Abstract
Background
Treating schizophrenia patients who fail to respond to antipsychotics is a major challenge, and the percentage of treatment-resistant patients is estimated to be 20–25 %. Recent studies indicate that yokukansan (YKS; D2 and 5HT1A partial agonist and 5HT2A and glutamate antagonist) to be safe and useful in treating behavioral and psychological symptoms associated with dementia and other neuropsychiatric conditions. We aimed at evaluating both the efficacy and safety of YKS in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia.
Methods
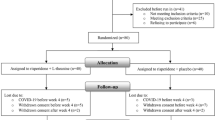
This randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted between May 2010 and August 2012. One hundred twenty antipsychotic-treated inpatients from 34 psychiatric hospitals in Japan were included. Patients were randomized to adjuvant treatment with YKS 7.5 g/day or placebo. During a 4-week follow-up, psychopathology was assessed using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) with five factors [excitement/hostility (P4, P7, G8, and G14), depression/anxiety (G1, G2, G3, G4, and G6), cognition (P2, N5, N7, G5, G10, G11, G12, G13, and G15], positive (P1, P3, P5, P6, and G9), and negative (N1, N2, N3, N4, N6, G7, and G16]]. Other assessments included, Clinical Global Impression—Severity (CGI-S), Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF), and Drug-Induced Extrapyramidal Symptoms Scale (DIEPSS). The primary efficacy outcome was the change in PANSS five-factor scores. The secondary outcomes were changes in the scores of CGI-S. The analysis was made on a modified intention to treat basis with the help of a last observation carried forward method.
Results
YKS showed a tendency of superiority to placebo in reducing total all PANSS five-factor scores in treatment-resistant schizophrenia, but the difference was not statistically significant in total, depression/anxiety, cognition, positive, and negative factors. However, compared to the placebo group, the YKS group showed statistically significant improvements in the PANSS excitement/hostility factor scores (p < 0.05). No substantial side effects were recorded.
Conclusion
The results of the present study indicate YKS to be a potential adjunctive treatment strategy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia, particularly to improve excitement/hostility symptoms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizawa R, Kanbayashi T, Saito Y, Ogawa Y, Sugiyama T, Kitajima T, Kaneko Y, Abe M, Shimizu T (2002) Effects of yoku-kan-san-ka-chimpi-hange on the sleep of normal healthy adult subjects. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 56:303–304
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn, text revision. APA: Washington, DC
Anderson G, Berk M, Dodd S, Bechter K, Altamura AC, Dell’osso B, Kanba S, Monji A, Fatemi SH, Buckley P, Debnath M, Das UN, Meyer U, Muller N, Kanchanatawan B, Maes M (2013) Immuno-inflammatory, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and neuroprogressive pathways in the etiology, course and treatment of schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 42:1–4
Citrone L, Meng X, Hochfeld M (2011) Efficacy of iloperidone in schizophrenia: a PANSS five-factor analysis. Schizophr Res 131:75–81
Conley RR, Buchanan RV (1997) Evaluation of treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 23:663–674
Demijaha A, Murray R, McGuire PK, Kapur S, Howes OD (2012) Dopamine synthesis capacity in psatients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 169:1203–1210
Egashira N, Iwasaki K, Ishibashi A, Hayakawa K, Okuno R, Abe M, Uchida N, Mishima K, Takasaki K, Nishimura R, Oishi R, Fujiwara M (2008) Repeated administration of yokukansan inhibits DOI-induced head-twitch response and decreases expression of 5-HT2A receptors in the prefrontal cortex. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:1516–1520
First MB, Spitzer R, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (1995) Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV Axis I disorders. American Psychiatric Press, New York
Furuya M, Miyaoka T, Tsumori T, Liaury K, Hashioka S, Wake R, Tsuchie K, Fukushima M, Ezoe S, Horiguchi J (2013) Yokukansan promotes hippocampal neurogenesis associated with the suppression of activated microglia in Gunn rat. J Neuroinflammation 10:145
