Introduction
Turbulence is a ubiquitous feature of geophysical flows. The challenge in dealing with turbulence is the broad range of spatial and temporal scales. For the Earth's core, the largest scales of motion  are set by the geometry of the core, whereas the smallest dissipative scales
are set by the geometry of the core, whereas the smallest dissipative scales  are determined by the low viscosity and chemical diffusivity of liquid iron alloys (Dobson, 2000; Vocadlo et al., 2000). The range of time scales is even greater (Hollerbach, 2003). Buoyancy‐driven inertial oscillations have diurnal periods (Zhang, 1994), whereas changes in the frequency of magnetic reversals occur on time scales of 108 years (McFadden and Merrill, 2000). Such a vast range of spatial and temporal scales prohibits direct simulations of the Earth's geodynamo (q.v.). Instead, modelers must confine their attention to the largest scales and deal with the problem of limited spatial resolution by parameterizing processes that operate at subgrid scales. Spatially constant eddy diffusivities...
are determined by the low viscosity and chemical diffusivity of liquid iron alloys (Dobson, 2000; Vocadlo et al., 2000). The range of time scales is even greater (Hollerbach, 2003). Buoyancy‐driven inertial oscillations have diurnal periods (Zhang, 1994), whereas changes in the frequency of magnetic reversals occur on time scales of 108 years (McFadden and Merrill, 2000). Such a vast range of spatial and temporal scales prohibits direct simulations of the Earth's geodynamo (q.v.). Instead, modelers must confine their attention to the largest scales and deal with the problem of limited spatial resolution by parameterizing processes that operate at subgrid scales. Spatially constant eddy diffusivities...
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Bibliography
Bardina, J., Ferziger, J.H., and Reynolds, W.C., 1980. Improved subgrid scale models for large‐eddy simulations. American Institute of Aeuronautics and Acoustics Journal, 34: 1111–1119.
Braginsky, S.I., and Meytlis, V.P., 1990. Local turbulence in the Earth's core. Geophysical and Astrophysical Fluid Dynamics, 55: 71–87.
Buffett, B.A., 2003. A comparison of subgrid‐scale models for large‐eddy simulations of convection in the Earth's core. Geophysics Journal International, 153: 753–765.
Buffett, B.A., and Bloxham, J., 2002. Energetics of numerical geodynamo models. Geophysical Journal International, 149: 211–221.
Chan, K.H., Zhang, K., Zou, J., and Schubert, G., 2001. A nonlinear 3‐D spherical
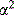 dynamo using a finite element method. Physical Earth Planet Interiors, 128: 35–50.
dynamo using a finite element method. Physical Earth Planet Interiors, 128: 35–50.Chen, S., Foias, C., Holm, D.D., Olson, E., Titi, E.S., and Wynne, S., 1999. A connection between the Camassa‐Holm equations and turbulent flow in pipes and channels. Physics of Fluids, 11: 2343–2353.
Christensen, U., Olson, P., and Glatzmaier, G.A., 1998. A dynamo interpretation of geomagnetic field structures. Geophysical Research Letters, 25: 1565–1568.
Christensen, U., Olson, P., and Glatzmaier, G.A., 1999. Numerical modeling of the geodynamo: A systematic parameter study. Geophysics Journal International, 138: 393–409.
Clune, T.C., Elliott, J.R., Miesh, M.S., Toomre, J., and Glatzmaier, G.A., 1999. Computational aspects of a code to study rotating turbulent convection in spherical shells. Parallel Computing, 25: 361–380.
Dobson, D.P., 2000. Fe‐57 and Co tracer diffusion in liquid Fe‐FeS at 2 and 5 GPa. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 120: 137–144.
Foias, C., Holm, D.D., and Titi, E.S., 2001. The Navier‐Stokes‐alpha model of fluid turbulence. Physica D, 152: 505–519.
Germano, M., 1986. A proposal for a redefinition of the turbulent stresses in the filtered Navier‐Stokes equations. Physics of Fluids, 29: 2323–2324.
Germano, M., Piomelli, U., Moin, P., and Cabot, W.H., 1991. A dynamic subgrid‐scale eddy viscosity model. Physics of Fluids A, 3: 1760–1765.
Glatzmaier, G.A., and Roberts, P.H., 1995. A three‐dimensional convective dynamo solution with rotating and finitely conducting inner core and mantle. Physics of Earth and Planetary Interiors, 91: 63–75.
Glatzmaier, G.A., and Roberts, P.H., 1996. An anelastic evolutionary geodynamo simulation driven by compositional and thermal buoyancy. Physica D, 97: 81–94.
Grote, E., Busse, F.H., and Tilgner, A., 1999. Convection‐driven quadrupolar dynamos in rotating spherical shells. Physical Review E, 60: R5025–R5028.
Grote, E., Busse, F.H., and Tilgner, A., 2000. Effects of hyperdiffusivities on dynamo simulations. Geophysical Research Letters, 27: 2001–2004.
Hollerbach, R., 2003. The range of timescales on which the geodynamo operates. In Dehant, V., et al., (ed.), Earth's Core: Dynamics, Structure, Rotation. Geodynamics Monograph, American Geophysical Union, Vol. 31, 181–192.
Holm, D.D., 2002. Lagrangian averages, averaged Lagrangians and the mean effect of fluctuations in fluid dynamics. Chaos, 12: 518–530.
