Abstract
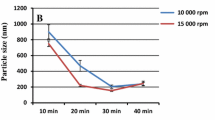
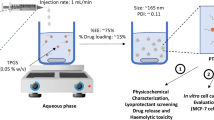
The large number of water insoluble drugs on the market and in the development pipeline provides challenges as well as opportunities for scientists to develop advanced drug delivery systems to meet the clinical needs. Liposomal formulations as drug carriers for insoluble drugs have not been extensively exploited. This chapter described a conceptually novel method using an insoluble drug cisplatin (CDDP) as a building material for the preparation of nanoparticles (NPs). The formulation was done using a reverse microemulsion method. The formation of the NPs was first initiated by mixing KCl and a highly soluble precursor of CDDP. The insoluble CDDP was precipitated and formed the nano-sized core. Dioleoylphosphatydic acid (DOPA), an anionic lipid, was employed as the inner leaflet lipid to stabilize and coat the nano-size CDDP precipitates. A suitable cationic lipid was then added as the outer leaflet lipid to form an asymmetric lipid bilayer structure, and PEGylation of NP was done by including a PEG-phospholipid conjugate in the outer leaflet lipid mixture. The resulting NPs were named lipid-Pt-Cl (LPC) NPs. LPC NPs were characterized with a controllable size (in the range of 12–75 nm) and high drug loading capacity (approximately 80 wt.%). LPC NPs exhibited sustained release profile in vitro drug release studies in medium and in cells. This method might be applicable in formulating other insoluble drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews PA, Wung WE, Howell SBA (1984) High-performance liquid chromatographic assay with improved selectivity for cisplatin and active platinum (II) complexes in plasma ultrafiltrate. Anal Biochem 143(1):46–56
Aryal S, C-MJ H, Zhang L (2010) Polymer−cisplatin conjugate nanoparticles for acid-responsive drug delivery. ACS Nano 4(1):251–258
Avgoustakis K, Beletsi A, Panagi Z, Klepetsanis P, Karydas AG, Ithakissios DS (2002) PLGA–mPEG nanoparticles of cisplatin: in vitro nanoparticle degradation, in vitro drug release and in vivo drug residence in blood properties. J Control Release 79(1–3):123–135
Baba M, Matsumoto Y, Kashio A, Cabral H, Nishiyama N, Kataoka K, Yamasoba T (2012) Micellization of cisplatin (NC-6004) reduces its ototoxicity in guinea pigs. J Control Release 157(1):112–117
Bala I, Hariharan S, Kumar MNVR (2004) PLGA Nanoparticles in drug delivery: the state of the art. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 21(5):387–422
Boulikas T (2009) Clinical overview on Lipoplatin™: a successful liposomal formulation of cisplatin. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 18(8):1197–1218
Burger KNJ, Staffhorst RWHM, de Vijlder HC, Velinova MJ, Bomans PH, Frederik PM, de Kruijff B (2002) Nanocapsules: lipid-coated aggregates of cisplatin with high cytotoxicity. Nat Med 8(1):81–84
Chen H, Khemtong C, Yang X, Chang X, Gao J (2011) Nanonization strategies for poorly water-soluble drugs. Drug Discov Today 16(7–8):354–360
Chen T, Öçsoy I, Yuan Q, Wang R, You M, Zhao Z, Song E, Zhang X, Tan W (2012) One-step facile surface engineering of hydrophobic nanocrystals with designer molecular recognition. J Am Chem Soc 134(32):13164–13167
Dhar S, Kolishetti N, Lippard SJ, Farokhzad OC (2011) Targeted delivery of a cisplatin prodrug for safer and more effective prostate cancer therapy in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(5):1850–1855
Guo S, Wang Y, Miao L, Xu Z, Lin CM, Zhang Y, Huang L (2013) Lipid-coated cisplatin nanoparticles induce neighboring effect and exhibit enhanced anticancer efficacy. ACS Nano 7(11):9896–9904
Guo S, Miao L, Wang Y, Huang L (2014) Unmodified drug used as a material to construct nanoparticles: delivery of cisplatin for enhanced anti-cancer therapy. J Control Release 174:137–142
Kalepu S, Nekkanti V (2015) Insoluble drug delivery strategies: review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm Sin B 5(5):442–453
Kolishetti N, Dhar S, Valencia PM, Lin LQ, Karnik R, Lippard SJ, Langer R, Farokhzad OC (2010) Engineering of self-assembled nanoparticle platform for precisely controlled combination drug therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(42):17939–17944
Li J, Chen Y-C, Tseng Y-C, Mozumdar S, Huang L (2010) Biodegradable calcium phosphate nanoparticle with lipid coating for systemic siRNA delivery. J Control Release 142(3):416–421
Liu Y, Hu Y, Huang L (2014) Influence of polyethylene glycol density and surface lipid on pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of lipid-calcium-phosphate nanoparticles. Biomaterials 35(9):3027–3034
Pabla N, Dong Z (2008) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int 73(9):994–1007
Plummer R, Wilson RH, Calvert H, Boddy AV, Griffin M, Sludden J, Tilby MJ, Eatock M, Pearson DG, Ottley CJ et al. (2011) A phase I clinical study of cisplatin-incorporated polymeric micelles (NC-6004) in patients with solid tumours. Br J Cancer 104(4):593–598
Sengupta P, Basu S, Soni S, Pandey A, Roy B, Oh MS, Chin KT, Paraskar AS, Sarangi S, Connor Y et al. 2012 Cholesterol-tethered platinum II-based supramolecular nanoparticle increases antitumor efficacy and reduces nephrotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(28):11294–11299
Sharma A, Sharma US (1997) Liposomes in drug delivery: progress and limitations. Int J Pharm 154(2):123–140
Smith A, Hunneyball IM (1986) Evaluation of poly(lactic acid) as a biodegradable drug delivery system for parenteral administration. Int J Pharm 30(2):215–220
Srinivas R, Satterlee A, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Huang L (2015) Theranostic etoposide phosphate/indium nanoparticles for cancer therapy and imaging. Nanoscale 7(44):18542–18551
Wang D, Lippard SJ (2005) Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(4):307–320
Zamboni WC, Gervais AC, Egorin MJ, Schellens JHM, Zuhowski EG, Pluim D, Joseph E, Hamburger DR, Working PK, Colbern G et al. (2003) Systemic and tumor disposition of platinum after administration of cisplatin or STEALTH liposomal-cisplatin formulations (SPI-077 and SPI-077 B103) in a preclinical tumor model of melanoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 53(4):329–336
Zhang W, Wang G, Falconer JR, Baguley BC, Shaw JP, Liu J, Xu H, See E, Sun J, Aa J et al.(2015) Strategies to maximize liposomal drug loading for a poorly water-soluble anticancer drug. Pharm Res 32(4):1451–1461
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry
Liu, Y., Huang, L. (2021). Lipid-Coated Cisplatin Nanoparticles for Insoluble Drug Loading. In: Lu, WL., Qi, XR. (eds) Liposome-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Biomaterial Engineering. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49320-5_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-49320-5_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-662-49318-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-662-49320-5
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Chemistry, Materials and Physics