Gibbons RD, Hedecker D, Elkin I et al (1993) Some conceptual and statistical issues in analysis of longitudinal psychiatric data: application to the NIMH treatment of Depression Collaborative Research Program dataset. Arch Gen Psychiatry 50:739–750
Guy W (1976) ECDEU assessment manual for psychopharmacogy-revised, Rockville, MD, US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service, Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration, NIMH Psychopharmacology Research Branch, Division of Extramural Research Programs; pp 218–222
Hayashi Y, Ishida Y, Inoue T, Udagawa M, Takeuchi K, Yoshida H, Kiue K, Ninomiya Y, Kawano J, Sameshima T, Kawahara T, Goto I, Shudo K, Kurayama S, Nakamura J, Okahara K, Mitsuyama Y (2010) Treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of Alzheimer-type dementia with yokukansan in clinical practice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 16:541–545
Howes OD, Vergunst F, Gee S, McGuire P, Kapur S, Taylor D (2012) Adherence to treatment guidelines in clinical practice: study of antipsychotic treatment prior to clozapine initiation. Br J Psychiatry 201:481–485
Ikarashi Y, Iizuka S, Imamura S, Yamaguchi T, Sekiguchi K, Kawakami Z, Yuzurihara M, Kase Y, Takeda S (2009) Effects of yokukansan, a traditional Japanese medicine, on memory disturbance and behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia in thiamine-deficient rats. Biol Pharm Bull 32:170101709
Inada T, Yagi G, Gardos G (2009) Inter-rater reliability of the drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms scale (DIEPSS). In abstract of the 20th Collegium International Neuropsychopharmacologium, Melborune, 23–27
Iwasaki K, Maruyama M, Tomita N et al (2005a) Effect of the traditional Chinese herbal medicine yi-gan san for cholinesterase inhibitor-resistant visual hallucinations and neuropsychiatric symptoms in patient with dementia with Lewy bodies. J Clin Psychiatry 66:1612–1613
Iwasaki K, Satoh-Nakagawa T, Maruyama M, Monma Y, Nemoto M, Tanji H, Fujiwara H, Seki T, Fujii M, Arai H, Sasaki H (2005b) A randomized observer-blind, controlled trial of the traditional Chinese medicine yi-gan san for improvement of behavioral and psychological symptoms and activities of daily living dementia patients. J Clin Psychiatry 66:248–252
Iwasaki K, Kosaka K, Mori H, Okitsu R, Furukawa K, Manabe Y, Yoshida M, Kanamori A, Ito N, Wada K, Kitayama M, Horiguchi J, Yamaguchi S, Fukuhara R, Oumura S, Nakano S, Hashimoto M, Kinoshita T (2011) Open label trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of yokukansan, a traditional Asian medicine, in dementia with Lewy bodies. J Am Geriatr Soc 59:936–938
Iwasaki K, Kosaka K, Mori F, Okitsu R, Furukawa K, Manabe Y, Yoshita M, Kanamori A, Ito N, Wada K, Kitayama M, Horiguchi J, Yamaguchi S, Takayama S, Fukuhara R, Ouma S, Nakano S, Hashimoto M, Kinoshita T (2012) Improvement in delusions and hallucinations in patients with dementia with Lewy bodies upon administration of yokukansan, a traditional Japanese medicine. Psychogeriatrics 12:235–241
Kajitani K, Kanba S (2012) Successful treatment of poststroke emotional incontinence with yokukansan, an Asian herbal medicine: report of two cases. J Am Geriatr Soc 60:379–381
Kanatani H, Kohda H, Yamawaki S et al (1985) The active principles of the branchlet and hook of Uncaria sinesis Oliv. Examined with a 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor binding assay. J Pharm Pharmacol 37:401–404
Kane JM, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H (1988) Clozapine in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Psychopharmacol Bull 24:62–67
Kang TH, Murakami Y, Mastumoto K et al (2002) Rhyncoohyline and isorhynchophyline inhibit NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 455:27–34
Kanno H, Sekiguchi K, Yamaguchi T, Terawaki K, Yuzurihara M, Kase Y, Ikarashi Y (2009) Effect of yokukansan, a traditional Japanese medicine, on social and aggressive behavior of para-chloro amphetamine-injected rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 61:1249–1256
Kapur S, Zipursky RB, Remington G (1999) Clinical and theoretical implications of 5HT2 and D2 receptor occupancy of clozapine, risperidone, and olanzapine in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 156:286–293
