Holt NL Parks GA Engh JM Lawrence (1997) ArticleTitleComparison of closed-suction drainage and no drainage after primary total knee arthroplasty Orthopedics 20 1121–1124 Occurrence Handle9415907
MJ Parker CP Roberts D Hay (2004) ArticleTitleClosed suction drainage for hip and knee arthroplasty. A meta-analysis J Bone Joint Surg Am 86 1146–1152 Occurrence Handle10.1302/0301-620X.86B8.14839 Occurrence Handle15173286
MA Ritter EM Keating PM Faris (1994) ArticleTitleClosed wound drainage in total hip or total knee replacement. A prospective, randomized study J Bone Joint Surg Am 76 35–38 Occurrence Handle8288663
MB Simpson KP Murphy HG Chambers AL Bucknell (1994) ArticleTitleThe effect of postoperative wound drainage reinfusion in reducing the need for blood transfusions in elective total joint arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized study Orthopedics 17 133–137 Occurrence Handle8190677
SV Slagis JB Benjamin RG Volz GF Giordano (1991) ArticleTitlePostoperative blood salvage in total hip and knee arthroplasty. A randomised controlled trial J Bone Joint Surg Br 73 591–594 Occurrence Handle1906472
D Warwick J Harrison S Whitehouse A Mitchelmore M Thornton (2002) ArticleTitleA randomised comparison of a foot pump and low-molecular-weight heparin in the prevention of deep-vein thrombosis after total knee replacement J Bone Joint Surg Br 84 344–350 Occurrence Handle10.1302/0301-620X.84B3.12372 Occurrence Handle12002490
D Willemen J Paul SH White DW Crook (1991) ArticleTitleClosed suction drainage following knee arthroplasty. Effectiveness and risks Clin Orthop 264 232–234 Occurrence Handle1997239
ST Woolson WW Wall (2003) ArticleTitleAutologous blood transfusion after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, prospective study comparing predonated and postoperative salvage blood J Arthroplasty 18 243–249 Occurrence Handle10.1054/arth.2003.50058 Occurrence Handle12728413
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mary E. Hardwick, RN, MSN for assistance in the preparation of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gordon, A.C., Pulido, P., Copp, S.N. et al. The Use of Reinfusion Drains after Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients Treated with Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Thromboembolic Prophylaxis. HSS Jrnl 1, 19–24 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-005-0122-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-005-0122-2