Abstract
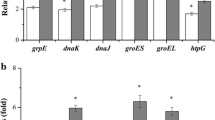
The purpose of this work was to investigate the induction of stress shock proteins in Burkholderia sp. YK-2 in response to the phenoxyherbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). The stress shock proteins, which contribute to the resistance of the cytotoxic effect of 2,4-D, were induced at different 2,4-D concentrations in exponentially growing cultures of Burkholderia sp. YK-2. This response involved the induction of a 43-kDa DnaK and 41-kDa GroEL proteins, characterized by SDS-PAGE and Western blot by use of the anti-DnaK and anti-GroEL monoclonal antibodies. The total stress shock proteins were analyzed by 2-D PAGE. Survival of Burkholderia sp. YK-2 with time in the presence of different concentrations of 2,4-D was monitored, and viable counts paralleled the induction of the stress shock proteins in this strain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 November 1999 / Accepted: 24 November 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, YS., Park, SH., Kim, CK. et al. Induction of Stress Shock Proteins DnaK and GroEL by Phenoxyherbicide 2,4-D in Burkholderia sp. YK-2 Isolated from Rice Field. Curr Microbiol 41, 33–38 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002840010087
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002840010087