Kawakami Z, Kanno H, Ueki Terawaki K, Tabuchi M, Ikarashi Y, Kase Y (2009) Neuroprotective effects of yokukansan, a traditional Japanese medicine, on glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity in cultured cells. Neuroscience 159:1397–1407
Kawanabe T, Yorita A, Shimura H, Oizumi H, Tanaka S, Hattori N (2010) Successful treatment with yokukansan for behavioral and psychological symptoms of parkinsonian dementia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:284–287
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizoph Bull 13:261–276
Kimura T, Hayashida H, Furukawa H, Takamatsu J (2010) Pilot study of pharmacological treatment for frontotemporal dementia: effect of yokukansan on behavioral symptoms. Psychiatry Clinical Neurosci 64:207–210
Lindenmayer JP, Grochowski S, Hyman RB (1995) Five factor model of schizophrenia: replication across samples. Schizophr Res 14:229–234
Miyaoka T, Horiguchi J (2009) Clinical potential of yi-gan san (yokukansan) for psychiatric disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rev 5:271–275
Miyaoka T, Furuya M, Yasuda H, Hayashida M, Inagaki T, Horiguchi J (2008a) Yi-gan san for treatment of borderline personality disorder: an open-label study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:150–154
Miyaoka T, Furuya M, Yasuda H, Hayashida M, Inagaki T, Horiguchi J (2008b) Yi-gan san for treatment of neuroleptic-induced tardive dyskinesia: an open-label study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:761–764
Miyaoka T, Furuya M, Yasuda H, Hayashida M, Inagaki T, Horiguchi J (2009a) Yi-gan san as adjunctive therapy for treatment-resistant schizophrenia: an open-label study. Clin Neuropharmacol 32:6–9
Miyaoka T, Nagahama M, Tsuchie K, Hayashida M, Nishida A, Inagaki T, Horiguchi J (2009b) Charles Bonnet syndrome: successful treatment of visual hallucinations due to vision loss with yi-gan san. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:382–383
Miyaoka T, Furuya M, Kristian L, Wake R, Kawakami K, Nagahama M, Kawano K, Ieda M, Tsuchie K, Horiguchi J (2011) Yi-gan san for treatment of Charles Bonnet syndrome (visual hallucination due to vision loss): an open-label study. Clin Neuropharmacol 34:24–27
Miyaoka T, Wake R, Furuya M, Liaury K, Ieda M, Kawakami K, Tsuchie K, Inagaki T, Horiguchi J (2012) Yokukansan (TJ-54) for treatment of pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified and Asperger’s disorder: a 12-week prospective, open-label study. BMC Psychiatry 12:215
Miyaoka T, Wake R, Furuya M, Liaury K, Ieda M, Kawakami K, Tsuchie K, Fukushima M, Ishihara K, Araki T, Hashioka S, Horiguchi J (2013) Yokukansan (TJ-54) for treatment of very-late-onset schizophrenia-like psychosis: an open-label study. Phytomedicine 20:654–658
Mizukami K, Asada T, Kinoshita T, Tanaka K, Sonohara K, Nakai R, Yamaguchi K, Hanyu H, Kanaya K, Takao T, Okada M, Kudo S, Kotoku H, Iwakiri M, Kurita H, Miyamura T, Kawasaki Y, Omori K, Shinozaki K, Odawara T, Suzuki T, Yamada S, Nakamura Y, Toba K (2009) A randomized cross-over study of a traditional Japanese medicine (kampo), yokukansan, in the treatment of the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:191–199
Monji A, Takita M, Samejima T, Takaishi T, Hashimoto K, Matsunaga H, Oda M, Sumida Y, Mizoguchi Y, Kato T (2009) Effect of yokukansan on the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia in elderly patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:308–311
Nakata K, Yokoyama E, Yamazaki T, Takano O, Maeda T, Takashi S, Terayama Y (2012) Effect of yokukansan on behavioral and psychological symptoms of vascular dementia: an open-label trial. Phytomedicine 19:524–528
Nishi A, Yamaguchi T, Sekiguchi K, Ikarashi Y, Kase Y (2010) Ameliorative effect of yokukansan an aggressive behavior in social isolated mice. The 40th Annual Meeting of Japanese Society of Neuropsychopharmacology. Abstract P176
Okahara K, Ishida Y, Hayashi Y, Inoue T, Tsuruta K, Takeuchi K, Yoshimura H, Kiue K, Ninomiya Y, Kawano J, Yoshida K, Noda S, Tomita S, Fujimoto M, Hosomi J, Mistuyama Y (2010) Effects of yokukansan on behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia in regular treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 16:532–536