Kageyama, A., and Sato, T., 1995. The Complexity Simulation Group, Computer simulation of a magnetohydrodynamic dynamo. Physics of Plasmas, 2: 1421–1431.
Kageyama, A., and Sato, T., 1997. Generation mechanism of a dipole field by a magnetohydrodynamic dynamo. Physical Review Letters E, 55: 4617–4626.
Kageyama, A., and Sato, T., 2004. Yin‐Yang grid: An overset grid in spherical geometry. Geochemistry, Geophysics, and Geosystems, 5, Q09005.
Katayama, J.S., Matsushima, M., and Honkura, Y., 1999. Some characteristics of magnetic field behavior in a model of MHD dynamo thermally driven in a rotating spherical shell. Physics of Earth and Planetary Interiors, 111: 141–159.
Kono, M., Sakuraba, A., and Ishida, M., 2000. Dynamo simulation and paleosecular variation models. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, A358: 1123–1139.
Kuang, W., and Bloxham, J., 1997. An Earth‐like numerical dynamo model. Nature, 389: 371–374.
Landau, L.D., and Lifshitz, E.M., 1981. Physical Kinetics, Course of Theoretical Physics, Vol. 10, Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Leonard, A., 1974. Energy cascade in large‐eddy simulations of turbulent flow. Advances In Geophysics, 18: 237–248.
Lesieur, M., and Metais, O., 1996. New trends in large‐eddy simulations of turbulence. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 28: 45–82.
Matsui, H., and Okuda, H., 2004. Development of a simulation code for MHD dynamo processes using the GEOFEM platform. International Journal of Computational Fluid Dynamics, 18: 323–332.
Matsui, H., and Buffett, B.A., 2005. Subgrid‐scale modeling of convection‐driven dynamos in a rotating plane layer. Physics of Earth and Planetary Interiors, 153: 108–123.
Matsushima, M., Nakajima, T., and Roberts, P.H., 1999. The anisotropy of local turbulence in the Earth's core. Earth, Planets and Space, 51: 277–286.
Matsushima, M., 2004. Scale similarity of MHD turbulence in the Earth's core. Earth, Planets, Space, 56: 599–605.
McFadden, P.L., and Merrill, R.T., 2000. Evolution of the geomagnetic reversal rate since 160 Ma: Is the process continuous? Journal of Geophysical Research, 105: 28455–28460.
Meneveau, C., and Katz, J., 2000. Scale invariance and turbulence models for large‐eddy simulation. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 32: 1–32.
Moffatt, H.K., 1978. Magnetic Field Generation in Electrically Conducting Fluids, Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 343 pp.
Montgomery, D.C., and Pouquet, A., 2002. An alternative interpretation for the Holm alpha model. Physics of Fluids, 14: 3365–3566.
Olson, P., Christensen, U., and Glatzmaier, G.A., 1999. Numerical modeling of the geodynamo: Mechanisms of field generation and equilibration. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104: 10383–10404.
Phillips, C.G., and Ivers, D.J., 2000. Spherical anisotropic diffusion models for the Earth's core. Physics of Earth and Planetary Interiors, 117: 209–223.
Phillips, C.G., and Ivers, D.J., 2001. Spectral interactions of rapidly rotating anisotropic turbulent viscous and thermal diffusion in the Earth's core. Physics of Earth and Planetary Interiors, 128: 93–107.
Phillips, C.G., and Ivers, D.J., 2003. Strong‐field anisotropic diffusion models for the Earth's core. Physics of Earth and Planetary Interiors, 140: 13–28.
Piomelli, U., and Zang, T.A., 1991. Large‐eddy simulation of transitional channel flow. Computer Physics Communications, 65: 224–230.
Roberts, P.H., and Glatzmaier, G.A., 2000a. Geodynamo theory and simulations. Reviews of Modern Physics, 72: 1081–1123.
Shimizu, H., and Loper, D.E., 1997. Time and length scales of buoyancy‐driven flow structures in a rotating hydromagnetic fluid. Physics of Earth and Planetary Interiors, 104: 307–329.
St. Pierre, M.G., 1996. On the local nature of turbulence in Earth's outer core. Geophysical and Astrophysical Fluid Dynamics, 83: 293–306.
Tennekes H., and Lumley, J.L., 1972. A First Course in Turbulence, Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
Vocadlo, L., Alfe, D., Price, G.D., and Gillan, M.J., 2000. First‐principle calculations of the diffusivity and viscosity of liquid Fe‐FeS at experimentally accessible conditions. Physics of Earth and Planet. Interiors, 120: 145–152.
Zhang, K.K., 1994. On the coupling between Poincare equation and the heat equation. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 268: 211–229.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer-Verlag
About this entry
Cite this entry
Buffett, B., Matsui, H. (2007). Core Turbulence. In: Gubbins, D., Herrero-Bervera, E. (eds) Encyclopedia of Geomagnetism and Paleomagnetism. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-4423-6_41
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-4423-6_41
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-3992-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-4423-6
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceReference Module Physical and Materials ScienceReference Module Earth and Environmental Sciences


 dynamo using a finite element method. Physical Earth Planet Interiors, 128: 35–50.
dynamo using a finite element method. Physical Earth Planet Interiors, 128: 35–50.