Shimada Y, Goto H, Itoh T (1999) Evaluation of the prospective effects of alkaloids from the hooks and stems of Uncaria sinesis of glutamate-induced neuronal death in cultured cerebellar granule cells from rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 51:715–722
Shimada Y, Goto H, Kogure T et al (2001) Protective effect of phenolic compounds isolated from the hooks and stems of Uncaria sinesis on glutamate-induced neuronal death. Am J Chin Med 29:173–180
Smith RS, Maes M (1995) The macrophage-T-lymphocyte of schizophrenia: additional evidence. Med Hypotheses 45:135–141
Stern RG, Schneider J, Davidson M (1997) Limitation of controlled augmentation trials in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 42:138–143
Sumiyoshi H, Mantani A, Nishiyama S, Fujiwaki S, Ohta S, Mastuda Y, Tomita Y, Tarumoto N, Yamawaki S (2011) Yokukansan treatment in chronic renal failure patients with dementia receiving hemodialysis: an open label study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 19:906–907
Tahara E, Shimizu T, Moriyama K (2003) Two cases with positive symptoms by dementia of elderly successfully treated with yokukan-san (in Japanese, abstract in English). Kampo-no-Rinsho 1:105–114
Taylor DM, Young C, Paton C (2003) Prior antipsychotic prescribing in patients currently receiving clozapine: a case note review. J Clin Psychiatry 64:30–34
Terawaki K, Ikarashi Y, Sekiguchi K, Nakai Y, Kase Y (2010) Partial agonistic effect of yokukansan on human recombinant serotonin 1A receptors expressed in the membranes of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Ethnopharmacol 127:306–312
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (2006) The Japanese pharmacopoeia, fifteenth Edition, English version, available from (http://jpdb.nihs.go.jp/jp 15e/).
Wake R, Miyaoka T, Inagaki T, Furuya M, Ieda M, Liaury K, Kishi K, Horiguchi J (2013) Yokukansan (TJ-54) for irritability associated with pervasive developmental disorder in children and adolescents: a 12-week prospective, open-label study. J Child Adolesce Psychopharmcol 23:329–336
Acknowledgments
This project (04 T-580) was supported by Grants-in-Aid for the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan.
The authors acknowledge the following investigators participating in the study: Syozo Hoshino, M.D., Koichi Ozonoe, M.D., and Sumie Kikuchi, M.D., at Takeda General Hospital; Haruo Seno, M.D., at Aoba Hospital; Kenji Fukuda, M.D., at Konan Hospital; Kei Tamai, M.D., and Terumichi Takahashi, M.D., at Mihara Hospital; Taro Fukushima, M.D., at Matsuda Hospital; Yoshitaka Ishioka, M.D., Ken Mayahara, M.D., Keiko Nakano, M.D., at Hikarinooka Hospital; Masakuni Ikeda, M.D., Masaharu Sagawa, M.D., Hiroshi Saito, M.D., at Koigaoka Hospital; Yasushi Sasaki, at Miyoshi Hospital, M.D.; Hiroyuki Kodama, M.D., at Kodama Hospital; Koji Maeda, M.D., at Rifure Maeda Hospital; Kazuo Shiota, M.D., at Niihama Hospital; Naruhiko Maki, M.D., at Maki Hospital; Atumasa Edahiro M.D., at Toyookadai Hospital; Madoka Ogami, M.D., and Yuko Ichiki, M.D., at Kume Hospital; Akira Sasaki, M.D., at Saijo Dozen Hospital; Kentaro Kawabe, M.D., at Horie Hospital; Hirofumi Hosoe, M.D., at Akita Hospital; Dai Kuwakado, M.D., at Sakuragi Hospital; Humiaki Masuda, M.D., at Baba Hospital; Shigeki Kurayama, M.D., at Miyazaki Wakakusa Hospital; Takeshi Okamoto, M.D., at Iogaoka Hospital; Chikako Mizukoshi, M.D., at Okabe Hospital; Kazumi Hirata, M.D., at Sakuragaoka Hospital; Tsuyoshi Sugawa, M.D., at Kojin Hospital; Hirofumi Abe, M.D., at Shizuoka Mental Center Hospital; Naomi Ikegami, M.D., and Akinori Mizuno, M.D., at Shimizu Sunpu Hospital; and Kiminori Kawano, M.D., at Kaisei Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Trial registration: controlled-trials.com identifier: UMIN000005018
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyaoka, T., Furuya, M., Horiguchi, J. et al. Efficacy and safety of yokukansan in treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (a Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale, five-factor analysis). Psychopharmacology 232, 155–164 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3645-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3645-8